
Georgia Alcohol & Drug Awareness Program (ADAP) Student Manual


Revised October 2022
The information contained in this manual is not intended to be an official legal reference to the Georgia Traffic Laws. It is intended only to explain, in everyday language, those laws, driving practices, and procedures that you will use most often. It should be noted that the material in this manual is subject to change to comply with amended State and Federal legislation. The Departments primary statutory responsibilities are set forth in Title 40 of the Official Code of Georgia annotated (O.C.G.A.)
Messages

Governor Brian P. Kemp
“I wish you safe passage and encourage you to exercise good judgment, follow driving laws, and prioritize safety for yourself, fellow motorists, and passengers.”
Brian P. Kemp
Governor
Commissioner Spencer R. Moore

“Operating a vehicle is a tremendous responsibility, and we want you to be fully prepared to meet the challenges! Please take this information seriously. By obeying all traffic laws and never driving distracted, we can ensure that our roads are safer for drivers and passengers alike.”
Spencer R. Moore
Commissioner
Our Mission
To provide secure driver and identity credentials to our customers with excellence and respect.
Our Core Values
- Trusted Service
- Ethical Actions
- Accountable to All
- Motivated to Excellence
Our Hashtags
#LetsTransform
#ExceedExpectations
#EveryCustomer
#EveryTime
DDS Board of Directors
- David W. Connell – Chair
- Jeff Markey – Vice Chair
- Britt Fleck – Secretary
- Rachel Little – Member
- Bob Pierce – Member
- Kat Satterfield – Member
- Tony Guisasola – Member
- Christie Moore – Member
- Frank Reynolds – Member
The Department of Driver Services (DDS) Board of Directors would like to remind teens that driving in Georgia is a privilege that carries many responsibilities. Please strive to become a safe, sober, and dependable driver to ensure that this privilege will not be lost.
This manual has two main purposes:
- to inform the young people of this state of the dangers involved in consuming alcohol or drugs in connection with the operation of a motor vehicle; and
- to emphasize the importance of highway safety and crash prevention.
Title VI Policy Statement
The Georgia Department of Driver Services (DDS) is committed to compliance with Title VI of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 and all related nondiscrimination authorities. DDS assures that no person shall, on the grounds of race, color, national origin, sex, age, disability, low-income, and Limited English Proficiency (LEP), be excluded from participation in, be denied the benefits of, or be otherwise subjected to discrimination under any program or activity. DDS further assures that every effort will be made to ensure nondiscrimination in all its programs and activities, whether those programs and activities are federally funded. In addition, DDS will take reasonable steps to provide meaningful access to services for persons with Limited English Proficiency. Finally, DDS agrees to abide by the Title VI Program Assurances and to ensure that written agreements with any party for federally funded programs or services will include the applicable Title VI language as provided in the Title VI Program Assurances.
The DDS Title VI Program Coordinator is responsible for oversight of the Title VI Program and ensuring compliance with the requirements provided in 49 Code of Federal Regulations (C.F.R) Part 21 and 49 C.F.R. Part 303. The Title VI Program Coordinator and all Division Directors are authorized to effectively implement the Title VI Program on behalf of the Department.
Locations
DDS Customer Service Centers
DDS has 68 locations throughout the state. For complete information including driving directions, please visit Find a Customer Service Center on the DDS website.
DDS 2 GO Mobile App & DDS Online Services
Be certain to take advantage of DDS Online Services and the free mobile app DDS 2 GO to avoid an unnecessary trip to a Customer Service Center.
DDS Online Services and DDS 2 GO enable thousands of Georgia drivers to conduct many transactions via the DDS website and eliminate a visit to a DDS Customer Service Center (CSC). This saves customers valuable time and money. DDS does not charge an additional fee for choosing Internet Services and DDS 2 GO is free to download. A $5.00 discount may apply for eligible license types that are renewed without visiting in person.
For more information visit the DDS website and like DDS on Facebook!
DDS 2 Go

DDS 2 Go Long Description
Download our new free mobile app!
"It's like having a licensing office in your pocket!"
- Reinstatements
- Motor Vehicle Report
- Renewal
- Replacement
- Change of Address
- Custom Alerts
- Locations
- Pay fees
- And more!
Available on the Apple App Store and Google Play.
Save Time! Use DDS Online Services at DDS.Georgia.Gov

Save Time Long Description
Card Services
- Submit Proof of Residency and/or Social Security
- Address Change
- License/ID Renewal or Replacement
- Class D to Class C Upgrade
- CDL Self-Certification Medical Documents
- License Status
- Suspension or Reinstatement Information
Pay Fees
- Super Speeder
- License Reinstatement
- Pending Suspensions
Other Services
- Online For-Hire Endorsement Application
- Skip a Step! (Complete Form Online)
- Driving History (MVR)
- Motorcycle Safety Training Registration
- Make Road Test Appointment
- Reservation Status
Driving Ambition

Driving Ambition Long Description
Will my driving cost lives or save them?
Teen Laws and Responsibilities
Driving Ambition explains the new driving laws and looks at the results DUI, inexperienced and reckless driving have on society. Listen carefully tothe message of families and individuals whose lives have been shattered by motor vehicle crashes. Make a commitment to be a safe and responsible driver.
Watch online. A presentation of Children and Youth Coordinating Council, in association with Governor's Office of Highway Safety.
Chapter 1: TADRA
TADRA is an acronym for Georgia’s Teenage and Adult Driver Responsibility Act, which is a comprehensive set of laws enacted in 1997 with the intent of reducing fatal motor vehicle crashes involving teenage drivers.
TADRA significantly changed the way teens in Georgia earn and maintain driving privileges, most notably through the introduction of a three-step Graduated Driver’s Licensing process for newly licensed drivers 15 to 18 years of age. TADRA also contains important provisions specifically related to driving under the influence (DUI) prevention and enforcement and school enrollment requirements.
In a 2006 study conducted by Emory University, researchers found that in the 5½ years following the enactment of TADRA, the rate of fatal crashes in Georgia involving teenage drivers 16 years of age was 36.8% less than in the 5½ years immediately prior to its enactment. Moreover, researchers found that speed-related fatal crashes involving teenage drivers 16 years of age declined by nearly 50%, and alcohol-related crashes involving teenage drivers 16 years of age declined by 62%.
A study published in 2016 by the Traffic Injury Prevention journal reports that the decline in fatal crash rates has been maintained and even increased through 15.5 years after passage of the law. The greatest declines were among 16 and 17-year-olds; most of the gains were among male drivers.
Reference: Taylor & Francis Online
8 Danger Zones for Teen Drivers

Danger Zones for Teen Drivers Long Descriptions
- Driving Inexperience
- Driving with Teen Passengers
- Nighttime Driving
- Not Using Seat Belts
- Distracted Driving
- Drowsy Driving
- Reckless Driving
- Impaired Driving
Source: CDC
Georgia's Graduated Driver's License Process

Step One: Instructional Permit (Class CP)
A Georgia Instructional Permit (Class CP) is granted to persons at least 15 years of age upon passing a written knowledge exam.
Once issued an Instructional Permit (Class CP), you may operate any Class C vehicle only when accompanied by a person at least 21 years of age who is licensed to drive a Class C vehicle, who is fit and capable of exercising control over the vehicle, and who is occupying a seat beside the driver.
Step Two: Provisional License (Class D)
A Georgia Provisional License (Class D) is granted to persons 16 and 17 years of age that have held an Instructional Permit (Class CP) for 12 months and one day, have had no major traffic violations that resulted in the mandatory suspension of their permit, completed ADAP, satisfied Joshua's Law and TADRA requirements, and passed a road skills test.
Pursuant to O.C.G.A. §40-5-22, Joshua's Law requires teens ages 16 and 17 to show proof of having successfully completed an approved driver education course consisting of at least 30 hours of theoretical instruction (classroom or online) and 6 hours of practical behind-the-wheel training (instructor or parent taught) to obtain a Provisional License (Class D).
Once the Provisional License is obtained, the teen driver must follow the Class D License Restrictions.
Provisional License (Class D) Restrictions - O.C.G.A. §40-5-24
- A Class D license holder may not drive between the hours of 12:00 a.m. and 5:00 a.m. — NO EXCEPTIONS.
- During the first six months following issuance, only immediate family members may ride in the vehicle. "Immediate family member" includes the driver’s parents and stepparents, grandparents, siblings and step-siblings, children, and any other person who resides at the driver’s residence.
- During the second six months following issuance, only one passenger under 21 years of age who is not a member of the driver’s immediate family may ride in the vehicle.
- After the first and second six-month periods, only three passengers under 21 years of age who are not members of the driver’s immediate family may ride in the vehicle.
Step Three: Full License (Class C)
Provisional License (Class D) holders may apply for a Class C Georgia driver’s license upon reaching 18 years of age; provided, however, they have not been convicted of any of the following major traffic violations during the 12 months preceding application:
- Driving under the influence (DUI) (O.C.G.A. §40-6-391)
- Using a motor vehicle to flee or attempt to elude a police officer (O.C.G.A. §40-6-395)
- Racing on highways or streets (O.C.G.A. §40-6-186)
- Reckless driving (O.C.G.A. §40-6-390)
- Hit and run or leaving the scene of a crash (O.C.G.A. §40-6-270)
- Any violation that resulted in the assessment of four or more points against their driver’s license.
TADRA Suspensions (Non-DUI)
The State of Georgia applies strict penalties to teens who fail to obey the laws regarding the operation of a motor vehicle. The driver’s license of any person under 21 years of age convicted of any of the following offenses shall be suspended for a period of 6 months for a first conviction or for a period of 12 months for a second or subsequent suspension:
- Hit and run or leaving the scene of a crash (O.C.G.A. §40-6-270)
- Racing on highways or streets (O.C.G.A. §40-6-186)
- Using a motor vehicle to flee or attempt to elude a police officer (O.C.G.A. §40-6-395)
- Reckless driving (O.C.G.A. §40-6-390)
- Aggressive driving (O.C.G.A. §40-6-397)
- Underage possession of alcohol while operating a motor vehicle (O.C.G.A. §3-3-23(a)(2))
- Any other offense for which 4 or more points are assessed against the driver’s license
- The accumulation of four or more points in any 12-month period while under 18 years of age
TADRA Suspensions (DUI)
In Georgia, persons under 21 years of age are presumed to be DUI in violation of O.C.G.A. §40-6-391(k)(1) if they are operating a motor vehicle and their blood alcohol concentration (BAC) is .02 or greater.
First Suspension
- If your BAC was .02 or greater but less than .08, your license will be suspended for a minimum period of 6 months. However, if you have a previous conviction for an offense in the above list, your driver’s license will be suspended for a minimum period of 12 months. You will not be eligible for any type of limited driving permit.
- If your BAC was .08 or greater or you refused implied consent testing, your license will be suspended for a minimum period of 12 months. You will not be eligible for any type of limited driving permit.
Second Suspension
Pursuant to House Bill 407 (2013), the driver’s license of any person convicted of a second offense of driving under the influence, in violation of O.C.G.A. §40-6-391, within a 5-year period shall be suspended for a minimum of 18 months. During the first 120 days of the suspension, you will have no driving privileges whatsoever. Following the 120-day “hard suspension,” you may be eligible to have a certified and functioning ignition interlock device installed and maintained in any vehicle you intend to operate for a period of 12 months.
Third Suspension
You will be declared a habitual violator and your driver’s license will be revoked for a period of 5 years. You will also be subject to the 12-month ignition interlock requirement once you become eligible for reinstatement of your driving privileges.
NOTE: A fourth violation of DUI within a 10-year period is considered a felony in Georgia and, upon conviction, may result in a fine of up to $5,000 and 5 years imprisonment. See O.C.G.A. §40-6-391(c)(4).
TADRA School Enrollment Requirements
O.C.G.A. §40-5-22
Teens under 18 years old must be enrolled in and not under expulsion from a public or private school to obtain a driver’s license or instructional permit. One of the following is required for school enrollment proof: DDS Certificate of School Enrollment (DS-1) signed by the school and notarized, most recent school transcript, latest progress or grade report, or current school ID.
Home-schooled students may provide a Certificate of Enrollment from the Georgia Department of Education (DOE) or the Declaration of Intent to Utilize a Home Study Program form filed with DOE. Teens under 18 and not enrolled in school must provide a high school diploma, GED, special diploma, certification of high school completion, or proof of enrollment in a GED program or a postsecondary school.
TADRA Responsible Adult Requirements
All applicants under 18 years of age must have a responsible adult present to sign the application and complete the Responsible Adult Affidavit. A responsible adult is a person who is 18 years of age or older, competent to verify the application, and has personal knowledge of the applicant. He or she may be:
- A parent or legal guardian of the applicant (must provide school or military documents, tax information or a driver’s license/permit/ID card to show relationship to applicant),
- A social worker who has worked with the applicant (must provide an employee ID or a letter from the state agency),
- An employee of a homeless shelter where the applicant resides (must provide an employee ID or a letter from the shelter),
- A stepparent of the applicant (must provide a valid marriage license or document reflecting marriage to the biological parent of the applicant),
- Other persons who can be identified by a state agency or official, school official or certified school records, or documentation from a federal agency or entity.
Did You Know?
Fact: According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), about seven (7) teens ages 16 to 19 die everyday from motor vehicle injuries.
Fact: Georgia Department of Transportation (GDOT) reports that more than 1,000 crashes happen around the state daily and an estimated 31 people die each week on Georgia roadways.
Fact: Two or more peer passengers more than triples the risk of a fatal crash with a teen at the wheel.
Fact: The State of Georgia applies strict penalties to teens who fail to obey the laws regarding the operation of the vehicle.
Fact: The parent, legal guardian or responsible adult who signed a minor's application for an instructional permit or driver's license may request revocation of the permit or license at any time before the minor's 18th birthday.
Fact: Georgia law requires that all drivers, including bicyclists, obey all official highway signs and traffic control signals unless otherwise directed by a police officer or emergency worker.
Chapter 2: Traffic Laws & Safe Driving
Traffic laws alone cannot regulate every type of driving situation that may occur. There are some general rules which drivers should understand and follow. Read this chapter with care. These safety tips might help you avoid a crash, serious injury, or even death. These are only general statements and cannot dictate your actions in all situations. It is up to you to evaluate the situation and decide the best course of action.
- Occupant Safety (O.C.G.A. §40-8-76): Georgia Law requires that each occupant in a front seat be restrained by a seat belt.
- The Hands-Free Georgia Act (O.C.G.A. §40-6-241) prohibits the use of handheld devices while driving a motor vehicle.
Traffic Laws
Safety Belts
O.C.G.A. §40-8-76.1 requires that each occupant of the front seat of a passenger vehicle, while such passenger vehicle is being operated on a public road, street, or highway of this state, be restrained by a seat safety belt approved under Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard 208. In Georgia, the term “passenger vehicle” means every motor vehicle, including, but not limited to, pickup trucks, vans, and sport utility vehicles designed to carry 15 passengers or fewer and used for the transportation of persons.
Safety belts have proven to be the most effective occupant protection in all types of vehicle crashes. Using safety belts correctly is a health care habit that, in the event of a crash:
- helps you keep control of the vehicle,
- helps keep your head from striking the dash or windshield,
- helps keep people in the vehicle from hitting each other,
- helps spread the crash force across the stronger parts of the body, and
- helps keep you from being ejected from the vehicle.
Moreover, when used correctly, safety belts are effective at helping reduce the risk of death or serious injury. For this reason, safety belt use is encouraged for the driver and all car occupants.
Safety Restraints for Children
O.C.G.A. §40-8-76 requires children under 8 years of age be properly secured in an approved car seat or booster seat while riding in passenger automobiles, vans, and pickup trucks. The car seat or booster seat must be in the rear seat, be appropriate for the child’s weight and height, and be installed and used in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions. The restraint system must comply with the United States Department of Transportation Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard 213. Taxicabs and public transit vehicles are exempt from this law.
Distracted Driving
Distracted driving is one of the fastest growing safety issues. According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), 3,142 people were killed on U.S. roadways in 2020 because of distracted drivers. There were 202 teens between the ages of 15 to 19 killed in distraction affected crashes in 2018 (for more information see: Governor’s Office of Highway Safety (GOHS)). Distracted driving is doing another activity while driving. This takes the driver’s attention away from the primary task of driving and increases the risk of crashing. Common distractions include but are not limited to talking on a cell phone, texting, reading, eating, grooming, using a navigation device, and adjusting the stereo system. The presence of passengers and pets can also increase crash risk. Georgia law requires drivers to exercise due care in operating a motor vehicle and prohibits any action that distracts the driver from the safe operation of such vehicle.
Texting and Driving
The Hands-Free Georgia Act (O.C.G.A. §40-6-241) requires drivers (any age, any license type) to refrain from physically holding or supporting a wireless telecommunications device for any reason while operating a vehicle. Under this law, drivers are also prohibited from writing, sending, or reading any text-based communication and watching, recording, or broadcasting videos on a wireless communications device while operating a motor vehicle. Wireless communications device includes cellular telephones, portable telephones, text-messaging devices, personal digital assistants, computers, and any other portable wireless devices used to initiate or receive communication, information, or data. The phone or device can only be used with an earpiece, wrist device, mounted phone holder, or through the vehicle's Bluetooth connection. Penalties are fines and points added to your driving record that increase for each conviction.
Penalties
- 1st conviction — 1 point and fine not more than $50.00
- 2nd conviction — 2 points and fine not more than $100.00
- 3rd or more convictions — 3 points and fine not more than $150.00
Take the Pledge
- Teens can commit to distraction-free driving by taking the pledge to:
- Protect lives by never texting or talking on the phone while driving.
- Be a good passenger and speak out if the driver is distracted.
- Encourage friends and family to drive distraction-free.
The Parent/Teen Driving Agreement available in this manual can be used to take a pledge against distracted driving.
Safe Driving
Steering
Good posture while driving is important because it allows a better view of hazards and more control of the vehicle. As a general rule, when gripping the steering wheel, place your left hand at the 9 o’clock position and your right hand at the 3 o’clock position on the wheel. Some manufacturers recommend placing your hands at 8 o’clock and 4 o’clock positions when the vehicle is equipped with air bags. Check your owner’s manual or contact your vehicle manufacturer to determine which hand position is best for your vehicle. Always keep both hands on the wheel unless you are safely performing another driving-related task, such as activating your turn signal.
Driving after Sunset
Driving after sunset presents significant challenges like glare and reduced visibility. Young drivers may find it difficult to determine the size, speed, color, and distance of objects. According to the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS), the fatal crash rate of teenage drivers 16-19 years of age is about four times as high at night.
Vision can be severely limited at night. Since the vehicle’s narrow headlight beams limit the driver’s view, be sure to look at the outer fringes of headlight beams to get the best picture of possible dangers ahead and the sides of the vehicle. Fringe vision helps you to identify objects near your travel path. Utilize your peripheral vision to scan for landmarks and spot changes in your side and rear-view mirrors. Avoid using a light inside the car, as this, too, will greatly reduce your night vision. Also, remember to always slow down and increase following distance to reduce the potential of a crash when driving at night.
Speed
Speeding is one of the most common factors contributing to traffic crashes. It reduces a driver’s ability to steer safely around curves or objects in the roadway, extends the distance necessary to stop a vehicle, and limits the reaction time needed to avoid a dangerous situation. High speeds also reduce the ability of the vehicle restraint system and roadway safety equipment such as guardrails, barriers, and impact attenuators to protect vehicle occupants.
Speeding endangers everyone on the road and makes car crashes more deadly. In 2020, speeding killed 11,258 people (for more information see: National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA)). GDOT reported 380 speed-related deaths on Georgia roads the same year. Driving at high speeds or "going too fast" can be considered aggressive and reckless driving. Traffic, running late, anonymity, and a disregard for others and for the law are factors that tend to lead to speeding. Always know your speed and obey speed limit signs. Be mindful that hazards such as bad weather or dangerous road conditions may require a reduction in speed. While driving, try to carefully and lawfully keep your vehicle out of the way of speeding and aggressive drivers.
Space Management
Rear-end collisions are often caused by following another vehicle too closely. When following another vehicle, there must be enough distance for you to safely stop if the vehicle in front of you suddenly slows down or stops. One way to determine if there is enough distance between your vehicle and the vehicle in front of you is to measure the amount of time between when the vehicle in front of you passes a reference point and when your vehicle passes the same reference point. To do that, watch the car ahead of you. When it passes a reference point, such as a telephone pole or street sign, count “one-thousand one, one-thousand two, one-thousand three.” If you pass the same spot before you are finished counting, you are following too closely.
Maintaining at least a 3-second space margin between your vehicle and the vehicle in front of you not only provides you with visibility, time, and space to help avoid a rear-end crash, but also allows you time to steer or brake out of danger at moderate speeds. In addition, remember that while driving at night, during inclement weather, or when hazardous road conditions are present, the distance between your vehicle and the vehicle in front of you should be even greater. When stopping behind another vehicle, stop in a position that allows you to see the back tires of the car in front you.
Tire Pressure
Prior to entering the vehicle, use a tire pressure gauge to check your psi. The recommended psi should be listed in the door jamb of the vehicle. If your psi is above the recommended number, release air from the tire until it matches. If it is below, add air (or have a retailer help you) until it reaches the proper number.
Once every month or before you embark upon a long road trip, check your tires for wear and damage problems. One easy way to measure tread depth and check for wear is by using the penny test.
- Take a penny and hold Abraham Lincoln’s body between your thumb and forefinger.
- Select a point on your tire where the tread appears the lowest and place Lincoln’s head into one of the grooves.
- If any part of Lincoln’s head is covered by the tread, you are driving with the legal and safe amount of tread. If your tread gets below that (approximately 2/32 of an inch), your car’s ability to grip the road in adverse conditions is greatly reduced.
Chapter 3: Alcohol and Drug Awareness
| BAC | Physiological Effects | Effects on Driving Ability |
|---|---|---|
| .02 |
|
|
| .05 |
|
|
| .08 |
|
|
Alcohol
According to the CDC, alcohol is one of the most widely used drugs in the world and a leading cause of preventable deaths in the United States. It is used by young people more often than tobacco or illicit drugs. Among youth, the use of alcohol and other drugs has been linked to unintentional injuries, physical fights, academic and occupational problems, and risky or illegal behavior (for more information see: Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)).
All states, including Georgia, prohibit the purchase of alcohol by youth under 21 years of age. Consequently, underage drinking is defined as consuming alcohol prior to the minimum legal drinking age of 21. Zero tolerance laws in all states make it illegal for youth under age 21 to drive with a Blood Alcohol Concentration (BAC) of .02 or greater. In other words, driving under the influence is a crime that can result in a criminal record, jail time, loss of driving privileges and a costly fine. Drinking and driving also increases the risk of a traffic crash. Even a small amount of alcohol or a lower BAC can affect driving ability and cause an alcohol-related crash. There is an average of one alcohol-impaired driving death that occurs every 45 minutes. In 2020, 11,654 people were killed in alcohol-related crashes in the United States (for more information see: National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA)). There were 402 alcohol-related crash fatalities in Georgia that same year (for more information see: Governor’s Office of Highway Safety (GOHS)).
Alcohol impairs brain function needed to safely operate a motor vehicle. It can at any level affect coordination, reaction time, and the ability to think and make good decisions. The negative effects increase as alcohol levels increase in an individual’s system. Alcohol abuse is associated with liver disease, cancer, cardiovascular disease, and neurological damage, as well as psychiatric problems such as depression, anxiety, and antisocial personality disorder.
Excessive alcohol consumption which includes binge drinking, heavy drinking, and/or underage drinking can lead to alcohol poisoning. High levels of alcohol in the body can shutdown critical areas of the brain that manage breathing, heart rate, and body temperature (for more information see: Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)). Passing out and not being able to be awakened can be a sign of alcohol poisoning. Other symptoms include confusion, vomiting, seizures, slowed breathing, blueish skin, and low body temperature. In a suspected case of alcohol poisoning, immediate medical care is vital.
Marijuana
According to the National Institute of Drug Abuse (NIDA), marijuana is the most commonly used substance after alcohol. In 2018, more than 11.8 million young adults admitted to using marijuana (for more information see: National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA)). Research data provided by the CDC shows that users were 25% more likely to be involved in a traffic crash.
Driving under the influence of marijuana increases the risk of a traffic crash and the probability a fatality. The effects of marijuana on driving can be like those associated with alcohol. It impairs judgment, distorts perception, alters senses, and slows the ability to react. It also irritates the lungs which can cause similar breathing problems experienced by tobacco smokers (i.e., daily cough, frequent chest illnesses, lung infections). Marijuana smoke deposits four times more tar in the lungs and contains up to 70% more cancer-causing substances than does tobacco smoke. It can raise the heart rate increasing the chance of a heart attack and/or damage to the cardiovascular system. Per NIDA, there is scientific evidence proving marijuana use can negatively impact one’s functionality and wellbeing. It can cause difficulty thinking, learning, remembering, and concentrating and lead to mental health issues. Research further shows that marijuana can affect brain development permanently when use begins in adolescence.
Marijuana, also called Weed, Herb, Pot, Grass, Bud, Ganja, and Mary Jane, is dried cannabis sativa plant which contains the main psychoactive chemical, tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), and non-psychoactive chemical, cannabidiol (CBD). It is used in various ways such as a cigarette (joint), cigar (blunt), smoking pipe or vaporizer, food (edible), tea and oils. Marijuana use can be addictive and lead to the use of other drugs. As many as 1 in 6 teens who use marijuana develop an addiction and/or dependency (for more information see: Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)).
Cocaine
Cocaine is an illegal and highly addictive drug made from coca plant leaves but often used in the form of a white powder or crystal substance. Also known as Blow, Coke, Crack, Rock, and Snow, cocaine is considered a dangerous stimulant that speeds up the body, affects the brain, and increases the blood pressure and heart rate. Using cocaine, in any form, can cause hallucinations, paranoia, aggression, insomnia, anxiety/depression, seizures, a heart attack, respiratory failure, and even death. It can also cause permanent damage to the lungs, nasal passages, and intestines. An overdose can occur unexpectedly even on the first use. The CDC reported a decrease in cocaine use among high school students in 2019.
MDMA/Ecstasy
MDMA, Methylenedioxymethamphetamine, is commonly called Ecstasy or Molly. It is a synthetic stimulant and hallucinogenic drug distributed in the form of pills, powder, and liquid. MDMA affects the brain causing confusion, anxiety, depression, and paranoia. It increases the blood pressure and heart rate. Other physiological effects include tremors, fainting, blurred vision, muscle cramps, and nausea. MDMA use can interfere with the body’s ability to regulate its temperature, which can cause dangerous overheating (hyperthermia). This, in turn, can lead to serious heart, kidney, or liver problems, and even death. MDMA use among teens increased in 2019 (for more information see: Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)).
Hallucinogens
Hallucinogens are synthetically produced or plant-based drugs that change the way the brain interprets time, reality, and its environment. This usually results in the user hearing voices, seeing images, and feeling things that do not exist. The user may also feel confused, suspicious, and disoriented which can lead to panic, paranoia, and psychosis. The use of a hallucinogenic drug increases the blood pressure and heart rate which can result in heart and lung damage or failure. PCP, Angel Dust, and Mescaline are considered hallucinogens. According to the United States Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA), the most common hallucinogens abused by high school students are “Mushrooms”, LSD (“Acid”), and Ecstasy. These dangerous drugs come in many forms and colors and are usually made to appeal to teens. Hallucinogenic drug use among high school students decreased in 2021 (for more information see: National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA)).
Heroin
Heroin is an illegal and highly addictive drug made from morphine and often produced as a powder or sticky substance. Also known as Black Tar, Hell Dust, Horse, Smack, and Thunder, it enters the brain very quickly which tends to influence abuse, addiction, and physical dependency. This opiate drug slows the thought process, reaction time, and memory and affects the way the user acts and makes decisions. Heroin abuse is associated with serious health conditions. Chronic users may develop collapsed veins, infection of the heart lining and valves, abscesses, and liver or kidney disease. Pulmonary complications, including various types of pneumonia, may result from the poor health of a heroin user as well as from the drug’s depressing effects on respiration. In addition to the effects of the drug itself, street heroin often contains toxic contaminants or additives that can clog blood vessels leading to the lungs, liver, kidneys, or brain, causing permanent damage to vital organs. The CDC reports continued increase in overdose deaths mostly involve the use of opioids like heroin and fentanyl.
Inhalants
Inhalants are regular products and substances with invisible fumes or chemical vapors, like glue or paint, that are misused to get an immediate high. Misuse involves sniffing or “huffing” the fumes and vapors of the product which can cause irreversible physical and mental damage. This damage can occur with the initial use and before the user knows what is happening since it affects the brain with much greater speed and force than many other substances. Inhalants starve the body of oxygen and force the heart to beat irregularly and more rapidly; a loss of consciousness or even asphyxiation can result. An inhalant user can experience disorientation, impaired coordination, nausea, and nosebleeds; develop liver, lung, and kidney problems; and lose their sense of hearing or smell. Chronic users can experience muscle wasting, reduced muscle tone and strength, and damage to the nervous system. Inhalants are mostly used by teens. NIDA reported an increase in inhalant use in 2020 among high schoolers with the highest number of users being in 8th grade.
Methamphetamine
Methamphetamine is commonly called Meth or Crystal Meth. It is a synthetic stimulant made from other drugs and chemicals and can be in the form of a powder, pill, or crystals. This highly addictive drug affects the central nervous system and dangerously increases the body’s regulatory functions (i.e., heart rate, breathing, and blood pressure). This, in turn, increases the risk of a stroke or heart attack. Users experience dry mouth, increased sweating, dilated pupils, headaches, disorientation, severe depression, paranoia, fatigue, and, in some cases, hallucinations. Methamphetamine impairs decision making, judgement and coordination. Repeated use can negatively impact the brain function and cause psychosis, mental disorders, and cardiovascular and renal dysfunction. The CDC reported a substantial increase in methamphetamine related deaths in 2020.
Prescription and Over-the-Counter (OTC) Drugs
Prescription and OTC medications are widely available, free or inexpensive, and falsely believed to be safer than illicit drugs. The rates of non-medical use of prescription and over the counter (OTC) drugs among high school students remain high (for more information see: Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)). Prescription medications most commonly abused by youth include pain relievers, tranquilizers, stimulants, and depressants. These drugs include but are not limited to Oxycontin, Percocet, Vicodin, Codeine, Adderall, Ritalin, Valium, and Xanax. Prescription or OTC medication misuse can cause serious health effects, addiction, and death. Misuse of a drug can be defined as taking more than the amount prescribed or directed, taking it more often than prescribed or directed, taking it for non-medical reasons, and/or taking a drug prescribed or intended for someone else.
Designer and Synthetic Drugs
The State of Georgia has strict laws (O.C.G.A. §16-13-25) targeting the sale and possession of designer and synthetic drugs, which have the same physiological effects on the body as other controlled substances. These drugs include but are not limited to synthetic cannabinoids, synthetic cathinones, and synthetic opioids. Snorting, smoking, injecting, and/ or orally ingesting these synthetic drugs can lead to a stroke, heart attack, and even death.
Synthetic cannabinoids, also known as synthetic/new marijuana, K2/Spice and commonly marketed as incense, are dangerous chemical compounds produced for a psychoactive effect. Synthetic marijuana use can cause an elevated heart rate and blood pressure, unconsciousness, seizures, vomiting, intense hallucinations, and paranoid delusions. It is considered more potent than marijuana and likely to cause more severe side effects. K2 use has increased in the high schools at an alarming rate.
Synthetic cathinones, also called “bath salts,” “plant food”, or Flakka and distributed in a powder or capsule form, stimulate the central nervous system much like cocaine, methamphetamine, and MDMA. “Bath Salts” cause dizziness, vomiting, paranoia, hallucinations, delusions, seizures, suicidal thoughts, prolonged panic attacks, and a rapid heart rate.
Synthetic opioids like methadone and fentanyl are analgesic. They are more potent than morphine and heroin and often mixed with other opioids increasing the risk of an overdose. According to the DEA, a reemergence in the distribution and abuse of synthetic opioids started up again in 2013. In 2020, CDC reported a significant increase in related overdoses and deaths.
Drugs and Driving Privileges
In Georgia, pursuant to O.C.G.A. §40-5-75, the driver’s license of any person convicted of driving or being in actual physical control of any moving vehicle while under the influence of a controlled substance or marijuana shall be suspended by operation of law.
First Suspension
Your driver’s license or driving privileges will be suspended for a period of 180 days. After the required suspension period, you may apply for reinstatement of your driver’s license by submitting proof of completion of a DUI Alcohol or Drug UseRisk Reduction Program. You will not be eligible for any type of limited driving permit.
Second Suspension
Your driver’s license or driving privileges will be suspended for a minimum period of 3 years. Pursuant to House Bill 349 (2013), you may apply for reinstatement of your driver’s license by submitting proof of completion of a DUI Alcohol or Drug Use Risk Reduction Program after 1 year from the conviction date.
Georgia’s Implied Consent Law
Georgia’s Implied Consent law, O.C.G.A. §40-5-67.1, requires you to submit to state-administered chemical tests of your blood, breath, urine, or other bodily substances for the purpose of determining if you are under the influence of alcohol or drugs. If you refuse this testing, your Georgia driver’s license will be suspended for a minimum period of 1 year for each refusal. There is no limited driving permit available for suspensions related to implied consent refusals. Your refusal to submit to blood or urine testing may be offered as evidence against you in a court of law. If you submit to testing and the test results indicate a blood alcohol concentration at or above the legal limit (.02 for persons under age 21), your Georgia driver’s license or privilege to drive on the highways of this state may be suspended for a minimum period of 1 year.
Frequently Asked Questions
Question: What about other medications or drugs?
Answer: Medications or drugs will not change your BAC. However, if you drink alcohol while taking certain medications, you may become more impaired, which will affect your ability to perform driving-related tasks.
Question: Is it safe to drink alcohol and drive?
Answer: No. Alcohol use slows reaction time and impairs judgment and coordination, which are all skills needed to drive a car safely. The more alcohol consumed, the greater the impairment.
Question: Why do some people react differently to alcohol than others?
Answer: Individual reactions to alcohol vary and are influenced by many factors such as:
- Age.
- Gender.
- Amount of food consumed before drinking.
- How quickly the alcohol was consumed.
- Use of drugs or prescription medicines.
- Family history of alcohol problems.
Chapter 4: Summary & Discussion
O.C.G.A. §40-5-22(a) requires that any person under 18 years of age complete the Georgia Alcohol & Drug Awareness Program (ADAP) to obtain a Georgia driver’s license.
Chapter 1: TADRA
- TADRA is an acronym for Georgia’s Teenage and Adult Driver Responsibility Act.
- According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), motor vehicle crashes are the leading cause of death for U.S. teens, accounting for more than one in three deaths in this age group. About seven (7) teens ages 16 to 19 die everyday from motor vehicle injuries.
- Pursuant to “Joshua’s Law,” proof of having completed an approved driver training course consisting of at least 30 hours of theoretical instruction (classroom or online) and 6 hours of practical behind-the-wheel training (instructor or parent taught) is required to obtain a Provisional License (Class D) at age 16 or 17.
- During the first six months following the issuance of a Provisional License (Class D), only the teen driver's immediate family members may ride in the vehicle.
- The term “immediate family member” includes the license holder’s parents and stepparents, grandparents, siblings and step-siblings, children, and any other person who resides at the license holder’s residence.
- In Georgia, persons under 21 years of age operating a motor vehicle with a blood alcohol concentration (BAC) of .02 or greater are presumed to be DUI, in violation of O.C.G.A. §40-6-391(k)(1).
Chapter 2: Traffic Laws and Safe Driving
- Safety belts have proven to be the most effective occupant protection in all types of vehicle crashes.
- Driving at high speeds or "going too fast" reduces a driver’s ability to steer safely around curves or objects in the roadway, extends the distance necessary to stop a vehicle, and limits the reaction time needed to avoid a dangerous situation.
- The fatal crash rate of teenage drivers 16-19 years of age is about four times as high at night.
- In Georgia, the term “passenger vehicle” means every motor vehicle, including, but not limited to, pickup trucks, vans, and sport utility vehicles designed to carry 15 passengers or fewer and used for the transportation of persons.
- Two or more peer passengers more than triples the risk of a fatal crash with a teen behind the wheel.
- Maintaining at least a 3-second space margin between your vehicle and the vehicle in front of you not only provides you with visibility, time, and space to help avoid rear-end crashes, but also allows you to steer or brake out of danger at moderate speeds.
- The Hands-Free Georgia Act (O.C.G.A. §40-6-241) prohibits the use of handheld devices while driving a motor vehicle.
Chapter 3: Alcohol and Drug Awareness
- Alcohol is used by young people in the United States more often than tobacco or illicit drugs.
- The minimum legal drinking age in Georgia is 21.
- Marijuana continues to be the most commonly used illicit drug among youth in the United States.
- Georgia law bans the sale and possession of “bath salts” and K2, a substance more commonly referred to as “synthetic marijuana,” and marketed as incense.
- In Georgia, pursuant to O.C.G.A. §40-5-75, the driver’s license of any person convicted of driving or being in actual physical control of any moving vehicle while under the influence of a controlled substance or marijuana shall be suspended by operation of law.
- Refusal to submit to state-administered chemical tests of your blood, breath, urine, or other bodily substances for the purpose of determining if you are under the influence of alcohol or drugs will result in the suspension of your Georgia driver’s license and privilege to drive on the highways of this state for a minimum period of 1 year for each refusal.
Resources
- Governor’s Office of Highway Safety (GOHS)
- Georgia Department of Education (DOE)
- The Council on Alcohol and Drugs
- Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS)
- Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA)
- Georgia Department of Driver Services (DDS)
- National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA)
- Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
- National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA)
- United States Department of Justice Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA)
ADAP Crossword Puzzle

Test your knowledge - ADAP Crossword Puzzle
- This can be used as an inhalant or is a very sticky substance (4 letters)
- Who is the Governor of Georgia? (4 letters)
- Teenage and Adult Driver Responsibility Act? (4 letters)
- OTC? (3 words)
- Drag racing on highways and streets can lead to a (9 letters) license.
- DDS considers drivers with three DUI convictions in five years are considered as (8 letters) violators
- The best way to sober up (4 letters)
- The "A" in BAC (7 letters)
- The most prevalent factor contributing to traffic crashes (5 letters)
- (7 letters)'s Law requires 16-year-olds to pass a Drivers Ed. Course
- "(4 letters) Tolerance" laws in all states make it illegal for youth under 21 to drive with a BAC of .02 or greater
- Risk of a fatal crash is (6 letters) when two or more peer passengers are present with a teen driver.
Answers are provided at the end of this page under the heading "Answers to the ADAP Crossword puzzle".
Note: this crossword puzzle can be used to help review information covered in the course. It is meant to help create discussion and should not be part of the ADAP grade.
Parent/Teen Driving Agreement
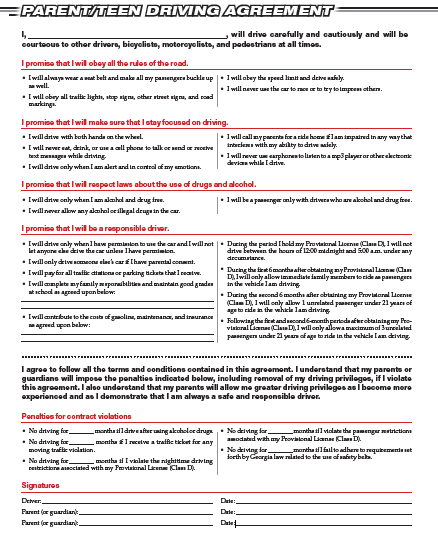
Parent / Teen Driving Agreement Long Description
I (insert name), will drive carefully and cautiously and will be courteous to other drivers, bicyclists, motorcyclists, and pedestrians at all times.
I promise that I will obey all the rules of the road
- I will always wear a seat belt and make all my passengers buckle up as well.
- I will obey all traffic lights, stop signs, other street signs, and road markings.
- I will obey the speed limit and drive safely
- I will never use the car to race or try to impress others.
I promise that I will make sure that I stay focused on driving.
- I will drive with both hands on the wheel.
- I will never eat, drink, or use a cell phone to talk or send or receive text messages while driving.
- I will drive only when I am alert and in control of my emotions.
- I will call my parents for a ride home if I am impaired in any way that interferes with my ability to drive safely.
- I will never use earphones to listen to a mp3 player or other electronic devices while I drive.
I promise that I will respect laws about the use of drugs and alcohol
- I will drive only when I am alcohol and drug free
- I will never allow any alcohol or illegal drugs in the car.
- I will be a passenger only with drivers who are alcohol or drug free.
I promise that I will be a responsible driver
- I will drive only when I have permission to use the car and I will not let anyone else drive the car unless I have permission.
- I will only drive someone else's car if I have parental consent.
- I will pay for all traffic citations or parking tickets that I receive.
- I will complete my family responsibilities and maintain good grades at school as agreed upon (insert agreement).
- During the period I hold my Provisional License (Class D), I will not drive between the hours or 12:00 midnight and 5:00 am under any circumstances.
- During the first 6 months after obtaining my Provisional License (Class D), I will only allow immediate family members to ride as passengers in the vehicle I am driving.
- During the second 6 months after obtaining my Provisional License (Class D), I will only allow 1 unrelated passenger under 21 years of age to ride in the vehicle I am driving.
- Following the first and second 6-month periods after obtaining my Provisional License (Class D), I will only allow a maximum of 3 unrelated passengers under 21 years of age to ride in the vehicle I am driving.
I agree to follow all the terms and conditions contained in this agreement. I understand that my parents or guardians will impose the penalties indicated below, including removal of my driving privileges, if I violate this agreement. I also understand that my parents will allow me greater driving privileges as I become more experienced and as I demonstrate that I am always a safe and responsible driver.
Penalties for contract violations
- No driving for (insert months) if I drive after using alcohol or drugs.
- No driving for (insert months) if I receive a traffic ticket for any moving traffic violation.
- No driving for (insert months) if I violate the nighttime driving restrictions associated with my Provisional License (Class D).
- No driving for (insert months) if I violate the passenger restrictions associated with my Provisional License (Class D).
- No driving for (insert months) if I fail to adhere to requirements set forth my Georgia law related to the use of safety bely.
Signatures
Insert signature and date of Driver
Insert signature of Parent or Guardian
Answers to the ADAP Crossword Puzzle
- Glue
- Kemp
- TADRA
- Over The Counter
- Suspended
- Habitual
- Time
- Alcohol
- Speed
- Joshua
- Zero
- Tripled