
Georgia Department of Driver Services Drivers' Manual

DDS Mission & Core Values
Our Mission
To provide secure driver and identity credentials to our customers with excellence and respect.
Our Core Values:
- Trusted Service
- Ethical Actions
- Accountable to All
- Motivated to Excellence
#2023ReimaginingDriverServices
Title VI Policy Statement
The Georgia Department of Driver Services (DDS) is committed to compliance with Title VI of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 and all related nondiscrimination authorities. DDS assures that no person shall, on the grounds of race, color, national origin, sex, age, disability, low-income, and Limited English Proficiency (LEP), be excluded from participation in, be denied the benefits of, or be otherwise subjected to discrimination under any program or activity. DDS further assures that every effort will be made to ensure nondiscrimination in all programs and activities, whether or not those programs and activities are federally funded. In addition, DDS will take reasonable steps to provide meaningful access to services for persons with Limited English Proficiency. Finally, DDS agrees to abide by the Title VI Program Assurances and to ensure that written agreements with any party for federally funded programs or services will include the applicable Title VI language as provided in the Title VI Program Assurances.
The DDS Title VI Program Coordinator is responsible for oversight of the Title VI Program and ensuring compliance with the requirements provided in 49 Code of Federal Regulations (C.F.R) Part 21 and 49 C.F.R. Part 303. The Title VI Program Coordinator and all Division Directors are authorized to effectively implement the Title VI Program on behalf of the Department.
DDS Online Services
Be certain to take advantage of DDS Online Services and avoid an unnecessary trip to a Customer Service Center.
DDS Online Services enable thousands of Georgia drivers to conduct many transactions via the DDS website and eliminate a visit to a DDS Customer Service Center (CSC). This saves customers valuable time and money. DDS does not charge an additional fee for choosing Internet Services. A $5.00 discount may apply for eligible license types that are renewed on the internet.
For more information visit the DDS website and like DDS on Facebook!
Save Time! Use DDS Online Services at DDS.Georgia.Gov

Save Time long description
Card Services
- Submit Proof of Residency and/or Social Security
- Address Change
- License/ID Renewal or Replacement
- Class D to Class C Upgrade
- CDL Self-Certification Medical Documents
- License Status
- Suspension or Reinstatement Information
Pay Fees
- Super Speeder
- License Reinstatement
- Pending Suspensions
Other Services
- Online For-Hire Endorsement Application
- Skip a Step! (Complete Form Online)
- Driving History (MVR)
- Motorcycle Safety Training Registration
- Make Road Test Appointment
- Reservation Status
Please note
The information contained in this manual is not intended to be an official legal reference to the Georgia traffic laws. It is intended only to explain, in everyday language, those laws, driving practices, and procedures that you will use most often. It should be noted that the material in this manual is subject to change to comply with amended State and Federal legislation. The department’s primary statutory responsibilities are set forth in Title 40 of the Official Code of Georgia Annotated (O.C.G.A.) This publication is produced by the DDS Governmental Affairs & Communications Division.
Messages
Governor's Message

"I wish you safe passage and encourage you to exercise good judgment, follow driving laws, and prioritize safety for yourself, fellow motorists, and passengers."
Brian P. Kemp
Governor
Commissioner's Message

"Operating a vehicle is a tremendous responsibility, and we want you to be fully prepared to meet the challenges! Please pay particular attention to the sections on Traffic Laws, Teen Driving Laws and Safety Guidelines. By obeying all traffic laws and never driving distracted, we can ensure that our roads are safer for drivers and passengers alike."
Spencer R. Moore
Commissioner
Check out DDS 2 GO!
Available on the Apple App Store and Google Play.
Board of Directors' Message
Board of Directors
- David W. Connell, Chair
- Jeff MarKey, Vice Chair
- Britt Fleck, Secretary
- Tony Guisasola, Member
- Rachel Little, Member
- Christie Moore, Member
- Bob Pierce, Member
- Sheriff Frank Reynolds, Member
- Kat Satterfield, Member
The Department of Driver Services (DDS) Board of Directors would like to remind our customers that driving in Georgia is a privilege that carries many responsibilities. Please be a safe and dependable driver to ensure that this privilege will not be lost. This manual has two main purposes:
- to help you qualify for a Georgia driver's license; and
- to help you become a safer driver.
This guide is designed to provide you with the information to obtain and keep this type of license. Other manuals are available for commercial drivers and motorcycle operators.
American Association of Motor Vehicle Administrators (AAMVA)
Our Vision
- Safe drivers
- Safe vehicles
- Secure identities
- Saving lives!
4401 Wilson Blvd, Suite 700, Arlington, VA 22203 | 703.522.4200 | aamva.org
What to Do and Expect When Pulled Over by Police
(Revised January 2021)
Police officers are responsible for conducting traffic stops when they have reasonable suspicion of a traffic violation or a criminal violation. Being stopped by an officer can be a stressful experience for the driver, any passengers, and for the officer, too. Knowing what to do during the stop will help ensure your safety and the safety of others.
When you see emergency lights behind you, it is important for you and your passengers to stay calm and cooperate.
Remember to:
- Activate your turn signal and pull off or to the side of the roadway as soon as it is safe to do so.
- Turn off the engine and any audio devices.
- Stay in your vehicle unless directed by the officer to exit.
- Turn on your interior lights if you are pulled over at night to assist with visibility. Officers may use a spotlight for additional visibility.
- Keep your hands on the steering wheel or in a visible location so they are easily observable.
- Follow all instructions the officer gives you or your passengers.
The officer may approach either side of the vehicle. When the officer approaches the vehicle, remember to:
- Lower the corresponding window so you and the officer can better communicate.
- Let the officer know if you have a weapon in the vehicle upon first contact.
- Wait for the officer's instructions before reaching for your driver's license or vehicle documents.
When conducting the stop, the officer will typically:
- Show their law enforcement credentials if they are not in uniform. If they do not show their credentials, you may ask to see them.
- Explain why you were stopped/ask questions about your trip.
- Ask for your driver's license, proof of insurance, and vehicle registration. If the documents are out of your reach, tell the officer where they are and wait for the officer's acknowledgement before reaching to retrieve the documents.
In some cases, the officer may:
- Ask you to exit the vehicle. In this case, keep your hands visible, exit the vehicle, and stand in a location as directed by the officer.
- Impose a sanction such as a warning, traffic ticket, which may include a fine, or arrest. The officer will typically explain whatever action is being taken. If they do not, you may ask them to do so.
If you have questions, respectfully ask the officer to clarify. If you disagree with the officer's decision or course of action, do not prolong the contact by arguing with the officer. Rather, you may seek to contest the decision in court through established legal channels. Your acceptance and signature on a traffic ticket is not on admission of guilt. However, the refusal to sign a traffic ticket may result in your arrest.
If you believe the officer acted inappropriately or have questions regarding their conduct you may request to speak to a supervisor. This is best done as soon as possible after the stop.
Following these procedures can help make a traffic stop a safe experience for all parties involved.
This guidance was approved by the AAMVA Driver and Law Enforcement Standing Committees, by the International Association of Chiefs of Police and the National Organization of Black Law Enforcement Executives.



Section 1: General Licensing Information
This Section Covers
- Requirement to Obtain a Georgia Driver's License
- Applicants under age 18
- Previous License, Instructional Permits, or Identification Cards
- Vision Requirements
- Classes of Licenses
- Fees/Forms of Payment
- License Restrictions
- Expired License
- Carrying and Displaying Your License
- Real ID Documentation Requirements
Requirement to obtain a Georgia Driver's License
Georgia law requires that any person wanting to operate a motor vehicle on the roadways of this state obtain a Georgia driver's License or permit within 30 days of becoming a resident. A person meeting at least one of the following criteria is considered a Georgia resident according to Georgia law (O.C.G.A. §40-5-1):
- A person who has a permanent home or abode in Georgia and, when absent, has the intent of returning;
- A person who accepts employment or engages in any trade or occupation in Georgia or who enters his/her children in school;
- Any person that has been in the state for 30 days or more.
Not required to obtain a Georgia Driver's License/Permit
- Any employee of the United States government who is operating a motor vehicle owned by or leased to the United States government or that is being operated on official business. This exemption does not apply if the employee is required by the United States government or any agency of the United States Government to have a state driver's license;
- A nonresident who is at least 16 years of age and who has in his or her immediate possession a valid license issued to him or her in his or her home state or country. However, any restrictions that would apply to a Georgia driver's license as a matter of law would apply to any person who has an out-of-state license;
- A nonresident who is on active duty in the armed forces of the United States if he or she has a valid license issued by his or her home state. This includes their spouse or dependent son or daughter who has a valid license issued by their home state;
- Any person who is on active duty in the armed forces of the United States and who has in his or her immediate possession a valid license issued in a foreign country by the armed forces of the United States. However, this license will only be accepted for a period of not more than 45 days from the date of his or her return to the United States;
- Any person temporarily driving or operating a farm tractor or farm equipment on a highway for the purpose of conducting farm business;
- Any member of the reserve components of the armed forces of the United States who is operating a motor vehicle owned by or leased to the United States government. However, the motor vehicle must be operated in accordance with the duties of the person as a member of the reserve components of the armed forces;
- Any person seeking to obtain a driver's license while he or she is taking the driving examination to obtain a license. This person must be accompanied by a Responsible Adult with a valid driver's license and be at least 21 years of age or a certified driver examiner or agent of the department;
- Any migrant farm worker who works in this state less than 90 days in any calendar year and who possesses a valid driver's license issued by another state;
- Any resident who is 15 years of age or over while taking actual in-car training in a non-commercial training vehicle and while under the direct personal supervision of a DDS-licensed driving instructor. A driving instructor must test the eyesight of any unlicensed person who will be receiving actual in-car training prior to the training, and the person must meet the vision requirements listed under the "Vision Requirements" heading of this manual;
- Any person who is operating a personal transportation vehicle on any roadway publicly maintained for the use of personal transportation vehicles only, or when crossing a street or highway used by other types of motor vehicles at a location designated for such crossing by a motorized cart;
- A nonresident of Georgia who is attending a school in this state, as long as:
- He or she is at least 16 years of age and has in his or her immediate possession a valid license issued to him or her in his or her home state or country and a valid international driving permit if the license is in a language other than English; provided, however, that any restrictions which would apply to a Georgia driver's license apply to the privileges given to this person; and
- He or she is currently enrolled or was enrolled during the immediately preceding period of enrollment in a school in this state, has paid the tuition charged by the school to nonresidents of Georgia for the current or immediately preceding period of enrollment, and has in his or her possession proof of payment of such tuition paid for the current or immediately preceding period of enrollment.
Applicants under age 18 - automobile or motorcycle
In addition to the requirements listed under the heading "Requirement to obtain a Georgia Driver's License" applicants under 18 years of age must present proof of the following:
- All applicants under 18 years of age must have a parent, legal guardian or responsible adult present to sign the application and complete a Responsible Adult Affidavit;
- Completion of Alcohol and Drug Awareness Program (ADAP);
- Satisfaction of school enrollment specified under the heading "School Enrollment Requirements";
- For a Class D license or for a Class M Instructional Permit (MP) at age 16 or age 17 proof of completion of a DDS approved driver education program plus evidence of at least forty (40) hours of supervised driving, six of which must be at night. Additional details concerning these requirements can be found under the heading "Driver Education Requirements" of this manual or on our website.
Previous Licenses, Instructional Permits or Identification Cards
In most cases, when applying for renewal, replacement or transfer of any license, instructional permit, or identification card (ID Card) previously issued in Georgia or any other state or foreign jurisdiction, customers must surrender, the previously-issued license/permit/ID to DDS. In some cases, surrender of all valid licenses/permits/ID cards will be required.
Most non-citizen customers with a valid out of country driver's license, permit, or ID, may retain their out of country document upon issuance of a Georgia-equivalent document. U.S. citizens will not be allowed to retain any licenses, permits, or identification cards issued to them by foreign countries.
Vision Requirements
Customers for initial issuance of a driver's license must demonstrate the ability to meet minimum vision requirements. The minimum acceptable vision for a noncommercial license is 20/60 in one eye, with or wi1hout corrective lenses, and a horizontal field of vision of at least 140 degrees. If you are unable to pass the vision screening administered at the DDS Customer Service Center, you will be given a Vision Report Form (DS-274) which must be completed by a licensed optometrist or opthalmologist and submitted to DDS. The completed form will be evaluated to
determine if you are eligible to obtain a driver's license. This form may also be used to document the need for bioptic lenses for driving and is available on our website.
If you must wear glasses or contacts to pass your initial vision screening, a corrective tenses restriction will be placed on your license when it is issued. Each time you complete a transaction, you will be required to indicate whether you require glasses or contacts for driving. If your answer differs from the response in our records, you may be required to complete another vision screening or submit a current DS-274 for verification.
Customers age 64 and over must successfully complete a vision screening every eight years. Customers who have obtained a license with a
bioptic lenses restriction must provide updated medical information to the Department every two years.
Classes of Licenses
The issuance of licenses and permits in Georgia is based on their categorization by Class. The various classes are associated with the types of vehicles that may be driven and the restrictions that apply to operation of those vehicles. Listed in the table titled "Non-Commercial Classes" are the non-commercial classes used in Georgia, along with a description of their purpose.
Pursuant to House Bill 136 (2017), three-wheel autocycles will not require a Class M Motorcycle Operator's License. Autocycles are defined as three-wheel motor vehicles that are equipped with a steering wheel and not handlebars. DDS will not administer road tests that involve the use of an autocycle.
Georgia also issues Class A, B, and C commercial licenses. Information concerning these licenses is included in the Georgia Commercial Drivers Manual, available at all DDS Customer Service Centers and on our website.
Non-Commercial Classes
| Class | Purpose |
|---|---|
| C | Non-commercial license for drivers age 18 and older. (Also for drivers new to Georgia who are age17 and who hold a valid Class C equivalent from another state.) |
| D | Provisional license issued to drivers ages 16 and 17. |
| M | License for motorcycle operators. |
| E, F | Non-commercial license for drivers who operate commercial motor vehicles and who are exempt from commercial licensing requirements. (Class E & F licenses are free for volunteer firefighters.) |
| CP, MP, EP, FP | All instructional permits are issued with the class designation followed by the letter "P." |
Fees/Forms of Payment
The fees for obtaining non-commercial driver's licenses, permits, and ID cards in person are listed in the table titled "License, Permit, and Identification Card Fees". This fee schedule is not adjusted to reflect the $5.00 discount for those who choose to renew online or via DDS 2 Go. All DDS Customer Service Centers accept cash, Visa and Mastercard credit and debit cards with a bank logo, and Discover and American Express credit cards and mobile pay options. We do not accept checks, money orders, or cashier checks.

License, permit and ID card holders are allowed one free name or address change per issuance term. Other changes can also be made at the time of the free name or address change at no charge. Any subsequent modifications require a full renewal at regular cost. Name changes must be in accordance with the requirements listed under the "Name Change" heading.
A replacement driver's license, permit or ID card is a duplicate of the replaced document (no modifications or changes) and maybe provided at a cost of $5.00 per occurrence. The replacement license/permit/ID card will expire on the original expiration date. However, if a replacement is requested within 150 days of the original expiration date (or within 30 days of the original expiration date for a motorcycle instructional permit), the license/permit/ID must be renewed for a new term at full cost.
License, Permit, and Identification Card Fees
| Type | Term | Fee |
|---|---|---|
| Driver's License (Class A, B, C, E , F, and M) | 8 years | $32 |
| Driver's License (Class E and F) for Volunteer Firefighters | 8 years | No Fee |
| Provisional License (Class D) | 5 years | $10 |
| Instructional Permit (Class A, B, C, and M) | 1 year | $10 |
| Replacement Duplicate License/Permit/ID Card (If a replacement license/permit/lD card is requested within 150 days of the original date, the license/permit/ID card must be renewed for a new term at full cost.) | Original Expiration Date | $10 |
| National Guard License | 8 years | No Fee |
| Veteran License (Combat Veteran) | 8 years | No Fee |
| Veteran License (Non-Combat) Class A, B, C, and M | 8 years | $32 |
| Honorary License | 8 years | No Fee |
| Controlled Substance Permit | Up to 3 years | $25 |
| Habitual Violator Probationary License | Up to 3 years | $210 |
| Limited Permit | Up to 1 years | $32 |
| Georgia ID Card | 8 years | $32 |
| Georgia ID Card for Voting Purposes Only (must provide proof of valid voter registration) | 8 years | No Fee |
| HVPL/Limited Permit Replacement | Original Term | $20 |
| Limited Permit Renewal | Equal to Original Term of Permit | $10 |
| Veteran ID Card (Combat Veteran) | 8 years | No Fee |
| Veteran ID Card (Non-Combat Veteran) | 8 years | No Fee |
| Handicap ID Card | 8 years | $5 |
| Address or Name Change | Original Expiration Date | Free Once per Term |
License Restrictions
When issuing a driver's license, DDS is authorized to impose restrictions on your driver's license, whenever there is good cause, to assure the safe operation of a motor vehicle. Any restrictions imposed will appear on your driver's license. If no restrictions are imposed, the letter "A" will appear in the License Restrictions area on your license. The tabled titled "DDS License Restriction Codes" lists the restriction codes used by DDS. Licenses may be issued with multiple restriction codes.
DDS License Restriction Codes
| Code | Meaning |
|---|---|
| A | no restrictions |
| B | corrective lenses required |
| C | vehicle mechanical aids required |
| D | prosthetic aids required |
| E | no manual transmission equipped CMV |
| F | right exterior mirror required |
| G | daylight hours only |
| H | employer vehicle only |
| I | left exterior mirror required |
| J | automatic transmission required |
| K | intrastate commerce only |
| L | no air brake equipped CMV |
| M | no class A passenger buses |
| N | no class A or B passenger buses |
| O | no tractor trailer CMV |
| P | no passengers in CMV bus |
| Q | no passengers allowed |
| R | no highway/interstate |
| S | power brakes or steering required |
| T | accompanied by disabled parent |
| U | accompanied by visually impaired parent |
| V | medical variance |
| W | valid farm waiver required |
| X | no cargo in CMV tank vehicle |
| Y | hearing aid required |
| Z | no full air brake |
| 1 | biopic lenses required |
| 2 | Pursuant to Court Order |
| 3 | Ignition Interlock Device restrictions apply |
| 4 | HPVL restrictions apply, no interlock |
| 5 | business purpose only |
| 6 | to and from medical only |
| 7 | to and from school only |
| 8 | Ignition Interlock required |
| 9 | limited permit, no interlock |
Expired License
To renew a driver's license that has be expired more than two years, you must pass a vision test, a driving test, and an exam to test your knowledge of road signs and road rules. You must also meet Real ID documentation requirements if you have not already done so. See the information under the heading "Read ID Documentation Requirements" for more information about Real ID requirements.
Carrying and Displaying Your License
You must have an appropriate driver's license or permit in your possession while operating a motor vehicle in the State of Georgia. If stopped while driving, you must display your driver's license/permit to any law enforcement officer upon his or her request.
Real ID Documentation Requirements
The following are examples of acceptable documents to bring with you to be issued a Real ID.
- Identity Document - An original or certified document to prove WHO YOU ARE such as an original or certified Birth Certificate, US Passport, Certificate of Naturalization, I-551, etc.
- You must know your full Social Security Number. It will be verified with the Social Security Office electronically.
- Two Documents showing Georgia residence (e.g. utility bill, phone bill); Must be dated within the last six (6) months.
- Name Change - If your name is currently different than the "identity document" presented (such as birth certificate, passport, etc.), you must provide a certified copy with seal; legal name change document (e.g. marriage certificate, divorce decree, etc.). NOTE: A Document is required even if your name is correct on current license/id.
- Minor's may present passport; however, proof of guardianship requires original/certified birth certificate or certified court ordered documents.
- Original immigration documentation must be submitted each time service is requested pertaining to a driver's license or identification card.
- Gender change - A gender update requires applicants to submit a court order or physician's letter certifying gender change. The letter or court order shall state the person's name, date of birth, date of gender reassignment operation and other identifying information.
Once you are issued a Real ID with a star in the upper right corner, you should be eligible to conduct future transactions without visiting a center. Download the DDS mobile app, DDS 2 GO, for free to have a licensing office in your pocket!
Important Notice: Beginning May 7, 2025, you will need a Real ID compliant card (with a star in the right corner) to fly within the U.S. or enter federal buildings or any nuclear power plant. For more information see the DHS website (www.dhs.gov).
If you would like to review and/or print a list of acceptable documents, please visit the DDS website.

Section 2: Obtaining a License, Permit or Identification Card
This Section Covers
- Current Georgia Residents
- Class C Instructional Permit (CP)
- Class D Provisional License
- Class C License
- State ID Card
- Other License Types
- Commercial Driver's License
- Motorcycle Operator's License
- Licenses for Veterans of the U.S. Armed Forces and their Spouses
- National Guard License
- New Georgia Residents
Current Georgia Residents

Class C lnstructional Permit (CP)
For first-time issuance of a Class C Instructional Permit (CP), you must meet all requirements to obtain a Secure DL/ID if you have not already done so. See information under the heading "Requirement to Obtain to Georgia Driver's License" for complete requirements.
Obtaining a Class C Instructional Permit (CP)
Upon reaching age 15, or anytime thereafter, you may apply for a Class C Instructional Permit (CP). The following information will help you prepare for your visit to a DDS Customer Service Center:
- You will be required to present documents verifying your identity, U.S. citizenship or lawful presence, and Georgia residency as explained under the "Read ID Documentation Requirements" heading.
- You must know your Social Security Number or provide proof of your ineligibility to obtain a Social Security Number. See the DDS website for more information.
- If you are under age 18, you will be required to present proof of school enrollment; see information under the "School Enrollment Requirements" heading for requirements;
- If you are under age 18, a parent, legal guardian or responsible adult will have to sign the application, thereby giving their consent for you to obtain a permit. The individual who signs your application may, for any reason, revoke your permit until you reach the age of 18;
- You will be required to pass a vision test. Your eyes will be tested by means of a mechanical device;
- You will be required to pass a knowledge exam related to Road Signs and Road Rules. Please refer to information under the heading "Knowledge Exam" for more information related to the knowledge exam;
- The test fee is $10.00 and must be paid prior to testing. If any part of the test is failed, no refund will be issued. The permit fee must be paid prior to every testing attempt.
Conditions of a Class C Instructional Permit (CP)
- Once issued a Class C Instructional Permit (CP), you may operate any Class C vehicle when accompanied by a person at least 21 years of age who is licensed to drive a Class C vehicle, who is fit and capable of exercising control over the vehicle, and who is occupying a seat beside the driver;
- Class C Instructional Permits (CP) are valid for up to 2 years.
Class D Provisional License
For first-time is issuance of a Class D License, you must meet all requirements to obtain a Secure DL/ID if you have not already done so. See Section 2: Obtaining a License, Permit or Identification Card for complete requirements.
Obtaining a Class D Provisional License
Upon reaching the age of 16, and after having held a valid instructional permit for one year and one day, you may apply for your Class D license.
The following information will help you prepare for your visit to a DDS Customer Service Center.
You will need to make a road test appointment; for more information see the heading "Road Test":
- You must surrender your Class C Instructional Permit (CP) or affirm on your application that you are unable to surrender the permit. See the information under the heading "Lost or Stolen License Replacement" for details concerning lost licenses and permits;
- You will be required to present proof of school enrollment; see information under the "School Enrollment Requirements" heading for requirements;
- You must present proof of completion of the Alcohol and Drug Awareness Program (ADAP). This program is taught in most schools, and is also available online. For information about ADAP, you may visit the DDS website;
- A parent, legal guardian or responsible adult will have to sign the application, thereby giving their consent for you to obtain a license. The individual who signs your application may, for any reason, revoke your license until you reach the age of 18;
- You must pass a road test designed to evaluate your ability to safely operate a motor vehicle. See the heading "Road Test" more information related to the Road Test;
- You must satisfy the driver education requirements listed under Driver Education Requirements. (NOTE: Teens with parents active in the U.S. Military can use an out of state driver's education certificate provided that it is within 9 months of their 16th birthday.)
Military Note
A 17-year-old will be exempt from holding their learners permit for one year and one day with proof that they are enlisted in the military. They will be issued a Class C license at issuance.
Driver Education Requirements
To obtain a Class D license at the age of 16 or 17 you must complete both a driver education course approved by DDS and the Alcohol and Drug Awareness Program (ADAP).
An approved driver education course consists of:
- either 30 hours of classroom instruction OR completion of an equivalent online virtual course;
AND
- 6 hours of on-the-road experience with a certified instructor OR completion of the DDS Parent Teen Driving Guide available Online or at any CSC. You must also have completed a cumulative total of at least 40 hours of other driving experience, including at least 6 hours at night. A DDS provided affidavit must be signed at the time of road testing to certify that this requirement has been met.
NOTE: If the teen obtains the on-the-road component of driver's education from a certified instructor, a separate document affirming that this requirement has been met must be completed at the time of the road test.
- If you have not completed the driver education requirements, you cannot obtain a Class D license. For information on approved driver education courses, see the DDS website.
- The Alcohol and Drug Awareness Program (ADAP) is taught in most schools and is also available online via the DDS website.
Conditions of a Class D Provisional License
- A Class D license holder may not drive between the hours of 12:00 a.m. and 5:00 a.m. NO EXCEPTIONS;
- During the first six months following issuance, only immediate family members may ride in the vehicle. 'Immediate family member' includes the driver's parents and step-parents, grandparents, siblings and step-siblings, children, and any other person who resides at the driver's residence;
- During the second six months following issuance, only one passenger under 21 years of age who is not a member of the driver's immediate family may ride in the vehicle;
- After the first and second six-month periods, only three passengers under 21 years of age who are not members of the driver's immediate family may ride in the vehicle;
- A Class D license holder must, for the 12 months preceding application for their Class C license, be free from any convictions for major traffic violations that result in the mandatory suspension of a driver's license.

Class C License
For first-time issuance of a Class C License, you must meet all requirements to obtain a Real DL/ID if you have not already done so. See information under the heading "Requirement to Obtain to Georgia Driver's License" for complete requirements.
Obtaining a Class C License - Exchanging a Class D License
A Class D license holder may apply for a Class C license upon reaching the age of 18. The applicant must have held a valid Class D license until the age of 18, or for one year and one day, without having been convicted of any major traffic violations in the 12 months preceding his/her application. Upon surrender of the Class D license or affirmation on the application that the customer is unable to surrender the license, the applicant will be issued a Class C license at the cost of $32 for an 8 year license. No other documentation or testing is required for U.S. citizens. See information under the heading "Lost or Stolen License Replacement" for details concerning lost licenses and permits.
Obtaining a Class C License - Exchanging a Class C Instructional Permit (CP)
A Class C instructional Permit (CP) holder may apply for a Class C license only if he or she has reached the age of 18.
To obtain a Class C license, you must surrender your previously issued Class C Instructional Permit (CP) or affirm on your application that you are unable to surrender the permit. You must also pass a road test designed to evaluate your ability to safely operate a motor vehicle. See information under the heading "Road Test" for more information related to the road test. Upon surrender of the Class C Instructional Permit (CP) or affirmation on the application that you are unable to surrender the permit, you will be issued a Class C license at the cost of $32 for an 8 year license. You must sign an affidavit verifying that you have completed 40 hours of supervised road driving which includes 6 hours of night driving. See information under the heading "Lost or Stolen License Replacement" for details concerning lost licenses and permits.
Obtaining a Class C License - Applicant Is Not Currently Licensed
If you are at least 18 years of age and would like to apply for a driver's license in Georgia for the first time, you have two options:
- Immediately apply for a Class C Driver's License. You must meet all documentation requirements listed under the heading "Requirement to Obtain to Georgia Driver's License", and successfully complete the knowledge and road test examinations (see information under the heading "Section 3: Testing Information"). You must also sign an affidavit affirming that you have completed 40 hours of supervised road driving which includes 6 hours of night driving;
- Apply for a Class C Instructional Permit (CP), which allows you to obtain practical driving experience under the supervision of a licensed driver. If you would like more information related to a Class C Instructional Permit (CP) Knowledge test, please see information under the heading "Road Test for Class C or D".

State ID Card
For first-time issuance of a State ID Card, you must meet all requirements to obtain a Real ID DL/ID if you have not already done so. See information under the heading "Requirement to Obtain to Georgia Driver's License" for complete requirements.
A State of Georgia ID Card may be obtained at any DDS Customer Service Center. The cost of this card varies depending on the type of card obtained.
- An 8-year ID card is $32;
- All previous ID cards must be surrendered;
- If you no longer have possession of your previous driver's license/ID card/permit to surrender, you must provide a certified copy of your Motor Vehicle Report (MVR) from the previous state.
Upon submission of a referral from a DDS-approved non-profit agency, the applicant will be permitted to obtain an ID card at a cost of $5.00.
A special ID card for persons with permanent disabilities is available for a term of eight years at a cost of $5.00. A card for persons with temporary disabilities is also available for a term of six (6) months at a cost of $5.00. This card serves as proof of the need for special transportation services, seating accommodations, and other facilities for the handicapped. Verification from a licensed physician may be required to obtain a permanent Handicap ID, and is always required to obtain or extend a temporary Handicap ID. The fee for this card is waived for those who meet the qualifications listed under the heading "Licenses for Veterans of the U.S. Armed Forces and their Spouses" for a veteran's driver's license.
Customers can also have the handicap symbol placed on any other type of license, permit, or identification card. Customers have the option to include certain medical information on the back of their card as well. This information is also available at our website.
A voter registration ID is also available at no cost for any individual who swears under oath that the ID is needed in order to vote in an election in Georgia.
All applicants for ID cards must provide proof of identity, proof of U.S. Citizenship or lawful presence, proof of Social Security Number or ineligibility for a Social Security Number, and proof of Georgia residency. See information under the heading "Real ID Documentation Requirements" for further information concerning these requirements.

Other License Types
Commercial Driver's License
Detailed information concerning licensing requirements for Commercial Driver's Licenses can be found in the Commercial Drivers Manual as well as on the DDS website.
Motorcycle Operator's License
Detailed information concerning licensing requirements for Motorcycle Operator's Licenses can be found in the Motorcycle Operators Manual as well as on the DDS website.
Licenses for Veterans of the U.S. Armed Forces and their Spouses
Important: Veterans must bring their DD214 to any DDS Customer Service Center to be issued a free Veteran's License. If they do not have a DD214, obtain a Certificate of Eligibility (DS-516) from the State Department of Veterans Service.
Applicants must meet the following requirements for eligibility of a veteran's license:
- All veterans who are GA citizens, actively served, and released with any discharge other than dishonorable, are eligible for a free Veterans License/ID Card.
- The veteran should present their original DD214 or a DS-516 issued by the State Department of Veterans Service to any DDS Customer Service Center along with any other documentation needed to prove identity, lawful presence, and residency for issuance of the license (see information under the heading "Requirement to Obtain to Georgia Driver's License" for complete requirements).
- The State Department of Veterans Service will denote eligibility on the DS-516;
- Successfully pass a vision test for the initial issuance of a Class C veteran's license. To obtain any other class of license, you must successfully complete examinations for the class of license desired.
Honorary License - NO FEE
The spouse of a disabled, honorably separated veteran who does not have a driver's license, or the unmarried surviving spouse of a deceased honorably separated veteran, is entitled to the same license available to the veteran. An applicant for this type of license must meet the same requirements as those required for a veteran's license. For the unmarried surviving spouse, the death certificate along with the DD-214 must be submitted to the State Department of Veterans Service to obtain a Certificate of Eligibility.
National Guard License
A free, distinctive, license may be issued to any member of the Georgia National Guard or active reserves in good standing who has had active duty.
A Certificate of Eligibility (DS-318) form must be obtained from the local National Guard Commanding Officer and presented to any DDS Customer Service Center. This license is renewable during the time of service in the National Guard or reserves until they are entitled to a Veteran's License. The form DS-318 must be presented to the DDS upon every renewal of a National Guard license.
New Georgia Residents
General Information
You must apply for a Georgia driver's license or permit within 30 days of becoming a Georgia resident if you wish to drive upon the highways of this state. Please see Section 1: General Licensing Information for more information about requirements to obtain a license or permit and exemptions for certain individuals.
New Georgia Resident Without a Valid License or Permit Issued by Another State
Please see the appropriate chapter of this manual for obtaining a license or permit for the first time in Georgia.
- Under 18 – see Teen Licensing Requirements in Section 6: Teen Driving Laws;
- 18 or Older – See information under the heading "Requirement to Obtain to Georgia Driver's License" for complete requirements..
Transferring from Another State or District of Columbia
Under Age 18 with valid out of state license or permit
If you hold a valid driver's license or instructional permit issued by any other state of the United States or by the District of Columbia, you will normally be eligible to obtain a comparable license or permit issued by Georgia. All Georgia requirements including school registration, driver education and ADAP are required before the out of state license can be transferred.
18 or Older with a valid out of state license or permit
- You must surrender a valid license issued by another state or territory of the United States or by the District of Columbia (expired less than 2 years). If you are unable to surrender a valid driver's license, you must present a certified Motor Vehicle Report/Driving History from the state of issuance, dated within 30 days, showing your status as valid. Non-citizens are not required to surrender their foreign non-commercial license or permit;
- Be at least 18 years of age, or 17 years of age if surrendering a valid license equivalent to a Georgia Class C license with no time, route, purpose or passenger restrictions;
- You must know your full Social Security Number which will be verified with the Social Security Administration.
- Provide proof of identity. For a complete list of acceptable documents, see information under the heading "Real ID Documentation Requirements";
- Provide proof of citizenship or lawful presence in the United States (see information under the heading "Real ID Documentation Requirements"). All documents must be originals or certified copies. Faxed copies will not be accepted;
- Provide two documents to prove Georgia residency. For a complete list of acceptable documents, see information under the heading "Real ID Documentation Requirements".
- Pass a vision test.
Transferring a License/Permit/ID From Another Country or U.S. Territory
- If you do not have the out of country license/permit/ID in your possession, you must provide a Motor Vehicle Report/Driving History (printed in English) dated within the last 30 days, from the country of license issuance;
- Most non-citizen customers with a valid out of country driver's license, permit, or ID may retain their out of country document upon issuance of a Georgia-equivalent document. U.S. citizens will not be allowed to retain any licenses, permits, or identification cards issued to them by foreign countries;
- Successfully complete the knowledge, road, and vision exams;
- Present mandatory documents to prove identity, citizenship or lawful presence, Social Security Number, and residency. See information under the heading "Real ID Documentation Requirements" for the complete list;
- If under the age of 18, additional requirements will apply. Please see Section 6: Teen Driving Licenses for more details on teen licensing requirements;
- Licenses, permits and IDs issued outside the District of Columbia or any other state of the United States are non-transferable. A customer holding any document issued outside of the 50 States or District of Columbia must complete the full process for issuance of a new document in Georgia, including all tests required for the class being requested, if applicable.
- Citizens of certain foreign countries may be exempt from knowledge and skills testing. For a list, visit the DDS website.
Danger: All DMVs are not Alike!!!
Beware of fake DMV websites that charge for training materials or informational material. Most customers arrive at these sites by doing a browser search for "Georgia DMV," "Georgia License Renewal" or similar generic searches.
Please read the pages of these sites carefully, because by law they are required to inform users that the site is not affiliated with any State or Government Entity.
They are privately owned sites that will have .com or .org at the end of their website address (url). The official state of Georgia websites will have .gov as is the case with www.dds.georgia.gov.
Section 3: Testing Information
This Section Covers
- Knowledge Exam
- Road Signs
- Road Rules
- Road Test
- Making Road Test Reservations
- Road Test for Class C or D
- Road Test for Class M
- Road Test for Class E and F Non-Commercial
- Road Test for Class A, B, and C Commercial
- Results of Pass/Fail
Knowledge Exam
Knowledge exams are given on a walk-in basis at every DDS Customer Service Center statewide. To ensure that an applicant has adequate time to complete the knowledge exam, customers must begin taking the written test at least 30 minutes prior to closing. Please check the hours of operation before you visit on our website.
We offer special assistance for customers with reading disabilities and hearing impairment. Please visit your local CSC to schedule an appointment for an oral exam or to schedule an interpreter for the hearing impaired.
The road rules tests are available in some non-English languages, but all drivers must show ability to read and understand simple English such as is used in highway traffic and directional signs. Road signs and the actual
driving test are conducted in English only.
These basic rules must be followed while a knowledge exam is being given:
- You may not bring pens, pencils, paper, or any other items into the testing area;
- All cellphones, text messaging devices, and other types of wireless devices are prohibited in the testing area;
- You may not speak to anyone during the test other than the examiner administering the test.
Any violation of these rules is considered misconduct. If misconduct occurs during the administration of the knowledge exam, the exam session will be counted as a failure.
The questions on the knowledge exam pertain to topics discussed in this manual and consist of the following components:
Road Signs
A set of questions on the meaning of standard highway signs will be given. This test is given in English only. You will be asked to identify certain signs, signals and markers. You must correctly answer 15 out of 20 questions to pass. You may take a practice test at the DDS website.
Road Rules
The road rules test consists of a set of questions about driver responsibility, knowledge of laws, and safe driving practices applicable to
the class of license for which you are applying. You must correctly answer 15 out of 20 questions to pass. You may take a practice test at the DDS website.
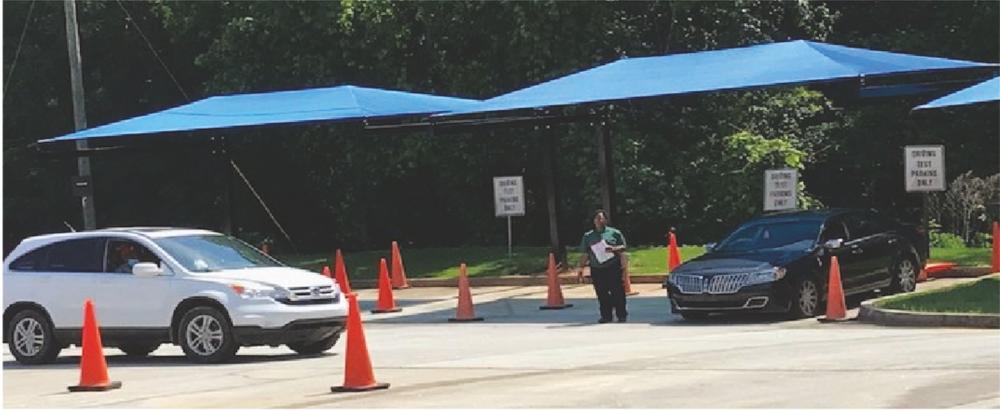

Road Test
Making Road Test Reservations
The Road Skills Test is administered by appointment only. Appointments allow us to maximize our resources and to serve all of our customers more efficiently. To make an appointment, please visit DDS Online Services at the DDS website.
Advanced Driver Assistance Systems
Drivers may perform the skills test in vehicles equipped with advanced driver assistance technology. However, the applicant must demonstrate their ability to operate the vehicle without such technology.
Road Test For Class C or D
- DDS will only administer a Class C or D road test in a four-wheel vehicle;
- You must provide the vehicle for the road test;
- All road test vehicles must have a valid registration/license plate, or if equipped with a temporary dealership tag, the applicant must provide the bill of sale for proof of purchase within the last 30 days (7 days if the vehicle is purchased from a third party);
- Your non-commercial road test may be administered in a virtual or traditional format.
Virtual Road Test
Conducted remotely by an Examiner who administers the test via a dual-facing camera and a hands-free cellular device. A parent, guardian, or other responsible adults; 21 years of age or older must serve as a passenger in the testing vehicle. They must have a valid driver's license.
Traditional Road Test
Conducted by an Examiner who administers the test while being seated in the passenger seat of the testing vehicle.
- All road test vehicles must be covered by liability insurance (you must show a valid insurance card or Motor Vehicle registration card that shows the VIN) and pass a safety inspection;
- If the vehicle is not equipped with illuminated turn signals, you must be able to pass the road test using hand signals;
- You may take the test in a rental vehicle. Please be advised that many rental agreements do not allow vehicle use for driver training or testing. Additionally, you must meet the following conditions:
- You must provide a copy of the rental contract (the contract will be reviewed to determine if testing is allowed);
- You must be listed as a driver on the rental contract;
- You must provide proof of valid insurance for the vehicle.
The driving test will not be conducted if weather conditions or any other conditions are determined to be unsafe for the driver or examiner. DDS will make every effort to ensure that impacted customers are rescheduled as soon as possible.
For the driving test you will be expected to demonstrate your ability to do all of the following:
- Parallel Parking: Park midway between two standards so that your car is not more than 18 inches from the curb. The standard parallel parking dimensions utilized in the driver's license test are 22 feet in length by 10 feet in depth;
- Straight Line Backing: Back your car for a distance of approximately 50 feet at a slow rate of speed (not more than 10 miles per hour) as straight and as smoothly as possible. You must turn your head and look behind the vehicle while backing. No boundary lines should be encroached;
- Stop for Signs or Traffic Signals: Give the proper hand or brake signal; approach in the proper lane; stop before reaching a pedestrian crosswalk and remain stopped until all pedestrians have cleared the crosswalk on the side of the roadway upon which you are traveling; move through the intersection only when you may do so safely;
- Turn About: Turn your car in a narrow space using a three-point turn;
- Use of Clutch: If your car has a manual transmission, you must shift smoothly and correctly;
- Approaching Intersections and Corners: You must be in the proper lane and look in both directions;
- Yielding Right-of-Way: Always yield right-of-way to pedestrians, vehicle operators, and bicyclists who move into the intersection before you by stopping and remaining stopped until they have cleared the intersection;
- Turning: Move into the proper lane and signal an adequate distance before the turn;
- Passing: Always check in front of and behind your vehicle to make sure you can safely pass without interfering with other traffic;
- Following: Do not follow other cars too closely. Follow at a safe distance from the vehicle in front of you in order to maintain control of the vehicle in case of any emergency situation or abrupt stops or turns;
- Maintaining Good Posture: Keep both hands on the steering wheel. Do not rest your elbow on the window and do not attempt to carry on a conversation with the examiner because he/she will be busy giving instructions and recording your score.
At the end of the Class C/D road test, the license examiner will gladly show you your score sheet and will provide you an opportunity to discuss the results if you wish to do so. You must achieve a minimum score of 75% to pass.
Road Test For Class M
You must furnish a motorcycle for the test and pass a safety inspection of the motorcycle by the license examiner before the driving test is given. All road test vehicles must have a valid registration/license plate or if equipped with a temporary dealership tag, the applicant must provide the bill of sale for proof of purchase within the last 30 days.
Motorcycle operator testing information is covered in the Motorcycle Operators Manual, which is available at all DDS Customer Service Centers and online at the DDS website.
If you hold a motorcycle permit, you may schedule a motorcycle skills test appointment online at the DDS website.
Motorcycle road tests cannot be conducted when the weather conditions make it unsafe for the driver or examiner, including when it is raining or when the pavement is damp.
Road Test For Class E and F Non-Commercial
There is no driving test for Classes E & F Non-Commercial; however, you must present an Application for Issuance of Non-Commercial E/F license (DS-36), establishing your ability to operate vehicles within the particular class, and pass a knowledge test for that particular class. You must also possess or be eligible to obtain a Class C Driver's license. Class E & F licenses are available to volunteer firefighters at no charge.
Customers who wish to take the non commercial Class E/F exam should study the Commercial Drivers Manual. The Commercial Drivers Manual can be located online at the DDS website or customers can obtain a hard copy at any DDS Customer Service Center.
Road Test For Class A, B, and C Commercial
Commercial vehicle operator's testing information is covered in the Georgia Commercial Drivers Manual, which is available at all DDS Customer Service Centers and online at the DDS website. You may schedule a Commercial skills test appointment Online at the DDS website. Pursuant to O.C.G.A. §40-5-25 and DDS Rule 1-1-.09(7), the $50.00 Commercial Driver's license (CDL) Road Skills Test fee is now required for each testing attempt.
Results of Pass/Fail
If you pass all the tests, you will be issued a temporary license/permit. Your permanent license/permit will be mailed to you.
If you fail any part of the Class C or D knowledge or road test, and it is your:
- 1st Failure: You must wait until the next day before retaking the portion you have failed.
- 2nd or Subsequent Failure: You must wait 7 days before retaking the portion you have failed.
For CDL Testing information please consult the Georgia CDL Manual.
Location Information
For a complete list of customer Service Centers and their hours of operation, please visit the DDS website or https://dds.georgia.gov/locations/customer-service-center.
Please remember that Tuesday is always the busiest day and the best time to visit in person is the middle of the week during the middle of the day.
Section 4: Other Services & Information
This Section Covers
- Renewal for Individuals Temporarily Located Out of the State of Georgia
- License, Permit, or Identification Card Number Changes
- Voter Registration
- Lost or Stolen License Replacement
- DDS Online Services
- Address Change
- Name Change
- Motor Vehicle Reports (MVR)
- Selective Service Registration
- Donations
Renewal for Individuals Temporarily Located Out of the State of Georgia
Renewal by mail is offered for certain groups of individuals who must be away from the State of Georgia at the time renewal of their license is required. Supporting documentation, a completed application and payment of fee (if required) must be submitted to verify that the applicant is eligible to renew in this manner.
This service is available to the following groups:
- Customers stationed out of state on active military duty, their spouse and any dependents living with them;
- Full-time students attending school outside Georgia, their spouse and any dependents living with them;
- Customers who are physically incapacitated and unable to visit a DDS Customer Service Center may be issued an ID Card only.
This service is subject to the following restrictions:
- The renewal will be granted for an 8-year renewal period, at the end of which the license holder must appear in person for renewal;
- A driver's license that has been expired for two (2) or more years cannot be renewed by mail.
- Changes (name, address, etc.) must be made in person at a DDS Customer Service Center. Changes cannot be made using the mail method of renewal.
Customers who choose to renew their license in this manner will not receive a Real DL/ID. To download the application package and complete instructions, please visit our website.
License, Permit, or Identification Card Number Changes
No licenses or identification cards may be issued in Georgia with a Social Security Number as the document number. If your license, permit or identification card number is identical to your Social Security Number, a randomly generated document number will be assigned to your document during the issuance/renewal process. Once your number has changed, you will need to ensure that any companies or entities using your driver's license, permit, or identification card number for tracking or verification purposes, such as insurance companies, are aware of this change.

Interest in Registering to Vote
DDS does not register customers to vote. DDS does confidentially transmit customer information needed to begin the voter registration process to the Georgia Secretary of State's Office (SOS).
Ultimately, each county voter registrar is responsible for completing voter registration including the issuance of a voter registration card. There is a voter registration section on each DDS license/ID issuance application, as required by law. In that section, customers are notified that their information will be used for voter registration purposes unless they choose otherwise. There is also a clear 'opt-out' box that the customers can check if they do not wish to register to vote or update their information.
Once the information is transmitted to the SOS, it is made accessible to the county registrars for processing and updating their voter records.
Important Points:
- If you do not receive your voter registration card within 30 days, contact your county voter registration office to determine the status of your application;
- Choosing this option does not guarantee that your voter registration information will be processed in time to meet specific election deadlines;
- If you want to register to vote for a particular election, please contact your county voter registration office to ensure that your most current registration information is recorded prior to the applicable voter registration deadline. Visit the Georgia Secretary of State Elections page for information.
Lost or Stolen License Replacement
Customers may apply for a replacement driver's license and/or ID card at a local DDS Customer Service Center or online. If you choose to apply online, you will go through an authentication process in order to verify identity. If you wish to apply at a DDS Customer Service Center, you will be required to show proof of identity. The fee online and at a DDS Customer Service Center is $10.00.
The following documents will be acceptable proof of identity for a replacement Georgia driver's license, permit or identification card:
ONE of these documents:
- Certified Copy of Birth Certificate with raised or impressed seal;
- Certificate of Naturalization or Certificate of Citizenship;
- Expired Georgia Driver's License, Permit or Identification Card;
- U.S. Passport or Passport Card - Must Be Valid
- Consular Report of Birth Abroad;
- Expired Georgia Interim;
- Non U.S. Citizens
- Valid foreign passport with valid I-94;
- Valid permanent resident card (l-551);
- Valid employment authorization card (l-766 or I-688A or I-6888) with proof of pending application to adjust status;
or TWO of these documents (only if replacing license, permit, or ID card):
- Social Security Card (original or copy);
- Original or Certified Copy of Marriage Certificate;
- Previous Year's Income Tax Return or W2;
- Current Auto, Home, Life or Health Insurance Policy (Cards Not Accepted);
- Current Auto Registration Receipt;
- Voter Registration Card;
- Valid or Expired Military ID Card and/or Military Orders;
- Valid Georgia Gun Permit.
- TWIC
- Check Stub
To change the number on your replacement Georgia driver's license, permit or identification card, you will be required to present a police report indicating that the license was stolen unless your license number and your Social Security number are the same. If the two numbers are the same, no police report is required.

DDS Online Services
Save Time, Go Online – Try DDS Online Services!
License, Permit, and ID Card Services*
- Make a road test appointment;
- Reinstate your driver's license;
- Renew your driver's license, permit or ID card;
- Replace a lost driver's license, permit, or ID card;
- Upgrade a Class D license to a Class C license;
- Change your address;
- Request an ID card (must have valid license or permit on file);
- Check license status and moving violation points;
- Check CDL Self Certification and Medical Documents status;
- Get suspension information.
Other Services Available
- Immediately create a secure user account and track updates to your license status;
- Conduct multiple services at one time;
- View and/or download a copy of your driving history (MVR);
- Request a certified driving history (MVR);
- Pay 'Failure to Appear' fee or reinstate a 'Failure to Appear' suspension;
- Pay 'Super Speeder' fee or reinstate a 'Super Speeder' suspension;
- Take a practice written test for a regular driver's license;
- Download the most recent version of the Drivers Manual;
- Complete and Submit form to DDS before arriving for service.
- Apply for For-Hire license endorsement;
- Register for a Motorcycle Safety course.
Note
Some online services are available if all requirements are met, including completion of Real ID requirements (see information under the heading "Real ID Documentation Requirements" for details).
Address Change
- You must update your record with DDS anytime your address changes. DDS correspondence will not be forwarded to new addresses by the U.S. Postal Service.
- If you have moved, you must visit a DDS Customer Service Center within 60 days to update your mailing and/or residential address, or you may visit our website to change your address. If you change your address in person, you must provide proof of the change in address. If you change your address online, your new address will be verified through USPS.
Name Change
- Name changes must be completed in person at a DDS Customer Service Center;
- If you change your name by marriage or other legal action, you must obtain a new license showing the correct name within 60 days. A free replacement license valid for the current term will be issued once in a license term;
- In order to change your name on your license or identification card, you must present a certified copy of a marriage license application (if the marriage occurred in Georgia), marriage license, state-issued marriage certificate, or court-ordered name change;
- You may change to a hyphenated surname on your license or identification card if the marriage occurred in the State of Georgia on or after November 1, 1982. A certified copy of the marriage license application reflecting the selection of the hyphenated surname must be presented at the time of the request.
Motor Vehicle Reports (MVR)
MVRs are available in 3-year, 7-year, or lifetime formats. A 3 year report is $6.00; a 7 year report is $8.00. A lifetime report is $8.00. Individuals may obtain a copy of their MVR in any of the following ways:
- Via Internet
- A non-certified copy of your Motor Vehicle Report (MVR) can be downloaded by using DDS Online Services. Please visit the DDS website for further details. You will be required to create an account if you have not already done so.
- In Person
- A certified copy of your Motor Vehicle Report (MVR) can be purchased in person at any DDS Customer Service Center. Proper identification will be required.
- If obtaining a motor vehicle report other than your own, the following is required:
- Completion of the Request for MVR form (DDS-18) from the licensee naming the person authorized to receive the record, including the full name, date of birth, and Georgia driver's license number of the licensee;
- The person receiving the report for another individual must also show proper identification.
- Via Mail
- You can obtain a certified copy of your MVR by submitting the Request for MVR form (DDS-18) OR a letter requesting either a 3-year, 7-year, or lifetime MVR, including the following:
- Your full name as it appears on your driver's license;
- Driver's license number;
- Date of birth; and
- Complete mailing address.
- You can obtain a certified copy of your MVR by submitting the Request for MVR form (DDS-18) OR a letter requesting either a 3-year, 7-year, or lifetime MVR, including the following:
Requests may be mailed to: Georgia Department of Driver Services, MVR Request, Post Office Box 80447, Conyers, Georgia 30013. When requesting a MVR, please include a money order, cashier's check, or personal check made payable to the Department of Driver Services in the amount of $6.00 for a 3-year or $8.00 for a 7-year or lifetime MVR.
Selective Service Registration
At the time of any license or identification card transaction, DDS is required to ask males age 18 whether they have registered with the U.S. Selective Service System and to report the responses to the U.S. Selective Service System.
Blindness Donation
When you obtain your driver's license, permit, or ID, you will have the opportunity to make a voluntary donation of $1 to Georgia's Blindness Education, Screening, and Treatment Program, which is administered by the Georgia Department of Public Health. Donations currently fund vision programs which provide screenings to save children's vision, eye exams for needy adults, training for people who have lost vision, and public education about eye donation. Your voluntary donation will be added to the total cost of your service.
Organ and Tissue Donation
The Donate Life Georgia Organ, Tissue and Eye Donor Registry was created in 2008 to allow Georgians an easy and user-friendly means of joining the state's donor registry. Georgians can join the registry through the website, when renewing their driver license or ID online, or when obtaining/renewing their license or ID at a local DDS Customer Service Center. You can also join the Donor Registry by calling Donate Life Georgia directly at 1-866-57-SHARE (1-866-577-4273) and requesting a donor registry form.
Other things to Remember:
- Organ donation can occur only after every measure has been taken to save your life, and only after death has been legally and medically declared;
- Georgia law prohibits the physician who declares a patient dead from participating in the removal or transplantation of that patient's donated organs or tissues;
- There is no cost to the donor's family for any expenses related to organ tissue/eye donation. Also, there is no delay in funeral arrangements;
- Georgia law requires hospitals to notify an organ/tissue/eye recovery center when a donation is possible;
- Recipients are selected by urgency of need, compatibility of blood type, body size, and tissue type, regardless of sex, race or creed.
More information concerning organ and tissue donation can be found at www.organdonor.gov.
GSFA Donation
DDS offers the opportunity to make a voluntary charitable contribution of $1, $5, or $10 to the Georgia Student Finance Authority (GSFA) during the license issuance or renewal process. Pursuant to HB 54 (2016), this donation will help to provide financial assistance toward the post-secondary educational costs of the children of law enforcement officers, firefighters, paramedics, emergency medical technicians, and prison guards employed by the state or other public employer who were permanently disabled or killed in the line of duty. The children of High-way Emergency Response Operators who were permanently disabled or killed in the line of duty are also included.
Section 5: Traffic Laws
This Section Covers
- Laws Governing Right-of-Way
- Georgia's Move-Over Law
- Passing
- How to Pass on a Two-Lane Road
- Passing is Prohibited on Two-Lane Roads
- Passing is Permitted When
- Passing On The Right
- When Someone Passes You
- Passing Stopped Cars
- Passing Bicyclists
- Passing Motorcyclists
- Weaving
- Turn Signals and Making Turns Safety
- Illegal Signals
- How To Make A Right Turn
- How To Make A Left Turn
- Watching for Pedestrians When Making Turns
- U-Turns
- Making Turns on Multi-Lane Highways
- Stopping, Standing, and Parking
- Steps to Parallel Parking
- Backing Up
- Traveling Speed
- Super Speeder
- Speed Limits
- Driving Too Slowly
- Railroad Crossings
- Highway Work Zones
- Reduce Your Speed
- Obey the Signs
- Obey Flaggers
- Yield to Amber Lights in Work Zones
- Adjust Your Lane Position
- Yield to Mobile Work Vehicles
- Work Zone Driving Tips
- Other Laws
- Controlled-Access Roadways
- Coasting
- Driving Under the Influence of Drugs or Alcohol
- Reckless Driving
- Racing
- Aggressive Driving
- Drag Racing/Reckless Stunt Driving
- Trucks and Vehicles Pulling Trailers
- Riding in Trailers
- Median Strip
- Impaired Hearing and Vision
- Obstructing the Driver's View
- Opening Vehicle Doors
- One Way Streets
- Stopping
- Use Headlights Properly
- Night Driving
- Georgia's Litter Control Law
- Safety Belts
- Safety Restraints for Children
- Distracted Driving/Following Emergency Vehicles
- Texting/Cell Phones/Passing Mail Carriers
3 Most Basic Traffic Laws
The three most basic traffic laws require drivers to:
- Obey traffic control devices (lights and signs);
- Obey the traffic directions of a law enforcement officer or firefighter, even if it goes against what the traffic control devices tell you to do;
- Never drive on a roadway that has been closed for construction, for the purpose of a special event, or for any other official reason.
Traffic laws are necessary to prevent crashes by defining the orderly movement of vehicles, pedestrians, and other users of public highways. Remember, traffic laws exist for your safety; failure to obey them can result in crashes that may seriously injure or kill you or others. To obey the laws, you must first know and understand them.
Laws Governing Right-of-Way
Right-of-way is a phrase used to describe who has the lawful authority to enter a roadway, change lanes within a roadway, make a turn from a roadway, travel through an intersection, or make any other traffic related movement. Georgia law establishes right-of-way in all situations. Vehicle drivers (including bicyclists) and pedestrians should always understand the rules related to right-of-way, and remember that right-of-way is something to be given, not taken. There may be instances in which you as a driver or pedestrian have the legal right-of-way over someone else, even though the other person does not realize it and is not obeying the rules of the road. In those instances, the right-of-way should be yielded in order to prevent a crash.
The following is a list of the most common situations in which right-of-way questions are faced in real life:
- When traveling on a roadway that intersects with another roadway, if you are faced with a stop sign, but other traffic is not, you may proceed only after stopping and yielding the right-of-way to any other vehicle or pedestrian either in the intersection, or so close to the intersection as to make it dangerous to travel through the intersection;
- At intersections where there are no stop signs, yield signs or other traffic signals, if two vehicles come to the intersection at the same time, the driver of the vehicle on the left must yield to the driver of the vehicle on the right;
- At a four-way intersection where all drivers are faced with stop signs, all drivers must yield to pedestrians; otherwise the vehicles should proceed through the intersection in a "first to arrive, first to proceed order." If two vehicles reach the intersection at approximately the same time, yield to any vehicles on your right.
- Important points to remember:
- Take your turn when it comes if it is safe to do so; do not unnecessarily delay traffic;
- If another driver tries to take your turn, even if you have the right-of-way, let the other driver proceed. It might prevent a traffic crash;
- Care, courtesy and common sense should govern your actions.
- Important points to remember:
- When making a left turn at an intersection, or into an alley or driveway, yield the right-of-way to all traffic coming from the opposite direction;
- When approaching a yield sign, slow down to a safe speed and be prepared to stop. If necessary, stop and only proceed when it is safe to do so;
- When the roadway you are traveling on is merging into other traffic without stopping, adjust your speed and vehicle position to allow you to merge into the new lane safely. If traffic from another roadway is merging into the roadway you are traveling on, safely change lanes away from the merging traffic if possible. If it is not possible to change lanes away from the merging traffic, adjust your speed and vehicle position to safely allow the traffic to merge;
- At intersections with traffic control lights, wait until the intersection is clear of traffic or approaching traffic before entering. Do not proceed "just because" you have the green light;
- If you are about to enter or cross a highway from an alley, private road or highway, you must stop and yield the right-of-way to all other pedestrians and vehicles already traveling on the roadway or sidewalk you are entering or crossing;
- If emergency vehicles are using their emergency lights (blue or red) and sirens, safely maneuver your vehicle out of their way. You should slow your vehicle and move over to the shoulder of the road, or if that is not possible, as far to the right of the roadway or lane as you can, and stop. You should always use caution to ensure that you do not endanger other motorists, bicyclists, or pedestrians while doing so. Do not position your vehicle so that it blocks an intersection or otherwise prevents the emergency vehicle from making a necessary turn;
- Yield to all highway maintenance vehicles and workers in a construction zone;
- Unless a sign posted at that intersection prohibits doing so, it is permissible to make a "right turn on red" at an intersection controlled by a traffic control light. You may proceed only after making a complete stop, yielding to all traffic and pedestrians, and making the determination that you can safely complete the turn;
- Unless a sign posted at that intersection prohibits doing so, it is permissible to make a "left turn on red" from the left lane of a one-way street onto a one-way street on which the traffic moves toward the driver's left. You may proceed only after making a complete stop, yielding to all traffic and stopping for pedestrians, and making the determination that you can safely complete the turn;
- When a school bus is preparing to stop to load or unload children, the driver of the bus will activate flashing yellow lights. When these flashing yellow lights are activated, all drivers approaching the school bus should slow down and be prepared to stop. All drivers should pay special attention to children who may be walking along or crossing the roadway. Once the flashing lights have turned red and the stop signs have extended from the side of the bus, it is unlawful for any vehicle to pass the stopped school bus while it is loading or unloading passengers. On a highway divided by a median, cars traveling on the opposite side from the stopped school bus are not required to stop, however drivers should remain attentive for children walking along or crossing the roadway.
Passing
How To Pass On A Two-Lane Road
- Wait for a passing zone to begin. A passing zone is indicated by striped lines to the right of the center line of the roadway. If the line nearest your vehicle is solid, you are not in a passing zone. Look ahead along the roadway to determine the length of the passing zone and if there is traffic approaching from the opposite direction.You must have sufficient time and space to execute your passing maneuver and return your vehicle completely to the right lane before the passing zone ends, before entering an intersection, and before oncoming traffic is within 200 feet of your vehicle;
- Before leaving your lane to begin passing, check your rear view and side mirrors, and turn your head and look back to check your "blind spot." Be certain that no one is passing you;
- Activate your left turn signal as you begin passing;
- Pass on the left and do not return to the right lane until your vehicle is safely clear of the overtaken vehicle. Wait until you can see the car you have just passed in your rear view mirror;
- Activate your right turn signal before returning to the right lane. Be sure to turn your signal off once you have returned to the right lane.
Passing is prohibited on two-lane roads:
- In area marked by a solid yellow line on the right of the center line, or a "Do Not Pass" sign, or double yellow lines;
- Within 100 feet of a railroad crossing;
- Within 100 feet of a bridge, viaduct or tunnel;
- When a car approaching from the opposite direction makes passing unsafe or will be within 200 feet of your vehicle prior to the completion of a passing maneuver;
- On a hill or curve where it is not possible to see oncoming vehicles which might be close enough to be a hazard;
- On the shoulder of the road;
- When a school bus is stopped to load or unload passengers.
Passing is Permitted When:
- Lawfully overtaking and passing another vehicle going in the same direction;
- An obstruction makes it necessary to drive to the left of the center line, but only after yielding to oncoming traffic;
- A roadway includes two or more marked lanes in the same direction;
- A roadway with more than one lane is restricted to one-way traffic. Upon a multi-lane, two way highway, you must never drive to the left of the center line except when authorized to do so by traffic control signals or signs or when making a left turn into an alley, private road or driveway.
Passing On The Right
You may pass on the right of another vehicle which is making or about to make a left turn if there is sufficient pavement width for both your vehicle and the vehicle making the left turn. You may also pass on the right when traveling on a multi-lane highway carrying two or more lanes of traffic in the same direction.
When Someone Passes You
When a driver behind you is overtaking your vehicle, be alert for any unsafe actions by the other driver. It is considered courteous to reduce your speed slightly, making it easier for the other vehicle to pass you. It is unlawful to increase your speed before you have been passed completely by the overtaking vehicle.
Passing Stopped Cars
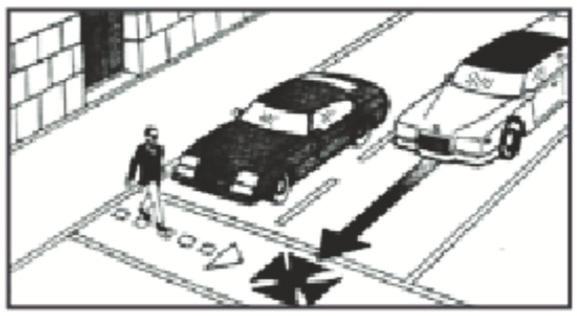
Whenever any vehicle is stopped to permit a pedestrian to cross the roadway at a marked crosswalk or at any unmarked crosswalk at an intersection, the driver of any other vehicle approaching from the rear shall not overtake and pass the stopped vehicle. When stopping to allow a pedestrian to cross in front of you, leave sufficient room between your vehicle and the crosswalk so that approaching traffic can see the entirety of the crosswalk.
Slow down and prepare to stop if you are approaching an intersection where other vehicles are stopped, even though the traffic control devices indicate they are authorized to proceed. If they are stopped because they are allowing a pedestrian to cross the roadway, their vehicle may block your view of the pedestrian.
Passing Bicycles
Motorists should approach bicycles with due caution and shall proceed as follows: (Violation is a misdemeanor punishable by a fine up to $250.00).
Make a lane change into a lane not adjacent to the bicycle if possible in the existing road and traffic conditions OR
If a lane change is impossible, prohibited by law, or unsafe, reduce the speed of the motor vehicle to a reasonable and proper speed for the traffic conditions, which speed shall be at least ten miles per hour less than the posted speed limit or 25 miles per hour, whichever is more and proceed around the bicycle with at least three feet between the vehicle and the bicycle at all times.
Passing Motorcyclists
A motorcyclist legally occupies the full width of a single lane when traveling. When passing a motorcyclist, a driver must pass in an adjacent lane. Drivers are not permitted to occupy the same lane as a motorcyclist while passing them.
Weaving
It is unlawful to weave from one lane of traffic to another in order to move faster than the flow of traffic. A motorist may change lanes on a multi-lane highway and pass slower moving vehicles only when it is safe to do so. A driver's signaling to change lanes should be clearly indicated so as to warn vehicles of the movement
The "Move Over" Law
All 50 States have "Move Over" laws to protect law enforcement officers and other workers stopped on our nation's roads. Georgia's "Move Over" Law helps ensure highway safety for motorists, emergency personnel, active sanitation workers, and utility service workers when their vehicles are stopped on the side of the roadway.
This law was created to reduce the number of injuries and fatalities to police officers, paramedics, firefighters, wrecker operators, and highway construction workers by maintaining an open buffer lane between passing highway traffic and authorized roadside emergency vehicles displaying flashing yellow, amber, white, red, or blue lights. It was amended to include active sanitation workers and utility service workers who are utilizing traffic cones and/or vehicles displaying flashing lights.

In Georgia, this law requires motorists to:
- Move over to the next lane if safely possible.
- If unable to move over, then slow down below the speed limit and be prepared to stop.
This law applies to any emergency, sanitation, or utility service vehicle parked on the shoulder of the roadway.
Why was the "Move Over" Law Passed?
- It saves lives. The "Move Over'' Law helps maintain traffic flow and protect the safety of motorists, emergency personnel, active sanitation workers, and utility service workers.
- Vehicles parked on the side of the roadway are vulnerable to crashes even when emergency lights are flashing.
- More police officers are killed by traffic crashes than in any other line-of-duty cause of death. More than one fourth of those killed are struck by passing vehicles while they work outside their patrol cars.
How does the "Move Over" Law make a difference?
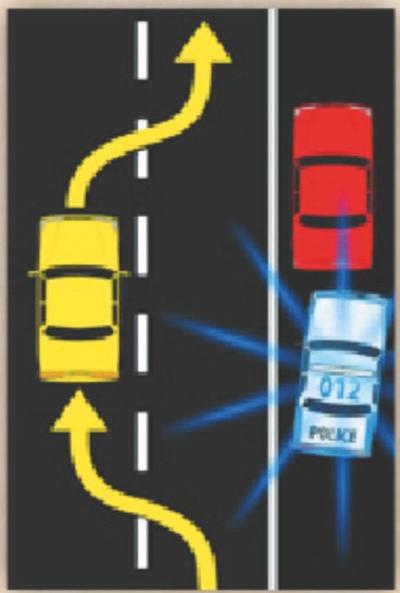
- Thirty percent of all crashes occur as the result of another crash.
- Providing a buffer lane for these vehicles when parked on the roadway shoulder actually reduces the risk of another crash.
- When the required clearance is given to these types of vehicles, the margin of safety is increased, not only for public safety, emergency personnel, active sanitation workers, and utility service workers, but for motorists and their passengers as well.
It's the Law!
- Violations can result in a fine of no more than $500 for the first offense.
- The "Move Over" Law is another reason to slow down on the highways and interstates.
Safely change lanes when approaching any emergency, sanitation, or utility service vehicle.
Turn Signals and Making Turns Safely
Turn movements by motor vehicles are regulated by law, and failure to observe or comply is a violation. Drivers must know and understand the law in order to turn safely and avoid crashes.



A turn signal must be given whenever a turn is made to the right or the left. You must give a continuous turn signal for an adequate distance to alert other drivers before turning. Never decide to make a turn at the "last minute." Turning quickly or erratically can be dangerous to you and other drivers.
Illegal Signals
It is against the law to flash turn signals as a courtesy or "do pass" signal to other drivers in the rear.
How To Make A Right Turn
- Using appropriate signals, and giving drivers ahead of and behind you adequate notice, activate your right turn signal;
- Approach the intersection in the right lane, staying as close as practicable to the curb or edge of the roadway;
- If there is a bicycle lane on the road on which you are traveling, you must yield to bicyclists traveling straight through the intersection before making a right turn;
- Make the turn in such a way as to end up in the right lane of the street into which you have turned and avoid entering any other lane of traffic. If there are multiple turning lanes on the street you are turning from, complete the turn so that your vehicle ends up in the corresponding lane on the street you are turning onto.
How To Make A Left Turn
- Using appropriate signals, and giving drivers ahead of and behind you adequate notice, activate your left turn signal;
- Move into the far left lane of the direction in which you are traveling, or into the turning lane if one is provided;
- Keep your wheels straight until you begin making the turn;
- Yield the right-of-way to all vehicles, including bicycles, which are approaching from the opposite direction, and pedestrians crossing either roadway;
- When safe to do so, and when traffic signals/signs permit, make your turn so that your vehicle ends up in the lane closest to the center lane(s) in your direction of traffic on the street you turned onto, or closest to the center line if there is no center lane;
- If there are multiple turning lanes on the street you are turning from, complete the turn so that your vehicle ends up in the corresponding lane on the street you are turning onto;
- Once you have entered an intersection to make a left turn, you cannot change lanes in the intersection;
- You must stop and remain stopped for any pedestrians in the crosswalk of the road you are turning onto until they have cleared the lanes of traffic that you are traveling on.
Watching for Pedestrians When Making Turns
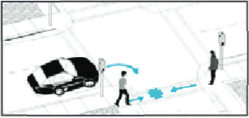
At most intersections where there is a pedestrian signal, the "Walk" signal of the crossing street corresponds to the green light of the roadway you are traveling on. This means that when you are authorized to turn, pedestrians are authorized to cross the street onto which you are turning at the same time. Therefore, before making your turn, you must stop and remain stopped for any pedestrians in the crosswalk of the road onto which you wish to turn until they have cleared the lanes of traffic upon which you are traveling.
U-Turns
Do not make a U-turn on a curve or near the top of a hill if you cannot be seen by other drivers approaching from either direction. Do not make a U-turn where signs prohibit doing so.
Making Turns on Multi-Lane Highways
On a multi-lane, two-way highway, you must never drive to the left of the center line except when making a left turn. If traffic control signals or signs are present, you may only complete the turn when authorized to do so by the traffic control signals or signs. When making left turns, you must always yield to oncoming traffic, and wait for pedestrians to clear the lanes of traffic, driveway, sidewalk, or alley you are turning into.
Stopping, Standing, and Parking
It is against the law to park on a highway. If the vehicle is disabled, you should make every practical effort to park off the highway, leaving free passage and a clear view of your vehicle for 200 feet in each direction.
Stopping, Standing or Parking is not permitted under the following conditions at any time:
- On the street side of any parked vehicle;
- On a sidewalk;
- Within an intersection;
- On a crosswalk;
- Between a safety zone and the adjacent curb;
- Alongside or opposite any street excavation or obstruction when stopping, standing, or parking would obstruct traffic;
- Upon a bridge or overpass, or within a highway tunnel;
- On any railroad tracks;
- On a controlled access roadway;
- In the area between roadways on a divided highway, including crossovers;
- At any place marked by a no-parking sign.
Stopping, Standing or Parking is permitted only momentarily to pick up or drop off passengers under the following conditions:
- In front of a public or private driveway;
- Within 15 feet of a fire hydrant;
- Within 20 feet of a crosswalk at an intersection;
- Within 30 feet of a stop sign, yield sign, or traffic control signal;
- Within 20 feet of a fire station driveway;
- Within 75 feet of the spot across the street from a fire station driveway;
- Within 50 feet of a railroad crossing;
- At any place where official signs prohibit standing.
Steps to Parallel Parking
When attempting to parallel park, drive past the parking space you wish to use and stop when you are approximately even with the car ahead of the space (you should be approximately 2 feet from the other car – door to door).
- Turn your wheels sharply to the right and back slowly toward the car behind the space you wish to use;
- As your front door passes the back bumper of the car ahead of the space you wish to use, quickly straighten your wheels and continue to back diagonally into the space in a straight line;
- When your front bumper is completely clear of the car ahead of you, turn your wheels sharply to the left and back slowly toward the car behind you;
- Stop before making contact with the car behind you. Place the car in drive, turn your wheels sharply to the right and pull toward the center of the parking space;
- Always give the appropriate turn signal prior to beginning your parking maneuver and when you exit from a parallel parking space.
Keep Right, Except to Pass
The "Slow Poke" Law (House Bill 459)
Slower drivers must move out of the passing lane (most left-hand lanes) and over to the right to allow faster-moving traffic to proceed. Regardless of the speed you are traveling, you must move from the lane when faster traffic is approaching. The only exceptions are:
- When traffic conditions make it necessary to drive in the passing lane;
- When inclement weather, obstructions, or hazards make it necessary to drive in the passing lane;
- When compliance with a law of this state or with an official traffic control device makes it necessary to drive in the passing lane;
- When your vehicle must be driven in the passing lane to exit or turn left;
- When it is necessary to pay a toll or use a pass on toll highways;
- Authorized emergency vehicles engaged in official duties; or
- Vehicles engaged in highway maintenance and construction operations.

It's the Law!
Backing Up
- Before backing, check all sides of your vehicle to make sure it is safe to do so. You should turn your head and look over your right shoulder while backing; do not depend on your mirrors;
- For buses and large vehicles, the driver should use all mirrors and utilize a reliable person to observe and direct while backing the vehicle.
Traveling Speed
Super Speeder
Any driver convicted of speeding 75 mph or more on a two-lane road or 85 miles per hour or more on any road in Georgia, will be assessed a $200 state fee. The state fee will be in addition to any local fines imposed in the jurisdiction where the speeding offense occurs. Failure to pay the state fee on time will result in a license suspension and additional $50 reinstatement fee.
Speed Limits
Maximum traveling speeds are determined based on the following general rules in Georgia unless otherwise posted:
- 30 miles per hour in any urban or residential district;
- 35 miles per hour on an unpaved county road;
- 70 miles per hour on a rural interstate;
- 65 miles per hour on an urban interstate or on a multi-lane divided highway;
- 55 miles per hour in all other areas.
These are only general rules. Local jurisdictions, the Georgia Department of Transportation,or the Georgia Department of Public Safety may deem it necessary to adjust speed limits based on local conditions, whether temporary or permanent.
Always watch for speed limit signs while driving. Some areas, such as school zones or construction zones may be posted for lower maximum speed limits at certain times of the day or for a short period of time. It is important to pay close attention to road signs while driving to ensure that when you approach a speed zone, whether temporary or permanent, you will have sufficient time to adjust your speed accordingly.
Driving Too Slowly
Drivers are prohibited from driving a motor vehicle at such a slow speed as to impede the normal and reasonable movement of traffic except when a reduced speed is necessary for safe operation. On road with two or more lanes, drivers cannot continue to operate a motor vehicle in the passing lane if that driver is being overtaken by a motor vehicle traveling at a higher rate of speed from behind. Penalties include fine up to $1000 and/or 3 points on the driving record.
When there are two or more lanes for traffic moving in the same direction, slower vehicles should use the right lane except when passing or making a left turn. Driving too slowly is dangerous because it impedes the regular flow of traffic. Minimum speed limits are posted on certain highways. If you are unable to drive at the minimum speed, you should seek an alternate route.
Railroad Crossings

You must always stop within 50 feet, but not less than 15 feet, from the nearest rail of a railroad crossing when any of the following apply:
- The signal is flashing;
- The crossing gates are lowered;
- A flagman is giving a signal;
- A train is approaching so closely as to create an immediate hazard;
- A train gives a warning signal and is an immediate hazard due to its speed or nearness to the crossing;
- A stop sign is posted.
Under no circumstances should a motorist drive through, around or under any crossing gate while the gate is lowered. After stopping, remain stopped until all tracks are clear, all railroad crossing warning signals stop flashing, the crossing gates are raised, and it is safe to proceed.
7 Steps for Safety at Highway-Rail Grade Crossings:
- Approach with care.
- Prepare to stop.
- Look both ways and listen carefully.
- If it won't fit, don't commit. Do not enter a crossing unless you can drive completely through without stopping!
- Look again.
- Cross tracks with care.
- Keep going once you start.
If your vehicle stalls on the tracks, do the following:
- Get out immediately
- Move away
- Locate Emergency Notification Systems (ENS) sign containing emergency contact information.
- Call for help! Tell them a vehicle is on the tracks.

Highway Work Zones
In an effort to minimize inconvenience, the Georgia Department of Transportation (GDOT) conducts most road construction and maintenance without closing roads to traffic. This poses a traffic hazard to drivers and their passengers, as well as the crew members working on the road. Over half of all fatal injuries to road workers are caused by being struck by a motor vehicle, and a third of these by vehicles intruding into the work space. Since 1973, 169 GDOT workers have lost their lives in work zones. However, motorists are more likely to be killed or injured in work zone crashes than GDOT workers. The general public accounts for 82% of work zone fatalities nationwide.
Highway work zones are defined as portions of a highway or street where construction, reconstruction, or maintenance work is being done to the road, its shoulders, or any other areas near the roadway. This definition also includes mobile work such as underground and overhead utility maintenance, snow removal, and land surveying activities. Highway work zones are set up according to the type of road and the work to be done on the road. Signing, roadway markings, and flaggers are used to direct drivers safely through work zones or carefully marked detours. Motorists are responsible for knowing how to read and react to these directions. Paying attention and driving cautiously and courteously are the most important steps to preventing crashes while driving through a work zone. Watch for the color orange. It means road work.
Obey the Signs
Warning signs in work zones have an orange background and black letters or symbols. They are used with other traffic control devices or flaggers to help direct traffic safely through work areas and to protect drivers, their passengers, and highway workers.
Reduce Your Speed
For safety reasons, the speed limit in most work zones is reduced. If the speed limit is not reduced in a work zone, drivers should obey the normal posted speed limit for the road on which they are traveling, but be more cautious of road conditions, lane position, and the presence of workers.
Advisory speed limits are used to identify safe speeds for specific conditions within a work zone. These black and orange signs are always used with warning signs. Official speed limit reduction requirements will be indicated with the standard black and white speed limit signs. Motorists who disobey regulatory speed limits in a work zone may be found guilty of a misdemeanor of a high and aggravated nature and will be punished by a fine of not less than $100.00 nor more than $2,000.00, or by imprisonment for a term not to exceed 12 months, or both.
Obey Flaggers
Flaggers are people used to direct traffic through and around work zones. In a work zone, a flagger has the same authority as a regulatory sign. Do not disobey a flagger's traffic control directions.
Yield to Amber Lights in Work Zones
Work vehicles and heavy equipment will typically have flashing or revolving amber lights.You must yield the right-of-way to these vehicles. Reduce your speed as you approach any work zone where vehicles have amber lights displayed.
Adjust Your Lane Position
Travel lanes are likely to be closed in work zones, and lane patterns may change as the work progresses. Sometimes, workers must operate within inches or feet of an open lane of traffic. When lanes are closed or narrowed, or workers are operating on the roadway near traffic, change lanes away from them if possible or shift slightly within the boundaries of your lane to give added distance between your vehicle and the workers. This will provide extra protection for you, your passengers and the workers along the roadway.
Yield to Mobile Work Vehicles
Some road work can be performed without actually closing lanes of travel. Pavement maintenance, debris removal, paint striping, utility work, and snow removal are examples of work accomplished while moving in traffic. Vehicles used in performing this type of work will have flashing amber lights and may have flashing arrows directing traffic to merge left or right. The vehicles may also display signs for the purpose of directing traffic or indicating hazardous conditions.
These vehicles usually work at very slow speeds, such as 5 miles per hour, and may occasionally be stationary in the road way. For your safety, and the safety of others, slow down, yield the right-of-way to these work vehicles, and follow any directions displayed by the work vehicles.

Work Zone Driving Tips

When you travel through a work zone, remember these four tips:
- Reduce your speed.
- Watch for speed limit signs. Fines are increased In most work zones.
- Adjust your lane position away from workers.
- Prepare for the unexpected!
Do your part to help protect the men and Women who work hard to make Georgia roads among the best in the nation.
Other Laws
Controlled-Access Roadways
- You are prohibited from entering or leaving any controlled-access roadway at unauthorized entrances or exits;
- Certain types of vehicles may be prohibited on controlled-access roadways if signs are posted to this effect;
- Backing up is prohibited on controlled-access roadways.
- An example of a controlled-access roadway includes any tolled facility in Georgia such as the I-85 Express Lanes or the reversible I-75 Express Lanes. Tolled lanes in Georgia require motorists to mount a registered Peach Pass transponder in their vehicle in order to access the lanes. Peach Pass can also be used in Florida and North Carolina. Registered owners of the vehicle that enters the tolled lane without an active Peach Pass will receive a violation notice in the mail.
- You are prohibited from entering the reversible Express Lanes when the access control gates are closed or closing.
Coasting
The driver of any motor vehicle, when traveling down a hill, must not coast with the gears or transmission of the vehicle in neutral.
Driving Under the Influence of Drugs or Alcohol
- It is unlawful for any person to operate a motor vehicle while under the influence of alcohol, a drug (prescription or illegal), or any other substance which impairs his/her ability to safely do so;
- A person 21 or more years of age is considered "Under the Influence of Alcohol" when 0.08 gm or more by alcohol weight is present in the blood;
- A person under 21 years of age is irrefutably considered "Under the Influence of Alcohol" when 0.02 gm or more by alcohol weight is present in the blood;
Certain drugs or other substances can also make a person irrefutably "under the influence." Having a prescription for certain medication is not a defense if the medication impairs your ability to safely operate a motor vehicle. Penalties for driving under the influence of intoxicants are severe, with fines up to $1000, jail sentences up to 12 months, and mandatory suspension of your driving privileges.
Reckless Driving
Reckless driving is defined as driving any vehicle in reckless disregard for the safety of persons or property. Examples of reckless driving include but are not limited to speeding, weaving in and out of traffic, improperly passing, etc. Penalties for reckless driving can include a fine of up to $1000, imprisonment for up to 12 months, and, if the driver is under 21 years of age, conviction will result in a suspension of all driving privileges.
Racing
The following behaviors are considered racing on highways and streets:
- When two or more people compete or race on any street or highway;
- When one motor vehicle is beside or to the rear of another driver, and one driver tries to prevent the passing or overtaking of the competing driver by acceleration or maneuver; or
- When one or more persons compete in a race against time.
Aggressive Driving
- A person commits the offense of aggressive driving when he or she operates any motor vehicle with the intent to annoy, harass, molest, intimidate, injure, or obstruct another person;
- Examples of aggressive driving include but are not limited to tailgating, cutting in front of another driver, blocking other drivers from passing or changing lanes, etc.
- A conviction for aggressive driving is considered a misdemeanor of a high and aggravated nature; The penalty for committing this violation may include imprisonment, fines, and, if the driver is under 21 years of age, conviction will result in a suspension of all driving privileges.
Drag Racing/Reckless Stunt Driving
"Reckless Stunt Driving" is operating "any vehicle while drag racing, in violation of Code Section 40-6-186, or laying drags, in violation of Code Section 40-6-251, in reckless disregard for the safety of persons on a highway or upon private property without express authorization from the owner of such property."
Penalties:
1st Conviction within 5 years
- 12-month suspension
- Eligible for early reinstatement at the end of 120 days
- Restoration Fee $210/$200 by mail
- Limited Permit Available
2nd Conviction within 5 years
- 3-year suspension
- Eligible for early reinstatement after 18 months from the date of conviction
- Restoration Fee $310/$300 by mail
- Limited Permit Available
3rd and Subsequent Conviction Within 5 years
- Habitual Violator (HY) Revocation
- No Limited Permit Available
- May apply for a probationary license per O.C.G.A. § 40-5-58
Trucks and Vehicles Pulling Trailers
When traveling upon a roadway outside of a business or residential district, drivers of trucks and vehicles pulling trailers must leave sufficient space between themselves and other vehicles of the same kind, so that the driver of an overtaking vehicle can enter and occupy the space without danger. This law prohibits the act commonly known as "caravanning."
Trailers wider than 8 feet, 6 inches are not permitted on Georgia's highways.
Riding in Trailers
Riding in a house trailer, or any other vehicular drawn trailer, is not allowed while it is being moved upon a street or highway. There is a high likelihood of injury or death if passengers are unrestrained in the trailer and the vehicle is involved in a crash or the trailer becomes disconnected from the vehicle.
Median Strip

It is unlawful to drive across a dividing section, barrier, or unpaved strip which separates two roadways at any point other than at an authorized opening or crossover.
Impaired Hearing and Vision
It is unlawful to operate a motor vehicle while wearing a headphone, headset, or any other device which would impair the driver's ability to hear. Also,the driver must not wear anything which would obstruct his or her vision while driving a motor vehicle. Not only is wearing these devices illegal, it is also unsafe.
Obstructing the Driver's View
If a vehicle is overloaded with passengers or freight so as to obstruct the view of the driver or interfere with the mechanical operation, it cannot be legally driven. Passengers must not ride in a position that interferes with the driver's view or his or her control of the vehicle.
Opening Vehicle Doors
Opening the doors of a vehicle on the side on which traffic is moving is prohibited unless it is safe to do so and unless it can be done without interfering with the movement of other traffic, including bicyclists that may be operating close to the lane of parked cars.
One Way Streets
Unless directed to by a traffic control device, authorized emergency personnel or construction workers, it is unlawful for a vehicle to be driven contrary to the direction posted on a one-way street or highway, except in situations where police vehicles or authorized emergency vehicles find it necessary to do so.
Stopping
When stopping or slowing down suddenly, the proper hand, arm, or brake operated stop signal must be given.
Use Headlights Properly
Use high-beam headlights only when driving in rural areas and when other cars are not nearby. You must use your headlights between one-half hour after sunset to one-half hour before sunrise; at any time when it is raining; or when visibility is limited.
You should dim (lower) your headlights when:
- You are within 500 feet of an approaching vehicle so as not to blind the driver;
- You are following closely (within 200 feet) behind another vehicle;
- You are driving on lighted roads;
- You are driving in rain, fog, snow, or smoke;
- Your vision is reduced to less than 200 feet.
Night Driving
Because of decreased vision at night and the glare of oncoming headlights, night driving presents its own unique challenges. Unfamiliar roads and unexpected situations are more likely to cause hazardous driving conditions. You can help ensure safe driving in several ways.
- Make sure your headlights are working properly and the lenses are kept clean. Periodically have them checked for correct aim/alignment;
- Don't "overdrive" your headlights. When traveling at night or in other situations that make the use of headlights necessary for safe travel, do not drive at a speed that requires a stopping time greater than the distance illuminated by your headlights;
- Slow down when oncoming traffic is approaching or when you are nearing a curve;
- If visibility is greatly reduced, use the edge line as a guide to maintaining your lane of travel. If there is no edge line, use the center line to guide yourself;
- Keep your windshield clean;
- Do not drive if you are tired. More frequent stops, more fresh air, lively radio programs and other measures can help you to avoid drowsiness and inattention;
- Watch carefully for highway signs; they are harder to see at night;
- Watch carefully for pedestrians and for vehicles stopped along the edge of the road;
- Do not stop on the roadway.
Safety Belts
Georgia law states that each occupant in the front seat of a passenger vehicle traveling on Georgia roads and highways must be secured by a seat safety belt (lap and shoulder). All occupants of any passenger vehicle must utilize a seat safety belt if they are under the age of 18.
Safety belts are needed because they are the most effective occupant protection in all types of vehicle crashes. According to Crash Stats from the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration, seat belts saved 12,802 lives in 2014. Georgia Department of Transportation reports that the risk of fatality in a crash is reduced by about 45% when seat belts are used. Using safety belts correctly is a preventable health care habit that:
- helps you keep control of the vehicle;
- helps keep your head from striking the dash or windshield;
- helps keep people in the vehicle from hitting each other;
- helps spread the crash force across the stronger parts of the body;
- helps protect you from injury;
- helps keep you from being ejected from the vehicle.
When used correctly, safety belts are effective at helping reduce the risk of death or serious injury. Georgia has a "primary" safety belt law, meaning that officers may stop and cite violators without observing another violation.
Safety Restraints for Children
Every driver transporting a child who is under eight years of age, except in a taxicab or public transit vehicle, must properly restrain the child in a child passenger restraining system appropriate for the child's height and weight. The restraint system must comply with the United States Department of Transportation Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard 213. Under limited circumstances, a child under eight may be exempt from this requirement. For further information, contact the Governor's Office of Highway Safety.
Distracted Driving
Distracted driving is one of the fastest growing safety issues. According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), 3,142 people were killed on U.S. roadways in 2019 because of distracted drivers. Distracted driving is doing another activity while driving. This takes the driver's attention away from the primary task of driving and increases the risk of crashing. Common distractions include but are not limited to talking on a cell phone, texting, reading, eating, grooming, using a navigation device, and adjusting the stereo system. The presence of passengers and pets can also increase crash risk. Georgia law requires drivers to exercise due care in operating a motor vehicle and prohibits any action that distracts the driver from the safe operation of such vehicle.
Following Emergency Vehicles
The driver of any vehicle, other than one on official business, must not follow any fire fighting apparatus traveling in response to a fire alarm, or other emergency vehicles, closer than 200 feet, or park any vehicle within 500 feet of any fire apparatus stopped in answer to a fire alarm.
Georgia's Litter Control Law
Each year, municipal, county and state government agencies spend thousands of dollars to clean up litter from the streets and highways of Georgia. Individuals who litter cause harm to the beauty of the state and impact the health, welfare and safety of others.
It is unlawful to dump, deposit, throw or leave litter on any public or private property in the State of Georgia, or any waters in the State of Georgia.
- "Litter'' means all sand, gravel, slag, brick bats, rubbish, waste material, tin cans, refuse, garbage, trash, dead animals or discarded materials of every kind and description;
- "Public or private property" means the right-of-way of any road or highway, any body of water or watercourse of the shores or beaches thereof, any park, playground, building refuge or conservation or recreation area and residential or farm properties, timberlands or forest.
Whenever litter is thrown, deposited, or dropped from any motor vehicle, the operator of the vehicle shall have violated the Litter Control Law. All Georgia law enforcement agencies are authorized to enforce compliance of the Litter Control Law.

Georgia's Litter Control Law classifies littering as damage to property. A conviction under this law is considered a misdemeanor in Georgia. Persons convicted of this law may be assessed a fine up to $1000 and a 12 month jail term. In addition, if convicted of littering, a judge could order the convicted person to pick up and remove litter from any designated area.
Passing a Postal Carrier or Sanitation Workers
The operator of a motor vehicle approaching a postal service vehicle or a vehicle with active sanitation workers that is displaying flashing yellow, amber, white, or red lights shall approach the vehicle with due caution and shall (unless directed by a peace officer) proceed as follows:
- Make a lane change into a lane not adjacent to the vehicle if possible in the existing safety and traffic conditions; or
- If a lane change would be impossible, prohibited by law, or unsafe, reduce the speed of the motor vehicle to a reasonable and proper speed for the existing road and traffic conditions, which speed shall be at least ten miles per hour less than the posted speed limit or 25 miles per hour, whichever is more, and be prepared to stop.
- Violation of subsection (b) of this Code section shall be punished by a fine of not more 71 than $250.00.
Texting & Cell Phones
Texting and Cell Phone Use While Driving
Georgia has a hands Free Law (HB 673) that mandates that drivers are not allowed to hold or support a phone for any reason. A phone can only be used with headphones, a wireless device, phone holder or mounted device. Penalties are fines and points added to your driving record increasing for each conviction.

Hands Free Georgia Law (HB 673)
Pursuant to 40-6-241(c), passed in 2018, all drivers operating a motor vehicle on any highway of this state. Holding or supporting, with any part of the body, a wireless telecommunications device or stand-alone electronic device.
- Writing, sending or reading any text-based communication, including a text message, instant message, e-mail or internet data.
- Watching, recording, or broadcasting a video or movie.
Penalties
- 1st conviction - 1 point and fine not more than $50.00
- 2nd conviction - 2 points and fine not more than $100.00
- 3rd or more convictions - 3 points and fine nor more than $150.00
Section 6: Teen Driving Laws
This Section Covers
- School Enrollment Requirements
- Joshua's Law
- Class C Instructional Permit (CP)
- Class D Provisional License
- Teens Moving to Georgia
- Revocation of Minor's License/Permit
- License/Permit Suspensions
- Suspension of Driver's License/Permit or Driving Privileges
- Convictions Other Than DUI
- Convictions for Driving Under the Influence of Drugs or Alcohol (DUI)
In 1997 The Teenage and Driver Responsibility Act (TADRA) established a graduated driver's licensing program for teens ages 15 to 18 in Georgia. This means that teens progress through a licensing process in three phases. As teens reach a certain age, complete certain requirements and have demonstrated their ability to safely operate a motor vehicle, they are allowed to progress to the next phase. Successful progression to the next phase also requires a demonstration of responsibility on the part of the teen by avoiding any violations during the term of the license held. TADRA also includes school enrollment requirements and license suspension/revocation provisions for dangerous behaviors (e.g. DUI, excessive speeding, etc.)
School Enrollment Requirements
Anyone younger than 18 years of age must present one of the following in order to obtain a driver's license or instructional permit:
- Certificate of School Enrollment (DS-1- obtained from school personnel);
- High School Diploma;
- General Education Development (GED);
- Special Diploma;
- Certificate of High School Completion;
- College or vocational school transcript dated within the last thirty days (official transcript with seal required);
- Certificate of Adult Literacy proving pursuit of a GED (available from the Technical College System of Georgia for those currently enrolled in a GED program);
- Declaration of Intent for Home Schoolers.
Responsible Adult Requirements
All applicants under 18 years of age must have a responsible adult present to sign the application and complete the Responsible Adult Affidavit. A responsible adult is a person who is eighteen (18) years of age or older, competent to verify the application, and has personal knowledge of the applicant. He or she may be:
- A parent or legal guardian of the applicant (must provide school or military documents, tax information or a driver's license/permit/ID card to show relationship to applicant),
- A social worker who has worked with the applicant (must provide an employee ID or a letter from the state agency),
- Certified Driver Training instructor authorized to act on behalf of the parent, legal guardian or responsible adult of the applicant with notarized documentation to verify,
- An employee of a homeless shelter where the applicant resides (must provide an employee ID or a letter from the shelter),
- A stepparent of the applicant;
- Other persons who can be identified by a state agency or official, school official or certified school records, or documentation from a federal agency or entity.
Joshua's Law
Joshua's Law promotes increased teen driving safety. The highlights of Joshua's Law include:
- Approved driver education training required to obtain a Class D Provisional license at ages 16 and 17;
- Approved driver education training required to obtain a Class M Instructional Permit (MP) at age 16;
- You must be 17 years of age to obtain a Class M Motorcycle Operator's License.
- The first stage of the graduated licensing program is a Class C Instructional Permit (CP).
Class C Instructional Permit (CP)
For first-time issuance of a Class C Instructional Permit (CP), you must meet all requirements to obtain a Real DL/ID if you have not already done so. See information under the heading "Requirement to Obtain to Georgia Driver's License" for complete requirements.
Obtaining a Class C Instructional Permit (CP)
Upon reaching age 15, or anytime thereafter, you may apply for a Class C Instructional Permit (CP). The following information will help you prepare for your visit to a DDS Customer Service Center:
- You will be required to present documents verifying your identity, U.S. citizenship or lawful presence, and Georgia residency as explained under the heading "Real ID Documentation Requirements";
- You must know your full Social Security Number or provide proof of your ineligibility to obtain a Social Security Number. See information under the heading "Real ID Documentation Requirements" for a list of acceptable documents;
- If you are under age 18, you will be required to present proof of school enrollment as explained in this section;
- If you are under age 18, a parent, legal guardian or responsible adult will have to sign the application, thereby giving their consent for you to obtain a permit. The individual who signs your application may, for any reason, revoke your permit until you reach the age of 18;
- You will be required to pass a vision test. Your eyes will be tested by means of a mechanical device;
- You will be required to pass a knowledge exam related to Road Signs and Road Rules. Please refer to information under the heading "Knowledge Exam" for more information related to the knowledge exam;
- The test fee is $10.00 and must be paid prior to testing. If any part of the test is failed, no refund will be issued. The permit fee must be paid prior to every testing attempt.
Conditions of a Class C Instructional Permit (CP)
- Once issued a Class C Instructional Permit (CP), you may operate any Class C vehicle when accompanied by a person at least 21 years of age who is licensed to drive a Class C vehicle, who is fit and capable of exercising control over the vehicle, and who is occupying a seat beside the driver;
- Class C Instructional Permits (CP) are valid for 2 years.
Class D Provisional License
For first-time issuance of a Class D License, you must meet all the requirements for a Real DL/ID if you have not already done so. See information under the heading "Real ID Documentation Requirements" for complete requirements.
Obtaining a Class D Provisional License
Upon reaching age 16 and after having held a valid instructional permit for one year and one day, you may apply for a Class D Provisional License by:
- You must schedule a road test appointment (for more information see the information under the heading "Road Test").
- You must surrender your Class C Instructional Permit (CP) or affirm on your application that you are unable to surrender the permit. See information under the heading "Lost or Stolen License Replacement" for details concerning lost licenses and permits;
- You will be required to present proof of school enrollment as explained in this section;
- You must present proof of completion of the Alcohol and Drug Awareness Program (ADAP). This program is taught in most schools, and is also available online. For information about ADAP, you may visit the DDS website;
- A parent, legal guardian or responsible adult will have to sign the application, thereby giving their consent for you to obtain a license. This person may, for any reason, revoke your license until you reach age 18.
- You must pass a road test designed to evaluate your ability to safely operate a motor vehicle.
- You must satisfy the Driver Education/Joshua's Law listed under the heading "Joshua's Law". (Note: Teens with parents active in the U.S. Military may use an out of state driver's education certificate provided that it is within 9 months of their 16th birthday.)
Driver Education Requirements
- To obtain a Class D license at the age of 16 or 17 you must complete a driver education course approved by DDS. An approved driver education course consists of:
- either 30 hours of classroom instruction OR completion of an equivalent online virtual course;
AND - 6 hours of on-the-road experience with a certified instructor OR completion of the DDS approved Parent/Teen Driver Guide;
- You must also have completed a cumulative total of at least 40 hours of other driving experience including at least 6 hours at night. Completion of the DDS approved Parent/Teen Driving Guide will serve as an affidavit certifying that this requirement has been met;
- either 30 hours of classroom instruction OR completion of an equivalent online virtual course;
- If the teen obtains the on-the-road component from a certified instructor, a separate document affirming that this requirement has been met must be completed at the time of the road test.
- You must present proof of completion of the Alcohol and Drug Awareness Program (ADAP). This program is taught in most schools, and is also available online. For information about ADAP, you may visit the DDS website.
- Exception
Any 17-year-old is exempt from holding their Class CP/instructional permit with proof that they are for enlisted in the military. They will be issued a Class C license after successfully passing the road test.
Conditions of a Class D Provisional License
- A Class D license Holder may not drive between the hours of 12:00 a.m. and 5:00 a.m. — NO EXCEPTIONS;
- During the first six months following issuance, only immediate family members may ride in the vehicle. 'Immediate family member' includes the driver's parents and step-parents, grandparents, siblings and step-siblings, children, and any other person who resides at the driver's residence;
- During the second six months following issuance, only one passenger under 21 years of age who is not a member of the driver's immediate family may ride in the vehicle;
- After the first and second six-month periods, only three passengers under 21 years of age who are not members of the driver's immediate family may ride in the vehicle;
- A Class D license Holder must, for the 12 months preceding application for their Class C license, be free from any convictions for major traffic violations that result in the mandatory suspension of a driver's license.
Teens Moving to Georgia
The following information applies to teens moving to Georgia from another state who wish to obtain a driver's license or permit in Georgia.
Under Age 18 without a valid license issued by another state
If you do not already hold a valid driver's license or instructional permit issued by another state, you will be subject to the licensing requirements of Georgia residents. Please see the preceding sections for more information.
Under Age 18 with valid out of state license
If you hold a valid driver's license or instructional permit issued by another state, you will normally be eligible to obtain a comparable license issued by Georgia. However, the state of issuance may have requirements for teenage drivers that differ from Georgia. For more information, please call the Customer Contact Center at (678) 413-8400.
Revocation of Minor's License/Permit
The parent, legal guardian or responsible adult who signed a minor's application for an instructional permit or driver's license may request revocation of the license or permit at any time prior to the minor's eighteenth birthday. The person requesting revocation of a minor's instructional permit or driver's license must submit his or her request for the revocation on the form designated by the Department. The form requires the person's notarized signature. The person requesting revocation of a minor's instructional permit or driver's license must pay a non-refundable fee of $10.00.
License/Permit Suspensions
Convictions Other Than DUI
The State of Georgia applies strict penalties to teens who fail to obey the laws regarding operation of a motor vehicle. The instructional permit or driver's license of any person under 21 years of age convicted of any of the following offenses shall be SUSPENDED for a period of six months for a first conviction, or for a period of twelve months for a second or subsequent conviction.
- Hit and run or leaving the scene of a crash;
- Racing on highways or streets;
- Using a motor vehicle in fleeing or attempting to elude an officer;
- Reckless driving;
- Aggressive driving;
- Any other offense for which four or more points are assessed:
- Unlawful passing of a school bus;
- Improper passing on a hill or curve;
- Exceeding the speed limit by 24 miles per hour or more.
- The accumulation of four or more points in any 12-month period while under 18 years of age.
A limited permit may be available only if the suspension resulted from a conviction for speeding 24-33 mph over the speed limit and the applicant is at least 18 years old.
Convictions for Driving Under the Influence of Drugs or Alcohol (DUI)
First DUI Suspension:
- If your Blood Alcohol Concentration was .02 or greater, but less than .08; or your implied consent test results were suppressed; or no test was given, your license will be suspended for a minimum period of 6 months, unless you have a previous conviction for an offense listed under the heading "Convictions other than DUI" list, in which case your license will be suspended for a minimum period of 12 months;
- If your Blood Alcohol Concentration was .08 or greater or you refused implied consent testing, your license will be suspended for a minimum period of 12 months;
- No limited driving permit is available.
Second DUI Suspension:
Your license will be suspended for a minimum period of 18 months, with ignition interlock permit eligibility after 120 days.
Section 7: Signs, Signals & Markings
This Section Covers
- Road Signs
- Shapes of Signs
- Regulatory Signs
- Warning Signs
- Guide Signs
- Construction and Maintenance Warning Signs
- Service Signs
- Traffic Signals and Signs
- Lane Control Signals
- Overhead Lane Signs
- Pedestrian Signals
- PHB/WALK Signal
- Pavement Markings
- Stop Lines
- Crosswalk Lines
- Railroad Crossings
- Center Lines
- No Passing Lines
- Edge Lines
- Lane Lines
- Traffic Striping
- Turn Lanes
- Bicycle Lanes
- Roundabouts
It's the Law
Georgia law requires that all drivers, including bicyclists, obey official highway signs and traffic control signals unless otherwise directed by a police officer or emergency worker.
Road Signs
Shapes of Signs
The State of Georgia uses seven basic shapes of signs to convey traffic control instructions. Drivers should know signs by their shapes and colors so that they may recognize them from a distance and begin reacting timely and appropriately.
Vertical rectangle signs

Vertical Rectangle signs are generally used for regulatory signs, which tell you what you must do. You must obey them in the same manner as traffic laws.
Horizontal rectangle signs

Horizontal Rectangle signs are generally used as guide signs. They show locations, directions, or other special information.
Octagon signs

An Octagon (eight-sided shape) always means stop. When you come to it, you must make a complete stop at a marked stop line. If there is no stop line, stop before the crosswalk on your side of the intersection. If there is no crosswalk, stop at a point from which you can best see oncoming traffic. You must not start again until all pedestrians have finished crossing on the side of the roadway you are traveling on, and you have yielded the right-of-way to closely approaching traffic.
Triangle signs
Triangle signs mean yield. You must slow down to a speed that is reasonable for existing conditions and stop if necessary. If you must stop, do so at a marked stop line, if it exists. After slowing or stopping, you must yield the right-of-way to other vehicles in the intersection or approaching closely on another roadway or auxiliary road leading into a major highway.
Diamond signs

Diamond shaped signs warn of existing or possible hazards on roadways or adjacent areas. They are yellow with black words indicating the potential hazard, or black symbols visually describing the potential hazard.
Round signs

A round sign means you are approaching a railroad crossing. This sign is posted a few hundred feet in front of the tracks and alerts you to slow down, look, listen and prepare to stop. If necessary, roll down a window and listen carefully for an approaching train. If a train is approaching, stop! Do not try to calculate whether you can "make it" across the track. Never try to beat a train through the intersection. Passing is prohibited at all railroad crossings.
Pentagon signs

Pentagon shaped signs mean you are approaching a school zone and/or school crossing. When used, they will be erected not less than 150 feet nor more than 700 feet in advance of the school grounds or school crossing. (These signs can sometimes be fluorescent green in color.)
Regulatory Signs
Regulatory signs tell drivers what they may or may not do. Drivers, including bicyclists, must obey them in the same manner as traffic laws. Remember, a red circle with a red slash from upper left to lower right means "No." The picture within the circle shows what is prohibited.
Wrong way sign

You are approaching a one-way highway or ramp. Driving on the highway or ramp in the direction you are traveling is not allowed.
No U turn sign

You cannot turn around to go in the opposite direction at this intersection.
Reduced speed ahead sign

You are approaching an area where a reduced speed limit has been established.
School speed limit sign

You are approaching a school zone. A reduced speed limit is in effect when the yellow lights are flashing.
One way sign

You may travel only in the direction of the arrow.
No right turn sign

You cannot make a right turn at this intersection.
Slower traffic keep right sign

When two or more traveling lanes are available in the direction you are traveling, slower traffic should travel in the right (outside) lane(s).
No bicycles sign

Bicycles are prohibited from entering this roadway.
Do not enter sign

This marks a one-way road. If you are facing this sign traffic is coming toward you. You must not continue down the road.
Keep right sign

Traffic is required to keep to the right of medians or obstructions.
Speed limit 55 sign

55 miles per hour is the maximum speed limit permitted in this area.
No right turn on red after stop sign

A right turn on red is prohibited, even after coming to a complete stop.
No trucks sign

Trucks are prohibited from entering this roadway.
Warning Signs
Warning signs are usually yellow with black markings. (Warning signs can also be fluorescent green with black markings.) They alert you to conditions that are immediately ahead. There may be road hazards, changes in traffic direction, or some other potentially hazardous situation that requires action on your part.
Sharp right turn then sharp left turn sign

Sharp turn to the right and then sharp turn to the left.
Side road enters at an angle sign

Side road enters highway ahead at an angle.
Narrow bridge sign

The bridge ahead allows room for only two lanes of traffic. Approach with caution.
Soft shoulder sign

Shoulder of the road is soft. Drive on the shoulder only in emergencies.
Two way traffic sign

Warning that you are leaving a separated one-way highway and will soon be driving on a two-way highway.
Sharp right turn sign

Sharp turn to the right.
Winding road sign

Winding road ahead.
Road crossing ahead sign

Another road crosses the highway ahead.
Dip sign

There is a dip in the road ahead. Slow down!
Divided highway sign

Divided highway begins. Prepare to change lanes or shift lane position.
Low clearance sign

Approaching a low underpass. Do not enter if your vehicle or cargo exceeds the maximum height indicated on the sign.
Right curve sign

Curve to the right.
Side road enters ahead sign

Side road enters highway ahead.
Road ends sign

The road you are traveling on ends straight ahead. Slow down and prepare to yield or stop before turning right or left.
Bump sign

There is a bump in the road ahead. Slow down!
Divided highway ends sign

Divided highway ends. Prepare to change lanes or shift lane position.
Hill sign

Steep hill ahead. Slow down and be ready to shift to lower gear to control speed and protect brakes from damage.
Signal ahead sign

Presence of traffic signals at intersection ahead. Slow down!
Slippery when wet sign

Roadway is slippery when wet. Remember, the first half-hour of rain is most hazardous.
Merge sign

Traffic merging from the right. Prepare to allow traffic to safely merge.
Yield ahead sign

There is a yield sign ahead. Slow down and prepare to stop if necessary.
Stop ahead sign

There is a stop sign ahead. Begin to slow down and be prepared to stop.
Pedestrian and animal crossing signs

These signs alert drivers in advance of areas where animals, people, and vehicles may be crossing.
Watch for pedestrians in the crosswalk sign

Drivers must stop and stay stopped when pedestrians are in the crosswalk.
No passing zone sign

This sign is on the left side of the highway and marks the beginning of a no passing zone. Any passing maneuver must be completed before reaching this sign.
Speed limit signs
These signs may be accompanied by speed advisory plaques that indicate the speed with which you should proceed.
Lanes reduced sign

Number of lanes reduced ahead.

Guide Signs
Guide signs may indicate what road you are on, and how to get to your destination. Many guide signs are rectangular, but some have other shapes. There are several different kinds of guide signs — route markers, information, destination, distance, and location signs. These signs may be accompanied by a "To" sign or an arrow, indicating the highway, facility, or location that can be reached by following the signs.
Here are some examples:
Exit 44 sign

Numbered interstate and highway signs
The numbers on these signs designate specific exits, interstates or highways.
Junction sign
Intersection of U.S. Route 47 & Ga. Highway 38. These roads are going to cross or meet the highway you are traveling on.
Milepost marker

Milepost markers are placed each mile along the edge of the roadway from one end of the state to the other. Zero always starts at the south or west border where a route begins.
Caution sign

Caution - a vehicle displaying this emblem is a slow-moving vehicle. A slow-moving vehicle is defined as any vehicle moving less than 25 miles per hour. They are required by law to display this emblem.
Bike route sign

This sign marks an officially designated bicycle route. Be cautious of bicyclists while traveling on this road.
Parking sign

This sign means there is a public parking area in the direction of the arrow.
Railroad crossing sign
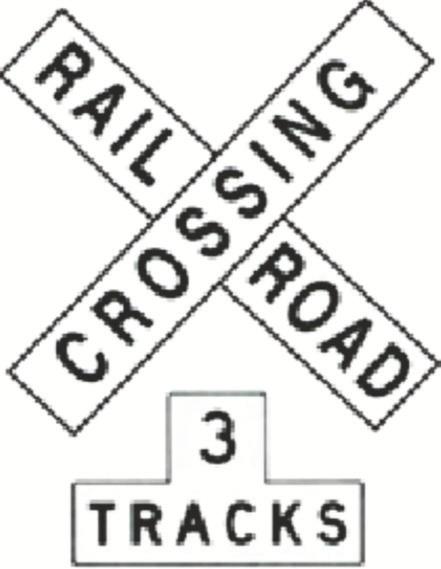
The cross-buck is placed at all railroad crossings. Yield to any approaching trains. Slow down, look and listen before crossing. A sign below the cross-buck indicates the number of tracks. A complete stop is required when a red light is flashing.
Construction and Maintenance Warning Signs
Road construction and Flagman signs

Warning signs for construction and maintenance projects are used to alert you to dangers ahead and give you enough time to adjust your speed accordingly. These signs are orange with black markings.
Road closed sign

Service Signs
While traveling along Georgia's highways, the following blue and white signs will give directions to service facilities.

Camping, hospital and picnic area signs
Express Lanes
Express Lanes offer motorists the option to pay a toll to bypass congestion in certain areas on the interstate. All vehicles with no more than two axles or up to six wheels can use Express Lanes if they have a registered Peach Pass. When the vehicle travels through the Express Lane, the toll amount will automatically be deducted from the pre-established account. There are currently two sets of Express Lanes in Georgia.
The I-85 Express Lanes are HOT Lanes along I-85 North in Gwinnett County. They are open 24-hours per day. On the I-85 Express Lanes, registered transit, three or more person carpools, motorcycles, emergency vehicles, and Alternative Fuel Vehicles (AFV) with the proper AFV license plate are allowed to use the lanes toll-free.
The I-75 South Metro Express Lanes are reversible lanes along I-75 South in Henry and Clayton counties. Reversible lanes change directions during the day to provide additional travel options during peak travel periods. When the travel direction is being reversed, signs will show the lanes are closed. On the I-75 South Metro Express Lanes, all vehicles, including motorcycles and electric vehicles, are required to pay a toll. Public transit buses, registered vanpools and emergency response vehicles may use the lanes toll-free if they have a Peach Pass.
Express lanes entrance sign

Express lanes closed sign

Traffic Signals and Signs
Traffic signals are placed at intersections to control the orderly movement of traffic and to prevent crashes. Drivers (including bicyclists) and pedestrians must obey these signals except when an officer is directing traffic. If a traffic signal is not functioning at all at an intersection, all drivers must treat the intersection as if a stop sign is posted for all directions. If a traffic signal is malfunctioning and flashing, drivers must proceed based on the color of the flashing signal they are facing: if the driver is facing a yellow flashing signal, the driver may proceed with caution; if the driver is facing a red flashing signal, the driver must stop and wait until it is safe to proceed.
Red light

A red light means you must make a complete stop before entering the crosswalk or intersection and wait until the light turns to green before proceeding.
Yellow light

A yellow light warns that the light is changing from green to red. Slow down and prepare to stop.
Green light

A green light means you may proceed if it is safe to do so after stopping for pedestrians and yielding to vehicles within the intersection.
Green up arrow

A green arrow means you may proceed carefully only in the direction the arrow is pointing after stopping for pedestrians and yielding to vehicles within the intersection. In this case you may go straight ahead only.
Green left arrow

A green arrow, in this case, means you may turn in the direction of the arrow after stopping for pedestrians and yielding to vehicles within the intersection.
Yellow right arrow

A yellow arrow may appear after a green arrow and warns you to clear the intersection.
Flashing red light

A red flashing light means you must stop completely (treat as you would a stop sign). Proceed with caution only after yielding the right-of-way to pedestrians and to other vehicles at the intersection.
Flashing yellow light

A yellow flashing light means you must slow down and exercise caution before proceeding through the intersection.
Flashing yellow arrow

A flashing yellow arrow means you may turn left after yielding to oncoming traffic and pedestrians (oncoming traffic still has the green light).
Lane Control signals
Some roadways are designed to accommodate different traffic demands during the day through the use of a reversible lane system. Appropriate travel lanes on a roadway utilizing a reversible lane system are indicated as follows:
No travel allowed signal

No travel allowed in this lane in the direction you are going.
Clear the lane or left turn permitted signal

"Steady" - clear the lane; "Flashing" - left turn permitted.
Travel in lane signal

Travel in lane.
Overhead Lane Signs
Left turn only sign

Left turn only.
Straight or left turn only sign
Straight or left turn only.
Right turn only sign

Right turn only.
Pedestrian Signals
Walk signal

Leave the curb to cross the street.
Orange Don't Walk signal

Do not leave the curb.
Red Don't Walk signal

Flashing - do not leave the curb, but complete walking across the street if already started.
Pedestrian safety guide sign
Pedestrian-Hybrid Beacons (PHB)
This signal is known as a Pedestrian Hybrid Beacon (PHB), and it is designed to help pedestrians safely cross busy streets. Pedestrians push a button to activate the overhead beacon and stop road traffic. When WALK appears on the Pedestrian signal, pedestrians can cross the street.
Dark

The PHB remains DARK for traffic unless a pedestrian activates the push-button.
Flashing

When a pedestrian presses the button, the signal is activated. Approaching drivers will see a FLASHING YELLOW signal for a few seconds.
Solid Yellow

The flashing yellow is followed by a SOLID YELLOW signal, indicating drivers should reduce speed and be prepared to stop.
Solid Red

The solid yellow is followed by double SOLID RED signals, requiring drivers to stop.
Flashing Red

The double solid red signals are followed by alternating FLASHING RED signals. This requires drivers to come to a full STOP, and proceed when pedestrians have cleared the crosswalk. The signal will then go dark until activated again by a pedestrian.

Pavement Markings
Pavement markings, like highway signs, are used to warn and direct drivers and to regulate traffic.
Stop Lines
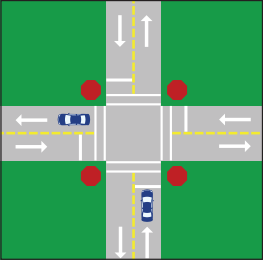
Stop lines are white lines painted across the pavement at intersections indicating the point beyond which your vehicle should not cross if you are stopping for a traffic control device. In urban areas, the line is usually located about four feet before the crosswalk. Drivers must come to a complete stop at the stop line, when present, not at the actual stop sign or traffic signal.
Crosswalk Lines
These white lines are painted across, or partially across the pavement. Sometimes they will be painted in a ladder pattern. When pedestrians are in the crosswalks, they have the right-of-way over motor vehicles. Crosswalks are sometimes in the middle of a block in residential areas, and in some cases, a pedestrian crossing signal is located at the white line.
Railroad Crossings
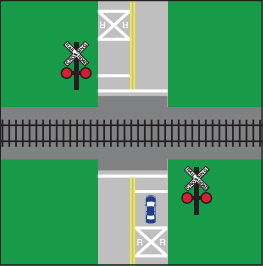
When a road is crossed by a railroad crossing, the pavement is usually marked with a large X and two R's. At railroad crossings, a yellow line is always placed on the right side of the center line to prevent passing. The crossing is sometimes equipped with control arms and/or emergency lights, to warn drivers of approaching trains. The driver of the vehicle must stop if warning signals indicate a train is approaching.
Center Lines
These are used to separate traffic moving in opposite directions on paved roadways. Broken yellow lines are used when there are only two lanes and it is safe to pass in either direction.
No Passing Lines
Single Lines
These single, solid yellow lines on two-lane roads indicate zones where passing is prohibited. They will be located on the right of the broken yellow line when they apply to the lane in which you are traveling. In some instances, both yellow lines will be solid, indicating it is not safe for passing in either direction.
Double White Lines
These are double white line (dashed or solid) pavement markings on roadways that indicate where vehicles can or cannot cross to access the adjacent lane. When the double white lines are dashed, vehicles are allowed to cross over to the adjacent lane. When the double white lines are solid, lane changes are prohibited.
Edge Lines
These are the solid white lines along the side of the pavement. They serve as safety guides, especially at night when it is difficult to see the edge of the road. A yellow edge line may be used on the left side to warn of narrow or raised medians.
Lane Lines
These are the white dashes that mark the individual lanes of travel on streets and highways having more than one lane for traffic moving in the same direction.
When there are four or more lanes with traffic moving in opposite directions, two solid yellow lines mark the center of the roadway. You may cross these lines only to make a left turn into or from an alley, private road, driveway, or another street. When traveling on a multi-lane road, stay in the right lane except to pass other vehicles traveling in the same direction
Traffic Striping
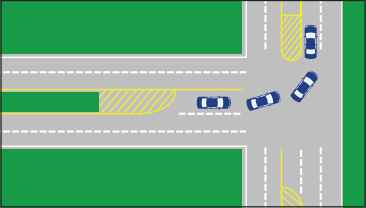
These markings, created by diagonal yellow lines, are on streets and highways indicating that the road is narrowing or there is an obstruction on the roadway. The area is similar to a triangle with solid yellow diagonal lines within the outside lines. Always keep to the right of these markings.
Turn Lanes
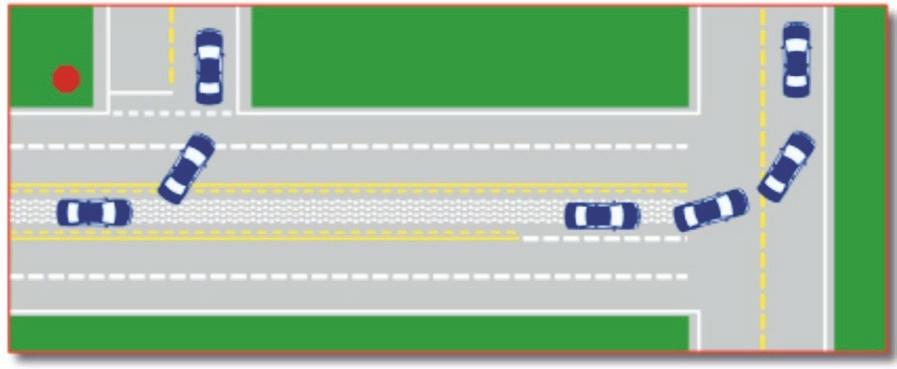
These lanes, bordered by solid yellow and/or broken yellow lines, is in the center of many streets and highways to make left turns. A motorist desiring to turn left should proceed to the turn lane just prior to making a left turn. Georgia law prohibits the use of this lane for any purpose other than making a left turn. You may enter this lane no more than 300 feet from the location of the left turn.
When a turning lane is provided for vehicles traveling in both directions, you should use extreme caution before entering the turning lane to make a left turn. There may be a vehicle traveling in the opposite direction also entering the turning lane to make a left turn. This is especially problematic in congested areas.
Bicycle Lanes
These are solid white lines typically located between the farthest right traffic lane and the curb or edge of the roadway. If there is a right-turn-only lane present, the bicycle lane will be located to the left of the right-turn-only lane in order to safely accommodate bicycles traveling straight through the intersection. Bicycle lanes may also be marked with painted symbols of a bicycle. Drivers of motor vehicles are prohibited from driving or parking in the bicycle lane, except to cross over it to make a turn. When crossing over a bicycle lane to make a turn, motorists must yield to bicyclists that are present.
Roundabouts
Navigating a roundabout
Roundabouts are sometimes used at intersections instead of stop signs. The purpose of a roundabout is to allow the intersection to handle heavier traffic flow without the need for a signal or a four-way stop. When entering a roundabout, traffic laws concerning right-of-way still apply. You must yield to other traffic that is already in the roundabout. You will always enter a roundabout to the right, and continue circling until you have reached the roadway onto which you want to turn. When reaching the desired road, you will always exit to the right.
Pedestrians
- Approach: At the pedestrian crosswalk, look to make sure cars stop for you. Use pedestrian crossing signal if available.
- Cross: Cross to the pedestrian refuge. Look to make sure cars stop for you. Finish crossing to the opposite sidewalk. Never cross to the center island.
Cyclists
Experienced cyclists may navigate roundabouts like motorists. Do not hug the curb. Ride in the middle of the lane to prevent vehicles from passing you. Stop for pedestrians in crosswalks.
Children or cyclists who are not comfortable entering the flow of traffic should walk their cycles and act as pedestrians.
Navigating a Single Lane Roundabout
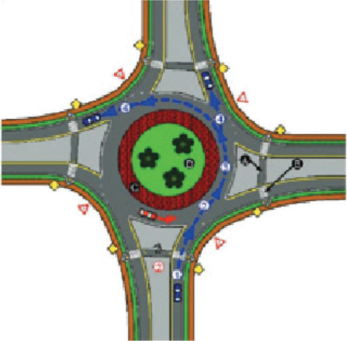
Motorists
- Approach: Slow down to the posted advisory speed. Stop for pedestrians in the crosswalk; they have the right of way.
- Enter: When entering the roundabout, yield to all circulating vehicles. Wait for a gap and then merge into traffic in the roundabout. Traffic in a roundabout always circulates counterclockwise.
- Proceed: Continue circling through the roundabout until you reach the roadway onto which you want to turn.
- Exit: Signal, then bear right to exit the roundabout. Slop for pedestrians in the crosswalk.
Navigating a Multilane Roundabout
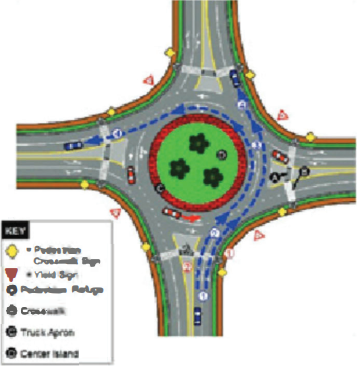
Motorists
- Approach: Follow the lane use signs & pavement marking arrows. Get into the correct lane before entering the roundabout. Slow down to the posted advisory speed. Stop for pedestrians in the crosswalk; they have the right of way.
- Enter: When entering the roundabout, yield to all circulating vehicles in both lanes. Wait for a gap and then merge into traffic in the roundabout. Traffic in a roundabout always circulates counterclockwise. Maintain your lane as you enter the roundabout.
- Proceed: Continue circling through the roundabout until you reach the roadway onto which you want to turn. Do not change lanes in the roundabout.
- Exit: Signal, then bear right to exit the roundabout. Stop for pedestrians in the crosswalk.
*Please note that these roundabout diagrams are examples only and do not represent all roundabout designs.
Section 8: Safety Guidelines
This Section Covers
- Entering the Car
- Steering
- Fog
- Hydroplaning
- Skidding
- Curves
- Leaving the Roadway
- Tire Blow-Out
- Winter Driving
- Carbon Monoxide
- Steering Locks
- Following Too Closely
- Speed and Stopping Distance
- Expressway Driving
- Entering Expressways
- Exiting Expressways
- Use of Lanes on Expressways
- Gores
- HOV Lanes
- Tips for Expressway Driving
- Other Highway Emergencies
- Protecting the Air
- Idling Engines
Traffic laws alone cannot regulate every type of driving situation that may occur. There are some general rules which drivers should understand and follow. Read this chapter with care. Someday these safety tips might help you avoid a crash, serious injury, or even death. These are only general statements and cannot dictate your actions in all situations. It is up to you to evaluate the situation and make a determination as to the best course of action.
Tire Pressure
Prior to entering vehicle check tire pressure using recommended psi located in the door jam of the vehicle. Use a tire pressure gauge to check your psi. If your psi is above the number listed on your door jam, let air out until it matches. If below, add air (or have a retailer help you) until it reaches the proper number.
You may also measure tread depth using the penny test. Once every month, or before you embark upon a long road trip, check your tires for wear and damage problems. One easy way to check for wear is by using the penny test.
- Take a penny and hold Abraham Lincoln's body between your thumb and forefinger.
- Select a point on your tire where the tread appears the lowest and place Lincoln's head into one of the grooves.
- If any part of Lincoln's head is covered by the tread, you're driving with the legal and safe amount of tread. If your tread gets below that (approximately 2/32 of an inch), your car's ability to grip the road in adverse conditions is greatly reduced.
Entering the Car
- Develop a routine for entering the car safely and preparing for your trip. If you are parked on the street, enter from the curb side of the vehicle. If this is not possible, wait until your entry can be made with reasonable safety and without interfering with the flow of traffic;
- Have your keys ready, and approach the vehicle facing traffic;
- Adjust your seat and mirrors;
- Check passengers to be sure they are properly seated and do not interfere with your view;
- Before starting your ignition, fasten your seat belt and make sure your passengers do the same;
- After starting your vehicle, check around your vehicle for hazards or approaching traffic, including bicyclists and pedestrians, give the proper signal and move cautiously into the stream of traffic.
Steering
Good posture while driving is important because it allows a better view of hazards and more control of the vehicle. As a general rule, when gripping the steering wheel, place your left hand at the 9 o'clock position and your right hand at the 3 o'clock position on the wheel. Some manufacturers recommend placing your hands at 8 o'clock and 4 o'clock positions when the vehicle is equipped with air bags. Check your owner's manual or contact your vehicle manufacturer to determine which position is best for your vehicle. Always keep both hands on the wheel unless you are safely performing another driving-related task, such as activating your turn signal.
Fog
If possible, avoid driving in heavy fog. If you must drive, follow these guidelines:
- Reduce driving speed;
- Reduce speed further when you see headlights or red tail Lights. These indicate the presence of another vehicle and, due to fog, it may be more difficult to accurately judge the distance between your vehicle and others;
- Dim your headlights. Bright lights produce a glare in heavy fog, actually making it more difficult to see than when using regular headlights;
- Do not drive with parking or hazard lights on.
Hydroplaning
Hydroplaning occurs when there is standing water on a roadway. At speeds up to 35 mph, most tires will channel water away from the tire similar to the way a windshield wiper cleans the windshield. As your speed increases, tires cannot channel the water as well, and your tires may start to lose contact with the road and ride over the water like a set of water skis. In a standard passenger car, partial hydroplaning can begin at speeds as low as 35 mph. At 55 mph, the tires may lose all contact with the road. If this occurs, there is no friction available to brake, accelerate, or steer. It is possible for the vehicle to go into an unpredictable and uncontrollable skid. If this occurs, take your foot off of the accelerator, letting the car slow down. To prevent hydroplaning, maintain good tires with adequate water-channeling thread on your vehicle. Most importantly, slow down when there is water on the roadway.
Skidding
A car skids when its tires lose their grip on the road surface. When a car skids, both the power that the engine sends to the wheels and the braking ability of the wheels are lost. Slick surfaces can exaggerate normal movements. If brakes are applied too hard, or the wheel is turned too sharp, a skid can occur.
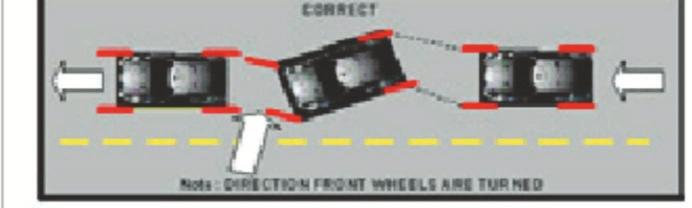
If you start to skid:
- ease your foot off of the accelerator;
- begin turning the steering wheel in the direction of the skid;
- once you have regained control of the vehicle, you can lightly apply brakes and steer in a safe direction.
Remember, the first half-hour of rainfall is the most dangerous because roadways become extremely slippery when the water mixes with oil and other chemicals on the road surfaces.
Curves
Curves in a roadway are potential sources of hazard for drivers. Because of the maneuvering involved, it is more likely that a less cautious driver may fail to maintain their lane while driving through a curve. When roadways are slick because of rain or other hazards, curves can be especially dangerous and require much lower speeds than when the road is dry. Sharper curves are usually marked with a safe miles-per-hour sign. Usually less than the posted speed limit, these advisory signs indicate that the reduced speed shown will make driving through a curve safer.
Reduce your speed before entering these curves. If, while driving through the curve, you realize that you are traveling too fast, do not forcefully apply brakes because this may cause your vehicle to skid. Instead, take your foot off the accelerator, carefully apply the brake, and continue steering in the lane of travel.
Leaving the Roadway
Uneven terrain and obstacles make it difficult to safely maneuver a vehicle once it has left the roadway. Serious injury or death can result from a crash if this happens.
To avoid leaving the roadway while driving, pay attention to road conditions. Drive at or below the speed indicated on a regulatory sign or an advisory sign indicating potential hazards. Drive defensively, being mindful of the actions of drivers around you.
If your vehicle leaves the roadway, try to follow these guidelines:
- Don't panic;
- Take your foot off the accelerator;
- Grip the steering wheel tightly and be prepared to withstand sudden shocks;
- Don't hit the brake pedal suddenly and hard; use your brakes carefully;
- Don't try to turn back onto the pavement immediately. Overcompensating ("jerking the wheel") when returning to the roadway can cause you to lose control of your vehicle by skidding or flipping, or may also cause your car to go into other lanes of traffic;
- Wait until your speed has reduced, check the traffic, and look for a place to safely return to the roadway by merging into traffic. If necessary, come to a complete stop before re-entering the roadway.
Tire Blow-Out
Unlike a slow leak which may cause a tire to go flat over time, a blow-out occurs when the tire ruptures and goes flat immediately. If this occur while your vehicle is in motion, it can cause you to lose control.
If you experience a sudden tire blow-out, do not panic. Follow these guidelines to maintain control of the vehicle.
- Apply brakes lightly if necessary and safe to do so;
- Grasp the steering wheel firmly and take your foot off the accelerator to allow the vehicle to roll to a stop;
- Do not move to the shoulder of the road until the car has slowed greatly. If the blow-out causes the car to swerve on to the shoulder, do not try to get back on the pavement. Let the car coast to a stop. See the guidelines in the section "Leaving the Roadway" above for what to do when your vehicle leaves the roadway.
Winter Driving
Winter weather can create many driving hazards. Because of the usually mild climate, most Georgians are not experienced in driving in winter weather. Here are several suggestions to help you drive safely in winter weather:
- Use chains or snow tires if road conditions require extra traction. Always check the manufacturer's instruction manual for your vehicle, the tires, and the chains before installing them on your vehicle and operating on a roadway;
- Keep windows clear. Remove snow and ice from all window surfaces before operating the vehicle on a roadway;
- When you first enter the roadway, and if it is safe to do so, get a "feel" for the road. Test your brakes gently. Determine how your vehicle will respond to turning the wheel by making slight adjustments. Never apply sudden braking. Instead, slow down gradually before you come to an intersection, make a turn, or stop;
- Keep a safe distance between you and other vehicles;
- Reduce speed according to conditions;
- Watch for hazards or changing road conditions ahead.
Tips for Safe Winter Driving
- Get your car serviced routinely.
- Check your battery.
- Check your cooling system.
- Fill your windshield washer reservoir.
- Check your windshield wipers and defrosters.
- Verify floor mat installation to prevent pedal interference.
- Inspect your tires.
- Check the age of your tires.
- Know your car.
- Plan your travel and route.
- Stock your vehicle with necessary tools and supplies.
- Learn what to do in a winter emergency.
Carbon Monoxide
Cars produce carbon monoxide, a deadly odorless and colorless gas. Symptoms of carbon monoxide poisoning are sudden weariness, yawning, dizziness, and nausea. Simple precautions to avoid carbon monoxide are:
- Don't leave the car motor running in a garage;
- Don't leave the car motor running and the window closed while the car is parked;
- Don't operate the heater or air conditioner in a parked car with the windows closed;
- Don't drive with a defective muffler or exhaust system.
Move a victim of carbon monoxide poisoning to fresh air, contact emergency medical services, and give artificial respiration if it is necessary and you are trained to do so.

Diverging Diamond Interchange
A Diverging Diamond Interchange (DDI) shifts traffic flow to the opposite side of the road to allow vehicles to enter the freeway by turning left onto an on-ramp without stopping. This reduces points of conflict and improves traffic flow and safety. The DDI is a proven, cutting edge, low-cost design that provides immediate traffic relief. Under normal, free-flowing traffic conditions on surrounding highways, the DDI can reduce delays in evening rush hours up to 20 percent.
View an informative video about Diverging Diamond Interchanges.
Steering Locks
Steering locks are anti-theft devices found in most cars manufactured since 1969.
Steering locks can cause dangerous situations for drivers who are not familiar with their operation. If a vehicle's ignition is placed in the lock position while the vehicle is in motion, the steering capability of the vehicle will be disabled, and the driver will be unable to steer the vehicle.
Further information concerning steering locks is available from the Automobile Safety Foundation.
Following Too Closely
A rear-end crash is caused by following another vehicle too closely. When following another vehicle on any street or highway, there must be enough distance for you to safely stop if the vehicle in front of you suddenly slows down or stops. One way to determine if there is enough distance between your vehicle and the vehicle in front of you is to measure the amount of time between when the vehicle in front of you passes a reference point and when your vehicle passes the same reference point. Watch the car ahead of you. When it passes a reference point, such as a telephone pole or street sign, count "one-thousand-one, one-thousand-two." If you pass the same spot before you are through counting, you are following too closely. During inclement weather, during construction, during heavy traffic, and always at night, the distance between your vehicle and the vehicle in front of you should be even greater.
Speed and Stopping Distance
The distance it takes to stop your vehicle is important in determining a safe driving speed. The chart titled "Estimated Emergency Stopping Distance" may be used as a guide, but actual stopping distance can depend on the following factors in addition to vehicle speed:
Estimated Emergency Stopping Distance
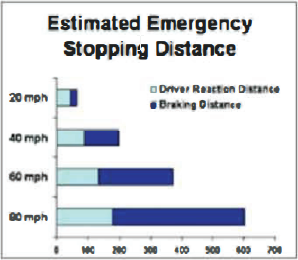
- Mental and physical reaction of the driver;
- Type and condition of the pavement;
- Kind of tires and tread composition;
- Chassis (frame) design;
- Type of brakes, condition, and balance of brakes;
- Wind direction and velocity.
Speed is a leading factor in serious injury and death as a result of traffic crashes. The greater the speed, the greater the force of impact. The illustration titled "Driving off a building" conveys the relative force of impact when you strike a fixed object.
Driving off a building
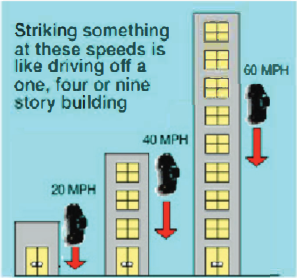
Striking something at these speeds is like driving off a one, four or nine story building
Expressway Driving
An expressway differs from normal roads or highways in that access to it is controlled. Vehicles can only enter and exit the expressway at specific places known as interchanges. Most expressways in Georgia are free, but there are a few that require a toll.
With the exception of the controlled enter/exit points and HOV lanes, expressways are similar to traveling on a divided highway. There is a median separating traffic traveling in opposite directions; lanes are marked with dashed lines, and the edge of the roadway is marked with a solid line; slower traffic should keep to the right; and all traffic laws and guidelines associated with safe driving still apply.
Entering Expressways
The entrance ramp is a short one-way road that leads to the expressway. From the entrance ramp, you should move into the acceleration lane. This is the lane that runs alongside the main roadway. In the acceleration lane, you can adjust your speed to the speed of the expressway traffic. When safe to do so, you should merge into traffic. Vehicles on the expressway have the right of way, but courteous drivers will permit you to move into the expressway traffic.
Exiting Expressways
Prepare to exit a controlled access highway by safely moving to the right lane for an exit on the right, or the left lane for an exit on the left. Guide signs will tell you of the approaching exit. At the exit, deceleration lanes are provided for slowing down when leaving the expressway. Posted exit speeds are usually low due to the design of the roadway. Drivers should use either brake lights or a turn signal to indicate a change in speed to the drivers behind if slowing down in the traveling lane when preparing to exit.
Use of Lanes on Expressways
Drivers operating vehicles on divided highways must drive to the right of the median unless directed to do otherwise by a sign, traffic control device, or police officer. Drivers must obey the yellow or white striping on the roadway that indicates lanes, the convergence of lanes, or areas in which vehicles should not operate. Drivers may only access or exit controlled-access roadways at designated entrances and exits.
Gores
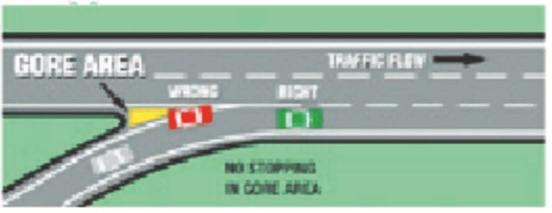
The term "gore" means the area of convergence between two lanes of traffic. The gore is the area, usually similar to a triangle, formed by solid white lines between an existing lane of travel and a merging lane of travel. Gores are most often seen at the convergence of an acceleration lane and the adjacent travel lane on a controlled access highway. The gore is the area bounded by solid white lines between the acceleration lane and the adjacent travel lane. Drivers entering the controlled access highway are prohibited by law from crossing this solid white line, and are required to continue traveling in the acceleration lane until the solid white line disappears.
HOV Lanes
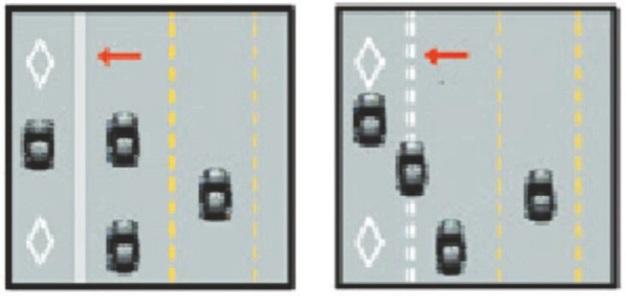
High Occupancy Vehicle (HOV) lanes are travel lanes that are restricted to vehicles with more than one occupant, buses, motorcycles, and vehicles with Alternative Fuel Vehicle license plates. The lanes are marked with a diamond symbol and the hours of restriction are posted. The penalty for violating HOV lane restrictions is a fine up to $75 for a first offense; up to $100 for a second offense; up to $150 for a third offense; and up to $150 plus one point added to the violator's driving record for a fourth or subsequent offense.
HOT Lanes
High Occupancy Toll (HOT) lanes are I-85 Express Lanes that allow registered transit, three or more person carpool, motorcycles, emergency vehicles, and Alternative Fuel Vehicles to use the lanes toll-free.
Tips For Expressway Driving
- Plan your trip carefully. Mark the map to indicate all entrances, service areas, and exits you plan to use. Doing these things will help you to have a safe, fast, and pleasant journey. You can check the GDOT 511 website for road construction, road closures, exit numbers, and other information to help plan your trip;
- Check your car before you start. Because expressways are designed for faster and smoother flowing traffic, there are fewer places to exit. It is important to check your gasoline gauge and make sure you have enough fuel. Also check the water, oil,and tires of your vehicle;
- Be alert. Use your rear view mirror and side mirror to constantly check the traffic around you. Always make visual traffic checks before you change lanes;
- Stay out of another driver's blind spot. Traveling in a position where the driver ahead of you cannot observe your vehicle in the rear view or side mirrors is a dangerous practice; the driver might pull out in front of you to pass a car. Either stay far enough behind so that the other driver can see you, or pass the vehicle. This is especially true for driving near large vehicles. Tractor-trailer combinations, also known as "eighteen-wheelers", are limited in their visibility because of their size;
- Use turn signals. Be sure to activate your right or left turn signal to indicate that you are changing lanes BEFORE you begin the maneuver;
- Allow plenty of room when passing. Returning to your lane of travel before you have passed another vehicle and provided enough safe distance between the two can cause a crash. Carefully check the left lane behind you before pulling out to pass. Don't pull back into the right-hand lane until you can see the car that you just passed clearly in your rear view mirror;
- Always obey the posted maximum and minimum speed limits. These laws exist to regulate the flow of traffic and to create a safe environment for all drivers;
- In metro areas, expressways will usually have a dramatically increased amount of traffic during the hours that most drivers are traveling to and from their places of employment. The number of cars on the expressway during this time will lead to delays. During this time, drivers should be particularly cautious. Driving defensively, allowing a safe distance between vehicles, and obeying all traffic control signs and devices can help ensure a safe commute;
- Don't back up. Driving in reverse on an expressway is prohibited under any circumstances;
- Stopping on the expressway is prohibited. You will find rest areas and service signs at frequent intervals; use them. Stopping on the roadway shoulder is highly dangerous and permitted only in an emergency. Switching drivers, stretching, or retrieving an item from the back of the vehicle is NOT considered an emergency. If it is necessary to stop, raise the hood and activate your hazard lights to indicate difficulty. Don't walk along the expressway in search of help;
- Drowsiness and fatigue is a danger anytime you drive, but is especially dangerous on long trips along the expressway. Stop driving if you feel drowsy. Don't rely on stimulant drugs (also called Stay Awake Drugs). They are likely to make your driving even more hazardous. Expressway drivers are subject to "highway hypnosis," a condition of drowsiness or unawareness brought on by monotony, the sound of the wind, the tires on the pavement, and the steady hum of the engine. On long trips it is a good idea to "exercise your eyes" to help keep you alert. Keep shifting your eyes from one area of the roadway to another and focus on various objects, both near and far, left and right. Conversation with other passengers and lively radio programs may also help you remain more alert. Of course,always pay attention to the traffic around you and potentially hazardous highway conditions;
- Drive defensively. The key to defensive driving is awareness. You must keep your eyes moving so that you can keep track of what is happening around you at all times. Avoid staring at the center line on the roadway. Instead, look ahead for trouble spots which may endanger you or your passengers. A defensive driver will also frequently check the rear view and side mirrors to keep abreast of the traffic and road conditions to the rear and sides;
- Never trust other drivers to do what you think they are going to do or what you think they should do in a particular situation. The fact that a left turn signal is flashing does not necessarily mean that the driver is going to make a left turn. You should constantly be thinking of an "escape route" as you drive. For example, if you are approaching a curve, you should be looking closely at the shoulder and nearby area to determine what you would do if a car approaching from the other direction crosses to your side of the road. After a little practice this will become more instinctive.
Other Highway Emergencies
| Fire | Accelerator Jammed | Brakes Fail | Wet Brakes |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Protecting the Air
The operation of motor vehicles has a significant impact on Georgia's air quality. Emissions from cars and light duty trucks contribute to the formation of ground-level ozone, a component of urban smog. Vehicle emissions can react with sunlight at high temperatures to produce unhealthy levels of this form of air pollution. This is especially true during warm weather. Vehicle emissions and ground-level ozone can be reduced by proper vehicle maintenance in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions, and by fewer trips and vehicle miles traveled.
In the thirteen-county metro Atlanta area, gasoline-powered cars and light-duty trucks that are less than 25 model years old must pass an emissions inspection every year prior to registering their vehicle with the county of residence (the most recent three model years are exempt from this requirement). The thirteen metro counties covered by the state's inspection and maintenance program are: Cherokee, Clayton, Cobb, Coweta, DeKalb, Douglas, Fayette, Forsyth, Fulton, Gwinnett, Henry, Paulding and Rockdale. For more detailed information about the emissions inspection program, call the Georgia Clean Air Force at 1-800-449-2471. Remember removing or disabling a vehicle's emissions control components is a violation of federal and state law.
In addition to proper vehicle maintenance, you can help reduce air pollution and traffic congestion by limiting driving to necessary travel, by planning ahead to consolidate trips, and by using carpools, transit and ridesharing. All drivers should do their part to reduce the impact of automobiles and trucks on air quality and the environment.
Idling Engines
Minimize your idling time. Eliminating unnecessary idling can reduce fuel consumption, engine wear and air pollution. When warming up the engine, follow the manufacturer's guidelines to assure sufficient engine performance for safe driving. Idling a vehicle for 10 seconds will consume more fuel than restarting the engine.
For more information on emissions testing regulations & protecting Georgia's air quality:
Section 9: Sharing the Road
This Section Covers
- Sharing the Road With Pedestrians
- Georgia's Law Concerning Pedestrians
- Crosswalks
- Respect Crosswalks
- Blind Pedestrians
- Always Remain Alert for Pedestrians When Driving
- Turning Right at a Red Traffic Signal
- Passing Stopped Cars in Lanes of Travel
- Exiting and Entering Driveways
- Vehicle Speed
- Sharing the Road With Bicycles
- Important Reminders Concerning Bicycle Riders
- Arm Signals Used by Bicyclists
- Sharing the Road With Motorcycles
- Allow a Full Lane
- Road Conditions
- Intersections
- Following Too Close
- Passing and Being Passed
- Partners on the Road
- Sharing the Road With School Buses
- Sharing the Road With Commercial Motor Vehicles
- Tips for Trailering
Sharing the Road With Pedestrians
While there has been an increase of motor vehicles on our roads, the number of persons traveling by foot is also growing. According to the Georgia Department of Transportation, pedestrians account for almost 15% of motor vehicles deaths. In 2016, Georgia had a 15% increase in pedestrian deaths. Distractions are believed to be a contributing factor. It is critical that pedestrians and motorists pay attention to safely share the road.
Georgia's Law Concerning Pedestrians
The driver of a vehicle shall stop and remain stopped to allow a pedestrian to cross the roadway within a crosswalk:
- When the pedestrian is upon the half of the roadway on which the vehicle is traveling, or when the pedestrian is approaching and is within one lane of the half of the roadway on which the vehicle is traveling or onto which it is turning. "Half of the roadway" means all traffic lanes carrying traffic in one direction of travel;
- When making a left or right turn at any intersection;
- At stop signs, after coming to a complete stop and before proceeding;
- At traffic signals, even when the light is green, if pedestrians are still in the crosswalk;
- When entering a street or highway from an alley, driveway, or private road;
- When approaching a blind person who is crossing a street or highway if he/she is carrying a white cane or being guided by a dog.

Crosswalks
Crosswalks exist on all four corners of intersections even when they are not marked by painted lines. A crosswalk is the part of the pavement for pedestrian traffic where the sidewalk would extend across the street. Crosswalks can also exist mid-block if they are marked.
Respect Crosswalks
When pedestrians are in crosswalks, they have the right of way over motor vehicles. Do not block crosswalks. When stopping at red lights or stop signs, always stop your vehicle before the crosswalk so pedestrians can cross safely.
Even at crosswalks without traffic signals, drivers must stop and remain stopped for pedestrians in the crosswalk when the pedestrian is upon the half of the roadway or approaching and within one lane of the half of the roadway upon which the vehicle is traveling. "Half of the roadway" means all traffic lanes carrying traffic in one direction of travel.
Blind Pedestrians
Pedestrians using guide dogs or white walking canes must be given the right of way at all times.
Always Remain Alert for Pedestrians When Driving
Look for pedestrians on both sides of the street when approaching intersections, when turning, or near schools, parks, bus stops and other places people are likely to walk. Look behind your car for children or other pedestrians before backing up in driveways and parking lots.
Turning Right at a Red Traffic Signal
Before turning right on red, drivers must come to a full and complete stop before the crosswalk. Do not block the crosswalk when waiting to make a right turn at a red light. This puts pedestrians at risk, forcing them to walk around your vehicle. After looking to your left to find a gap in traffic, you must look to your passenger side to ensure a pedestrian is not crossing in front of your vehicle.
Passing Stopped Cars in Lanes of Travel
Use extreme caution when passing stopped cars on multi-lane roads. A pedestrian you can't see may be crossing in a marked or unmarked crosswalk. This is a frequent cause of serious or fatal pedestrian injuries. When you stop at a crosswalk on a multi-lane road, stop at least 10 feet before the crosswalk so a driver in the next lane can see the pedestrian.
Exiting and Entering Driveways
When exiting or entering a driveway, alley, or parking garage, drivers must stop before the sidewalk area and proceed only after pedestrians have safely passed. Drivers waiting to turn left into a driveway must wait not only for a gap in oncoming traffic, but also for pedestrians to finish crossing the sidewalk portion of the driveway.
Vehicle Speed
Pedestrians are less protected from the harmful effects of a crash than occupants of motor vehicles. The risk of serious or fatal pedestrian injuries increase exponentially with driver speed.
The chart titled "Vehicle speed" illustrates the effect of speed upon a pedestrian who is struck by a motor vehicle. When a pedestrian is struck by a motor vehicle traveling 40mph, the risk of pedestrian death is at least 80%.
Vehicle Speed chart
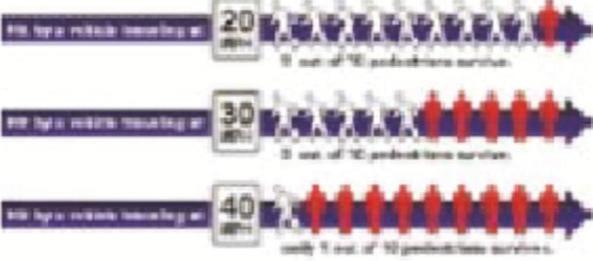
Sharing the Road With Bicycles
Bicycle riding is an important type of transportation, particularly for traveling to work and to school. Because bicyclists may be on any road at any time, drivers must always be alert for bicycle traffic.
Bike-car crashes often happen because drivers do not see bicyclists soon enough. In Georgia, as in other states, most crashes occur during daylight hours on straight, dry roads, typically near intersections or driveways.
Bicyclists are legally entitled to use every road in Georgia except the interstate and interstate-like highways (limited access highways). The law allows bicyclists use of the full lane. They are not required to be in a bike lane even when one is present. Although their slower pace may slow motorists occasionally, it is important for drivers to respect the bicyclist's right to be there. Yield the right of way to the bicyclist in the same way that you would yield to another motorist. If possible, make eye contact with the bicyclist, especially at intersections.
Road defects cause more problems for bicycles than for cars. When passing a bicycle rider, leave the bicyclist plenty of room in case he or she has to swerve to miss a pothole or other danger in the road. The minimum legal space for a motorist to pass a bicyclist is 3 feet.
Important Reminders Concerning Bicycle Riders
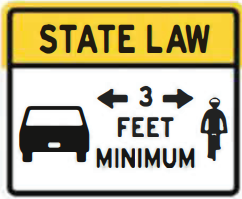
Motorists should approach bicycles with due caution and shall proceed as follows: (Violation is a misdemeanor punishable by a fine up to $250.00).
Make a lane change into a lane not adjacent to the bicycle if possible in the existing road and traffic conditions OR
If a lane change is impossible, prohibited by law, or unsafe, reduce the speed of the motor vehicle to a reasonable and proper speed for the traffic conditions, which speed shall be at least ten miles per hour less than the posted speed limit or 25 miles per hour, whichever is more and proceed around the bicycle with at least three feet between the vehicle and the bicycle at all times.
- Watch for bicyclists who may appear to suddenly swerve or turn in front of you. Bicyclists sometimes forget or do not have the opportunity to merge left due to traffic speed, in order to be in the left turn position.
- Night time bicyclists will not always have lights, and some may not even have reflectors. If you meet an oncoming bicyclist, please dim your lights to avoid blinding the bicyclist.
- Bike lanes and any other bicycle infrastructure are for the use of bicycles only. Motorists are not to drive or park in a bike lane.
- Bicyclists are able to pass on the right side of motorists if there is a dedicated lane or sufficient room in a shared lane, and it is safe to do so.
Arm Signals Used by Bicyclists
Bicyclists should use their arms to signal to other motorists when they are going to make a turn, and the direction of the turn or when they are slowing or stopping. The signals used by bicyclists are listed in the image titled "Bicyclist Arm Signals".
Bicyclist Arm Signals
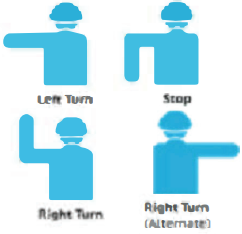
Sharing the Road With Motorcycles
Today's motorcycle riders are friends, relatives, and neighbors, but many car drivers still have not adjusted to motorcycles appearing in traffic. Traveling by motorcycle is appealing to some people; they are fuel and space efficient and can be fun to ride. Motorcyclists have the same rights and responsibilities as automobile drivers. While everyone must follow the same traffic laws, motorcyclists face additional dangers because motorcycles require exceptional handling ability and motorcyclists are more vulnerable to injury and death than car drivers if involved in a crash. It is important to understand more about motorcycle operation.
From ahead or behind, a motorcycle's outline, whether 2 or 3 wheels, is much smaller than a passenger vehicle's outline, and most drivers expect to see larger vehicles on the road and are not looking for motorcycles. The small profile of the motorcycle may make it appear farther away and traveling slower than it actually is. Drivers need to take a second look, and then a third. Always make a visual check (mirrors, too) of blind spots before entering or leaving a lane of traffic and at intersections. Be alert for a motorcyclist to appear unexpectedly.
Allow a Full Lane
Motorcycles are allowed the full width of a lane in which to maneuver. Although it may seem that there is enough room in the traffic lane for a motor vehicle and a motorcycle, the motorcycle needs the room to maneuver safely. Do not share the lane. Understand that motorcyclists may adjust lane position for their own safety, not to be reckless or show off. Motorcyclists often adjust position within a lane to be seen more easily or to minimize the effects of road debris, passing vehicles, or other conditions. Often, this means riding in the left portion of the traffic lane to allow a better view of some traffic and road situations. It also makes the motorcycle more visible to other traffic. However, as traffic and road conditions change, the rider may move. This move could be to the center of the lane or even to the right side to avoid traffic or to be seen by others on the road.
Road Conditions
Remember that road conditions which are minor annoyances to motorists can pose major hazards to motorcyclists. Motorcycle riders may change speed or adjust position within a lane suddenly in reaction to road and traffic conditions such as potholes, gravel, wet or slippery surfaces, pavement seams, railroad crossings, and grooved pavement.
Intersections
Intersections are the most likely places for car/motorcycle crash to occur. This usually is the result of a car driver NOT SEEING the motorcycle and turning into the motorcycle's path. Misinterpreting a rider's intentions can also lead to crashes. The rider will move to one side of the lane in preparation for a turn or possibly to move away from a hazard unseen by other motorists. Do not assume the rider's intention until the maneuver is unmistakably started, such as a turn into an intersection or driveway. Don't be fooled by a flashing turn signal on a motorcycle – motorcycle signals may not be self-canceling and motorcyclists sometimes forget to turn them off. Wait to be sure the rider is going to turn before you proceed.
Following Too Close
Allow more following distance -- three or four seconds - when following a motorcycle so the motorcycle rider has enough time to maneuver or stop in an emergency. Space between the two vehicles should be increased to avoid sudden braking. In dry conditions, motorcycles can stop more quickly than cars. Both riders and drivers are more likely to make incorrect decisions if there is not enough stopping distance or ability to see and react to conditions. This leads to crashes. A rider's chance of injury is greater if forced to avoid obstacles ahead, as well as a driver following too closely.
Passing and Being Passed
The rules for passing other vehicles are similar for motorcycles. The motorist being overtaken by a motorcycle should maintain lane position and speed. Allow the motorcyclist to complete the pass and assume proper lane position as quickly as possible. When passing a motorcycle, allow a full lane to the motorcycle. Never crowd into the same lane as the motorcycle. Returning to the original lane too soon can force a rider to swerve to the right into traffic or off the road.
Partners on the Road
What all this means is, motorcycles are full partners in the traffic mix and must be treated with the same courtesies. Watch for the unexpected and give them their share of the road; a rider may be the neighbor next door.
Share the Road
This section is designed to encourage drivers of all other kinds of vehicles and motorcyclists to "share the road" with each other and is provided through the courtesy of the Motorcycle Safety Foundation and the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration.


Sharing the Road With School Buses
In most cases, all drivers are required to stop when approaching or meeting a stopped school bus that has its lights flashing and is loading or unloading passengers. The exception to this rule is when highways are separated in the center by median strips. In this situation, only vehicles following or traveling alongside a school bus in the same direction must stop.
A warning will be given in advance by the flashing red or amber lights on the front and rear of the bus. After stopping, you must remain stopped until the bus resumes motion or deactivates its warning signals AND all loading or unloading passengers have cleared the roadway.
Georgia Fines & Penalties
- Mandatory court appearance;
- Up to $1000 fine;
- Up to 6 points on driving record;
- A conviction under 21 years of age constitutes license suspension.
Operation Stop Arm

Operation Stop Arm long description
Know the Law. Obey the Law. Georgia School Bus Stop Law.
Two-lane roadway:
- When school bus stops for passengers, ALL traffic from both directions must stop.
Two-lane roadway with a center turning lane:
- When school bus stops for passengers, ALL traffic from both directions must stop.
Divided highway of four lanes or more with a median separation:
- When school bus stops for passengers, only traffic following the bus must stop.
Four-lane roadway without a median separation:
- When school bus stops for passengers, ALL traffic from both directions must stop.
Roadway of four lanes or more with a center turning lane:
- When school bus stops for passengers, ALL traffic from both directions must stop.
Respect The Bus! A school bus stop safety guide. Find us on Facebook.
Sharing the Road With Commercial Motor Vehicles
Commercial motor vehicles are vital to the economy of Georgia and the United States. Most of the products used in every day life were delivered to stores by commercial motor vehicles. Drivers of commercial motor vehicles are trained, specially licensed driving professionals.
Sharing the road with commercial motor vehicles is a necessary part of travel. Heavy trucks typically weigh 80,000 pounds or more, and drivers should use caution when driving near them.
Everyone should be aware of the differences between trucks and cars and behave accordingly. These include:
- A fully loaded tractor-trailer, traveling 55 mph, needs 3 times the distance a car needs to stop;
- Large trucks are more difficult to maneuver, are longer and heavier, and require much more room to turn;
- Large trucks have larger blind spots, called “No-Zones.”
The “No-Zone” represents the danger areas around trucks and buses where crashes are more likely to occur. Some No-Zones are actual blind spots or areas around trucks and buses where your car “disappears” from the view of the drivers. These blind spots are the Side No-Zone, Rear No-Zone, and Front No-Zone areas.
- Side No-Zones - Trucks and buses have big No-Zones (blind spots) on both sides. They are much larger than a car's blind spots. If you cannot see the driver's face in the side-view mirror, the driver cannot see you. The right side No-Zone is particularly dangerous because truck and bus drivers must make wide right turns.
- Rear No-Zones - Unlike cars, trucks and buses have huge No-Zones directly behind them. Trucks and buses have no rear view mirror. The truck or bus driver cannot see your car there and you cannot see what is going on ahead of the truck or bus. It is critical to keep a safe distance behind a truck or bus in case the driver slows or stops suddenly.
- Front No-Zones - Trucks and buses require more room and time to stop than cars. Because of this, more space should be given in front of trucks and buses. It is not safe to "cut in front" of a truck and then slow down. To avoid the Front No-Zone, make sure that you can see the entire front of the truck or bus in your rear-view mirror before you merge or pull into that lane of traffic.
The Georgia Tact Project
Targeting Aggressive Cars & Trucks
Law Enforcement officers are stopping people who drive unsafe around commercial motor vehicles, whether they are driving a car or commercial motor vehicle.
What to do to avoid getting a citation:
- Don't cut off commercial motor vehicles. For safety, one car length for every 10 miles per hour of speed is recommended;
- Don't tailgate. Unlike cars, commercial motor vehicles have big blind spots behind them. Also, car drivers who tailgate commercial motor vehicles can't see traffic ahead. If the commercial motor vehicle brakes suddenly, you have no time to react and no place to go;
- Don't speed. Speed is a factor in nearly one-third of all fatal crashes;
- Allow commercial motor vehicles plenty of room. Be careful when you or the commercial motor vehicle are entering a highway or merging with traffic.
Don't get a citation.
Tips for Trailering
For many drivers, towing a trailer is a whole new experience with many challenges — here are a few tips to stay safe on the road.
- Take Your Time
- If You Lose Control, Stay Calm
- Stay Within Capacity
- Distribute the Weight
- Inspect Your Trailer
- Know Your Trailer and Practice Handling It
- Secure Your Load
- Maintain your Trailer and Vehicle
- Consider Tow Mirrors
- Get the Right Equipment
- Consider Additional Safety Equipment
More information can be found at AAMVA.org on Safe Trailering.
DDS 2 GO

- Reinstatements
- Motor Vehicle Report
- Renewal
- Replacement
- Change of Address
- Custom Alerts
- Locations
- Pay fees
- And More!
Get the DDS 2 GO mobile app on the Apple App Store and Google Play.
Section 10: Losing Your Driving Privileges
This Section Covers
- Types of Withdrawals
- Reporting Convictions
- Types of Suspensions
- Implied Consent
- The Points System
- Points Reduction
- Points Avoidance
- Safety Responsibility Law
- Mandatory Revocations
- Limited Driving Permits
- Commercial Driving Disqualifications
- Major Traffic Violations
- Serious Traffic Violations
- Other Violations
The State of Georgia considers dangerous and negligent drivers to be a direct and immediate threat to the welfare and safety of the general public, and it is in the best interest of the citizens of Georgia to immediately remove such drivers from the highways of this state. Therefore, the Department of Driver Services is authorized to withdraw the license or driving privileges when evidence is obtained that the licensee is a habitually dangerous or negligent driver of a motor vehicle (from Georgia law §40-5-57)
Types of Withdrawals
The driver's license of any individual, the eligibility to obtain a driver's license, or the ability to legally operate a motor vehicle in the State of Georgia may be impacted by one or more of the following actions:
Cancellation
The Department of Driver Services is authorized to cancel a license if the applicant fails to give the required or correct information needed at the time application is made, or if the individual becomes otherwise ineligible after application has been made. A resident may reapply for a license once the requirements have been satisfied and the resident is otherwise eligible.
Revocation
If a license is revoked, all driving privileges are terminated and withdrawn until the end of the period of time prescribed by the formal action of the Department. At the end of the revocation period, a resident may apply for a new license. Non-residents may apply for reinstatement of driving privileges.
Suspension
If a license is suspended, all driving privileges are temporarily withdrawn for a specific period of time or until reinstatement requirements have been completed. At the end of the withdrawal period, a resident may apply for reinstatement and return of the license or the eligibility to obtain a license. Non-residents may apply for reinstatement of driving privileges.
Disqualification of Commercial Driver's License
If a commercial driver's license is disqualified, all privileges to operate a commercial motor vehicle are withdrawn for a specific period of time. At the end of the disqualification period, if a licensee holds a CDL license that is not expired, the licensee's commercial privileges will be automatically restored without any action required, provided that the licensee is otherwise eligible to still maintain a commercial driver's license. If the licensee does not hold a CDL at the expiration of the disqualification period, the licensee's ability to apply for a CDL will be restored.
A disqualification of commercial driving privileges does not, by itself, result in the suspension or revocation of a licensee's privileges to operate a NON-commercial motor vehicle. However, many offenses that result in a commercial disqualification also result in a non-commercial suspension, though the periods of withdrawal may differ. In Georgia, it is possible to lose commercial driving privileges for LIFE upon the conviction of certain offenses. More information related to the commercial driver's license program is available on our website.
Reporting Convictions
Georgia courts are required by law to report the conviction of any offense that will result in a negative impact on a licensee's driving privilege or that is otherwise required to be posted to the permanent driving history of an individual. This includes most traffic-related offenses as well as certain non-traffic related offenses.
When the DDS receives a conviction for a Georgia license holder, the record is updated to reflect the conviction. If a conviction is received for an individual who holds a license from another state or is the resident of another state, the conviction information will be forwarded to the licensing authority of that state. If a non-resident, or a resident of Georgia who does not have a driver's license, is convicted of certain offenses, the eligibility to obtain a Georgia driver's license and/or driving privileges in Georgia will be suspended.
Convictions reported to the Georgia DDS by licensing authorities or courts in other states and nations will be placed on the driving record of a Georgia licensee or resident. The Department will treat such convictions as if they had occurred in this state for the purpose of imposing license withdrawals.
Types of Suspensions
The Department will suspend the driving privileges of an individual in any of the following non-conviction situations:
- Refusal to take a chemical test for intoxication;
- Failure to appear in court or respond to a citation;
- Non-payment of Child Support;
- Non-payment of the Super Speeder fee;
- Safety responsibility;
- Medical revocation;
- Parent requested revocation (under age 18).
The Department is required by law to suspend the privileges of an individual for a conviction of any of the following offenses:
- Homicide by vehicle;
- Feticide by Vehicle (1st degree);
- Serious injury by vehicle;
- Driving under the influence of alcohol or drugs;
- Any felony in the commission of which a motor vehicle is used;
- Using a motor vehicle in fleeing or attempting to elude an officer;
- Hit and run or leaving the scene of a crash;
- Racing;
- Operating a motor vehicle with a revoked, canceled, or suspended registration;
- Driving without insurance;
- Driving while license is suspended, revoked, or canceled;
- Refusal to weigh commercial motor vehicle;
- Violation of license restriction (at the discretion of the trial court).
In addition to the offenses listed in the previous bulleted list, the license and/or driving privileges of an individual under the age of 21 on the date of the conviction will be suspended for the following offenses:
- Reckless driving;
- Aggressive driving;
- Speeding 24 mph or more over the speed limit;
- Unlawful passing of a school bus;
- Improper passing on a hill or a curve;
- Any 4-point offense;
- Four or more points in 12 months prior to age 18;
Implied Consent
Georgia law requires you to submit to state administered chemical tests of your blood, breath, urine, or other bodily substances for the purpose of determining if you are under the influence of alcohol or drugs. If you refuse this testing, your Georgia driver's license or privilege to drive on the highways of this state will be suspended for a minimum period of one year. Your refusal to submit to blood or urine testing may be offered into evidence at trial. If you submit to testing and the results indicate a blood alcohol concentration (BAC) at or above the legal limit, your Georgia driver's license or privilege to drive on the highways of this state may be suspended for a minimum period of one year. After first submitting to the required state tests, you are entitled to additional chemical tests of your blood, breath, urine, or other bodily substances at your own expense and from qualified personnel of your own choosing.
Violations and points demerited
| Violation Resulting in Conviction | Points |
|---|---|
| Violation of Hands Free Law – 1st Conviction | 1 |
| Child Restraint – 1st Offense | 1 |
| HOV Lane Violation – 4th and Subsequent Offense | 1 |
| Violation of Hands Free Law – 2nd Conviction | 2 |
| Possessing an Open Container of an Alcoholic Beverage While Driving | 2 |
| Speeding – 15-18 mph over the posted speed limit | 2 |
| Child Restraint – 2nd and Subsequent Offense | 2 |
| Failure to Adequately Secure a Load | 2 |
| Violation of Hands Free Law – 3rd or more Convictions | 3 |
| Impeding Traffic | 3 |
| Disobedience of Any Traffic-Control Device or Traffic Officer | 3 |
| Speeding – 19-23 mph over the posted speed limit | 3 |
| All Other Moving Violations | 3 |
| Reckless Driving | 4 |
| Improper Passing on Hill or Curve | 4 |
| Speeding – 24-33 mph over the posted speed limit | 4 |
| Aggressive Driving | 6 |
| Speeding – 34 mph or more over the posted speed limit | 6 |
| Unlawful Passing School Bus | 6 |
Before Visiting, Fill Out Your Form

Anytime. Anywhere. Any device.
Fill out the form for your Permit, License or ID Card with DDS Online Services (https://dds.drives.ga.gov/_/) before arriving at any of our Customer Service Centers.
Faster. Secure. Convenient. 24/7.
Please remember to bring your parent or guardian and proof of school enrollment when you come in for your visit.
The Points System
The Department is required by law to suspend the Georgia license of an individual for an accumulation of points resulting from certain convictions. Points are assessed against Georgia residents for out-of-state violations which would be assessed points if committed within Georgia. Georgia licenses will be suspended as follows:
- For any person who accumulates 15 or more points within 24 months;
- For any person under the age of 21 with a conviction for any 4-point violation;
- For any person under 18 years of age with an accumulation of 4 points within twelve months.
Points are accumulated on a person's driving record as a result of certain convictions. The previous table labeled "Violations and points demerited" lists these convictions and the number of points associated with each. The date the violation occurred is used as the basis for determining the 24-month period (or 12-month period for persons under age 18). When a license is suspended due to an accumulation of points, the point total is restored to zero.
In the case of a person age 18 up to 21, the suspension of the license for a single 4-point offense is determined by the date the conviction occurred. A plea of nolo contendere is considered a conviction for purposes of imposing suspensions that apply to persons under age 21.
Points Reduction
Licensed Georgia residents may request that DDS reduce the number of points assessed against their Georgia driver's license up to 7 points once every 5 years.
To qualify for a points reduction, you must successfully complete a certified 6-hour driver improvement (defensive driving) course and present the original certificate of completion to the DDS by mail or in person at one of our Customer Service Centers.
If you request a points reduction by mail, please mail the original driver improvement (defensive driving) certificate of completion to the Georgia Department of Driver Services, P.O. Box 80447, Conyers, Georgia 30013. A list of certified driver improvement (defensive driving) courses can be found on the Georgia Department of Driver Services web site.
Points Avoidance
A defendant may successfully complete a certified 6-hour driver improvement (defensive driving) course after the issuance of a citation for a moving violation and prior to the court appearance, or as ordered by the court. When the original certificate of completion is presented to the court, the court shall reduce the fine assessed by 20 percent and no points shall be assessed against the driver. This plea may be accepted by the court once every five years.
Safety Responsibility Law
The purpose of this law is to remove irresponsible drivers from Georgia highways and to protect insured motorists from uninsured motorists. In the event you should fail to satisfy a claim for damage resulting from a motor vehicle crash, and a claim is filed against you under the Safety Responsibility Law, you will receive an order suspending your license.
To avoid the suspension, you may:
- Have your insurance carrier file Form SR-21 with the DDS if you were covered by liability insurance at the time of the crash; or
- File either a general or a conditional release that has been signed by the claimant (injured party in the crash) with the DDS; or
- Post security to cover the damages with the DDS, which may be a cashier's check, certified check, money order, real property bond or surety bond, in addition to posting of financial responsibility, Form SR-22A.
Any security or bond posted with the Department will be held for one year and thereafter until proof is furnished to the Department that you have not been sued as a result of the crash.
You are entitled to a hearing, if desired, and if requested within ten (10) days of the receipt of the order of suspension.
Mandatory Revocations
Your driver's license will be revoked in Georgia if any of the following occur:
- You are declared a Habitual Violator based upon the third conviction of any combination of these offenses within 5 years:
- Driving under the Influence (DUI);
- Homicide by vehicle;
- Feticide by vehicle;
- Serious injury by vehicle;
- Hit and run or leaving the scene of a crash;
- Racing;
- Using a motor vehicle in fleeing or attempting to elude an officer;
- Reckless Stunt Driving
- Operating a motor vehicle with a suspended, canceled, or revoked registration;
- Any felony in the commission of which a motor vehicle is used; or
- Refusal to submit to a re-examination of driving skills or knowledge of driving rules after receiving notice giving reasonable grounds for such a request;
- If you have been declared incompetent or if there is sufficient evidence that you are unsafe to drive, due to mental health or physical disability or disease, or by alcohol or drug addiction.
If you are declared a Habitual Violator, you may be eligible for a Probationary License after serving two years of the revocation period.
Limited Driving Permits
In some situations, a limited driving permit may be available for a fee of $32 during the suspension period. A limited driving permit would allow you to only:
- Drive to your place of employment;
- Receive scheduled medical attention or obtain prescribed drugs;
- Attend classes at a college or school in which you are enrolled as a student;
- Attend regularly scheduled sessions or meetings of support organizations for the treatment of alcohol or other drugs;
- Attend a driver education program or alcohol/drug assessment and treatment program;
- Attend court, report to a probation office or officer, or perform community service;
- Transport unlicensed immediate family members to work, medical care and to obtain prescriptions, and to school.
The Department may also specify the places you may travel to, specific routes of travel, times of travel, and indicate vehicles, or other restrictions deemed necessary. Limited driving permits are not valid for driving a commercial vehicle.
A limited driving permit will be revoked by the Department if you are convicted of violating any state law or local ordinance relating to the movement of vehicles or if you are convicted of violating any of the conditions or restrictions of your permit. In addition, a conviction will extend the underlying suspension of your driving privilege for an additional 6 months.
Limited driving permits are not available for convictions of the following offenses or in the following situations:
- Implied Consent refusal (may be available if no prior DUI conviction within past 5 years);
- No Insurance convictions;
- Driving while license suspended convictions;
- Failure to pay super speeder fee;
- Failure to pay child support;
- Failure to appear in court or respond to a citation;
- Medical revocation;
- Safety responsibility;
- Parent requested revocation;
- DUI Drugs
- DUI convictions prior to age 21; and
- Refusal to weigh (CMV).
A limited driving permit may be available in the following situations, depending on your age and the number of convictions on your driving record:
- 1st DUI (non-drugs);
- 2nd DUI conviction in 5 years;
- DUI ALS;
- Under 21 speeding violation but only if age 18 or older, speeding was 24-33 mph over the posted speed limit, and approved by the sentencing court judge;
- 1st or 2nd suspension for accumulation of 15 or more points within a 24 month period;
- 3rd controlled substance violation after a 2 year suspension and age 21 or over;
- Homicide by vehicle 2nd Degree (age 21 or over);
- Any felony in the commission of which a motor vehicle is used (age 21 or over);
- Using a motor vehicle in fleeing or attempting to elude an officer (age 21 or over);
- Fraudulent or fictitious use of, or application for, a license/ID card (age 21 or over);
- Hit and run or leaving the scene of a crash (age 21 or over);
- Racing (age 21 or over);
- Operating a motor vehicle with a revoked, canceled, or suspended registration (age 21 or over);
- If approved by the sentencing Court Judge involving license suspensions for certain drug offenses
In all cases, the Department will make the final determination of eligibility for a limited driving permit. Please contact DDS at 678-413-8400 for further information.
Commercial Driving Disqualifications
When commercial driving privileges are disqualified, the licensee is prohibited from operating a Commercial Motor Vehicle (CMV). Commercial driving privileges can be disqualified even if you do not have a commercial driver's license (CDL). If you do not have a CDL, but your commercial driving privileges are disqualified, you will not be eligible to obtain a CDL during the period of the disqualification.
The commercial driving privileges can be withdrawn for:
- Conviction of a Major traffic violation;
- Conviction of two or more Serious traffic violations;
- Use of a CMV in the commission of any felony involving a controlled substance or marijuana (other than mere felony possession);
- Violation of an out-of-service order; or
- Conviction of a railroad grade crossing offense in a CMV.
Major Traffic Violations
The commercial driving privileges of any person convicted of one of the following "major traffic violations" in this state, or any other state, in a commercial or, unless otherwise specified, a noncommercial vehicle will be disqualified for one year:
- Driving a CMV if your BAC is .04 gm. or higher;
- DUI;
- Hit and run or leaving the scene of a crash;
- Failure to report striking an unattended vehicle;
- Failure to report striking a fixed object;
- Failure to report a crash;
- Any felony in the commission of which a motor vehicle is used;
- Driving a CMV while the CDL is revoked, suspended, canceled, or disqualified;
- Homicide by vehicle;
- Racing;
- Using a motor vehicle in fleeing or attempting to elude an officer;
- Fraudulent or fictitious use of, or application for, a license/ID card;
- Operating a motor vehicle with a revoked, canceled, or suspended registration;
- Commercial vehicle cargo theft; or
- Refusal to submit to state administered chemical testing when requested by a law enforcement officer.
If convicted of any of these offenses while you are operating a CMV that is placarded for hazardous materials, you will be disqualified from driving a CMV for at least three years for a first offense.
A second conviction from a separate incident of any of these major traffic violations will result in a lifetime disqualification of commercial driving privileges.
Serious Traffic Violations
Your commercial driving privileges will be disqualified for a period of 60 days upon a second conviction in three years for a serious traffic violation (provided that the two convictions arose from separate incidents). Your commercial driving privileges will be disqualified for a period of 120 days upon a third or subsequent conviction in three years for a serious traffic violation (provided that the various convictions arose from separate incidents).
The following violations are defined as "serious traffic violations" when committed in this state, or any other state, when operating either a CMV or, unless otherwise specified, a noncommercial motor vehicle:
- Speeding 15 or more miles per hour above the posted speed limit;
- Reckless driving;
- Following another vehicle too closely;
- Improper or erratic lane change, including failure to signal a lane change;
- A violation of state law or a local ordinance relating to motor vehicle traffic control arising in connection with a fatal crash, excluding parking, weight, length, height, and vehicle defect violations, and excluding homicide by vehicle;
- A railroad grade crossing violation in a noncommercial motor vehicle;
- Driving a commercial motor vehicle without obtaining a commercial driver's license;
- Driving a commercial motor vehicle without a commercial driver's license in your immediate possession, but not if it is because your commercial driving privileges have been suspended, revoked, canceled, or disqualified;
- Driving a commercial motor vehicle without a commercial driver's license of the proper class and endorsements for the specific vehicle you are operating or for the passengers or type of cargo you are transporting;
- Use of a wireless device for text based communications while operating a commercial motor vehicle.
Other Violations
A felony conviction involving the manufacturing, distribution, trafficking or possession of a controlled substance or marijuana using a CMV (other than mere felony possession) will result in a lifetime disqualification of commercial driving privileges.
Violation of an out-of-service order will result in a disqualification of:
- not less than 180 days and not more than one year for a 1st offense;
- not less than 2 years and not more than 5 years for a 2nd offense; and
- not less than 3 years and not more than 5 years for a 3rd or subsequent incidents.
An additional disqualification period will apply when an out-of-service order is violated while transporting hazardous materials or transporting more than 15 passengers.
Conviction of any railroad grade crossing offense while operating a CMV will also result in a disqualification of 60 days for a 1st offense up to 1 year for a third or subsequent violation within a 3 year period.
Section 11: Crashes
This Sections Covers
- If You Are Involved In A Crash
- Aiding the Injured
- Moving Vehicles Following a Crash
- Deer-Automobile Crashes
If You Are Involved In A Crash
- Stop immediately in a safe place.
- Notify the nearest law enforcement agency immediately if anyone is injured or killed, or if property damage exceeds $500.00;
- Provide reasonable assistance to any person injured;
- Warn approaching motorists if you can do so without jeopardizing your own safety or that of others. Activate your hazard lights, if possible, and use reflective triangles, when available;
- Give your name, address, license plate number, and driver's license number to anyone else who was involved in the crash. Get the same information from the other driver;
- If you damage an unattended vehicle, you must either locate the owner or leave your name, address, and the name of the owner of the vehicle you were driving, in a conspicuous place where the owner will find it.
Aiding the Injured
Do not assume that a person is not injured simply because that person says he/she is not. Send for professional help as soon as possible. Unskilled handling can cause further and more severe injuries. Do not move or lift the victim unless it is absolutely necessary. If the victim is moved, get help and try to maintain the victim in the position in which they were found. Stop serious bleeding with thick cloth pads, as clean as possible, applied with pressure by hand. Keep the victim warm. Cover the victim with blankets or coats, if necessary.
Georgia has a Good Samaritan Law. This law holds any person harmless for civil damages arising as a result of any act or omission in rendering emergency care.
Moving Vehicles Following a Crash
When a traffic crash occurs on a multilane highway or expressway, and if there is no apparent serious injury or death, it is the duty of the drivers of the vehicles involved to move their vehicles from the roadway to a safe location along the shoulder, emergency lane, median, or any other safe refuge. Driver should only do this if the vehicles are capable of being driven normally and successfully, and driving the vehicles will not present any further hazard or harm to the vehicles themselves, to the driver, to persons nearby, or to the roadway.
If the persons involved in the crash are incapable of moving the vehicle, they are authorized to request any other driver in the vicinity who has a valid license of the appropriate class to move their vehicles, and the other driver is authorized to comply.
Drivers who take these important steps will not be considered at fault simply because they moved the vehicles, nor does moving the vehicles affect their ability to file a written report with a local police agency. Moving a vehicle in this situation does not allow for the driver to be accused of failing to stop and provide information.
Deer-Automobile Crashes
Each year, deer cause thousands of crashes in Georgia. Understanding common habits of deer and knowing what to do when a deer runs out in front of the car can help to avoid serious crashes. Automobile crash data from the Georgia Department of Transportation indicate that though deer-automobile crashes are on the rise, they still account for less than six percent of automobile crashes reported each year.
It is important to remember that deer are wild animals and their actions are unpredictable. The deer you see calmly standing on the side of the road may bolt toward the road rather than away from it if startled by a car.
Follow these guidelines to minimize the chances of a crash with a deer:
- In areas with known deer populations, drivers should constantly scan the road and road shoulders for deer movements and sightings;
- Always slow down when a deer crosses the road in front of you or another car. Deer usually travel in groups and it is likely that there is another one following closely behind;
- If a deer is spotted on the road or roadside at night, the driver should slow down immediately, blink his/her headlights and switch to low beam so as not to blind the deer;
- Also, short horn blasts may help scare the deer from the road.
Should the deer or other animal run out in front of your car, slow down as much as possible to minimize the damage of a crash. Never swerve to avoid a deer. This action may cause you to strike another vehicle or leave the roadway, causing more damage or serious injuries. If you do have a crash, police should be alerted as soon as possible. Most insurance companies will require an accident report from the police before paying claims for this type of crash.
Deer are usually seen along the roadside during the early morning hours and late evening. Drivers should be alert for deer during these peak hours. Deer are most active in the fall months of October, November and December during the peak breeding season. Late February and early March are also critical months for deer-car crashes. During this period they concentrate along road shoulders to feed on new green food available following winter. However, deer are often spotted at midday during summer months. Therefore, it is important for drivers to remain cautious when traveling on rural roads or areas known to have a high deer population.


dds.georgia.gov